Plants & Animals on Earth: Grade 5 Science Lesson
advertisement

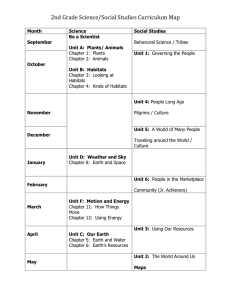
Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth PLANTS AND ANIMALS ON EARTH It is estimated that there are around 7,7 million different species of animals on Earth and around 400,000 species of plants. There are many more plants and animal species still to be discovered. Plants and animals live all over the world and are found in different habitats, such as deserts, forests, grasslands, water (aquatic) and in the arctic (tundra). A habitat is the place where plants and animals live. Plants and animals adapt to the conditions in their habitat. For more information on habitats, go to NS Grade 4 – Animal Habitats: https://mycyberwall.co.za/get-smart/science/grade-4/animal-habitats In South Africa many indigenous plants and animals are found. These are species that occur naturally only in a specific area. Animals such as the Cape Buffalo, the Knysna Woodpecker and the Geometric Tortoise and plants such as the King Protea (our national flower) are indigenous to South Africa. Many endemic species are unique to South Africa and found nowhere else in the world. King Protea – Our National Flower Version 1: September 2015 Geometric Tortoise © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 1 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth There are a variety of different habitats in South Africa. Because of this, South Africa has high biodiversity. Habitats found in South Africa and its neighbouring countries include: Desert In the north-west of South Africa, desert areas are found. The Karoo in the Northern Cape (and some parts of the Western Cape, Eastern Cape and Free State), is a semi-desert area. The oldest desert in the world, the Namib desert, is found in Namibia. Desert habitats support animals and plants that are adapted to the harsh conditions, such as lizards, scorpions, antelope, snakes, ostrich, foxes and meerkats. Lizard Antelope Fox Snake Forest Only a very small percentage (less than 1%) of the land in South Africa is covered with forest. Forests grow in the Knysna area in the Western Cape, around the Drakensberg mountains in KwaZulu-Natal and in Mpumalanga, in high rainfall areas. The Knysna forest is found in the Western Cape. Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 2 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Many years ago, herds of elephants lived in the Knysna forest, but these herds have been wiped out by humans and it is thought that only a few elephants survive here. Elephant Grasslands The north-east and eastern parts of South Africa, (Mpumalanga, Limpopo and KZN) are ‘bushveld’ areas, with savannah grasslands and open woodlands. Grassland areas are found mainly in the Highveld. A variety of grasses and small flowering plants grow here and the wildlife includes lion, zebra, elephants, rhino, giraffes, antelopes and birds such as South Africa’s national bird, the blue crane. Lion Version 1: September 2015 Our National Bird – The Blue Crane © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 3 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Birdlife Water (aquatic) Many plants grown in or near water and animals live all or some of the time in this environment. Freshwater and marine habitats are found in South Africa. Freshwater habitats include rivers, lagoons and wetlands, such as the St Lucia Wetland Park. A variety of species such as insects, frogs, fish, snakes, ducks, otters, hippos and crocodiles live on or near freshwater. Frogs Butterfly Otter Version 1: September 2015 Hippopotamus © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 4 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth South Africa has a very long coastline (2 798 km) and a variety of plants and animals live along the wet shoreline, such as crabs, seagulls and penguins. Coral reefs are found in areas off the east coast, such as Sodwana Bay. Many species of fish and animals are found here. Many Species of Fish Penguins Fish in Coral Reef Turtles Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 5 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Types of Plants Plants are found everywhere in the world and are essential to life on Earth, as they are the food source for all living creatures. Everything we eat comes either directly or indirectly from plants. Plants are found on land, in oceans and in freshwater and include the following: trees shrubs and bushes grasses flowers vegetables herbs cacti mosses, lichens and ferns creepers and climbers aquatic plants Various Cacti Wikipedia Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike: Citron Herbs Wikipedia Creative Commons; Flickr.com Attribution Share-Alike: RJFerret Version 1: September 2015 Moss Wikipedia Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike: Fred Fsu © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 6 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth There are two main types of plants: Angiosperms – these are flowering plants that produce their seeds in flowers. Gymnosperms – these are non-flowering plants that produce their seeds in cones. Angiosperm – Water Lily Gymnosperm – Zululand Cycad Types of Animals Animals can be divided into two groups: - Vertebrates – These are animals that have a backbone. - Invertebrates – These animals do not have a backbone. They usually have a hard outer ‘skin’ or shell. Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 7 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Vertebrates Mammals There are around 5,500 species of mammals on planet Earth and nearly 300 species are found in South Africa. They are warm-blooded, which means they have a constant body temperature. Mammals live on land and in water. The mother feeds her young with her milk. Examples: cows, horses, lions, antelope, cats, dolphins, whales, bats, kangaroos, giraffes. Mammal on Land – Cows Mammal in the Water - Dolphin Birds There are around 10,000 species of birds found on Earth, of which 858 species live in South Africa. The largest bird, the ostrich, is found in South Africa. Birds are warm-blooded and live on land and in the air. They have wings for flying, although some birds, like the ostrich and the penguin do not fly. Examples: Eagles, falcons, vultures, owls, sparrows, kingfishers, swallows, ducks. Mammal in the Water Fish Eagle Version 1: September 2015 Ducks © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 8 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Fish There are more fish species than any other type of vertebrate on the planet, with over 30,000 known species. Fish are found in both marine (sea) and freshwater habitats. The South African coast has a great variety of fish, however, there are limited number of freshwater fish. Fish are cold-blooded, meaning they can vary their body temperature. They live in water and breathe by using their gills. Examples: trout, salmon, dorado, mackerel, hake, halibut, tuna, marlin. Salmon Trout Reptiles There are over 10,000 species of reptiles, of which the majority are lizards, followed by snakes. In South Africa, more than 400 species of reptiles are found, of which 130 species are snakes. Reptiles are cold-blooded. Most live on land, but some spend time in the water. Examples: lizards, chameleons, snakes, crocodiles, alligators, turtles. Chameleon Version 1: September 2015 Snake (Puff Adder) © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 9 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Amphibians There are about 7000 species of amphibians. Around 90% of amphibians are frogs. The only amphibians found in South Africa are frogs and toads. Amphibians are cold-blooded. They live in the water when they are young and mainly on land as adults, returning to the water to breed. Examples: frogs, toads, salamanders, caecilians. Toad Salamander Invertebrates Invertebrates make up around 98% of the known animal species on Earth. All invertebrates have one characteristic in common – they do not have a backbone. Some invertebrates have a body divided into segments, for example, worms, insects like flies, as well as spiders and crabs. Worm Version 1: September 2015 Spider © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 10 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Other types of invertebrates have non-segmented bodies. These are known as molluscs. There are more than 800,000 species of molluscs, for example, snails, mussels and oysters. They have either an inner or an outer shell. Insects are invertebrates with segmented bodies. There are around a million known species of insect. Around 100,000 species of insect are found in South Africa. Insects have six legs and either fly, for example, bees, flies and butterflies, or crawl, for example, ants. Bees Butterfly There are 100,000 species of arachnids (spiders), of which 2000 are found in South Africa. Spiders have eight legs and do not have antennae. Kalahari Scorpion Spider Some invertebrates like crabs and lobsters have shells and five pairs of legs. Hermit Crab in Shell Version 1: September 2015 Lobster © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 11 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth Inter-dependence of Plants and Animals Many species of plants and animals depend on each other in order to survive. They are interdependent. The insects, lizards and rodents who are the primary consumers (herbivores) depend on plants to survive. In turn, the secondary consumers, i.e. the spiders, scorpions, lizards and snakes, depend on the primary consumers as their food source, and so on. For more information on food webs, go to: Grade 5: Natural Science: Food Chains: https://mycyberwall.co.za/get-smart/science/grade-5/food-chains-new If we look at the food chain below for animals and plants in a desert habitat, we can see that a variety of plants are found in the desert, such as cacti, acacia and some flowering plants (angiosperms). Example of a Desert Food Chain Both plants and animals also depend on the resources available in their habitats, such as air, water, soil, food and shelter. If the resources in their environment changes, for example, if there is not enough water, they will not survive. Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 12 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth An ecosystem is a community of living and non-living things that depend on each other. Inter-dependence in an ecosystem can be: 1) Between Living Things Animals depend on plants and other animals for food. We have seen that: A herbivore is an animal that eats only plants. A carnivore is an animal that eats only animals. An omnivore is an animal that eats plants and other animals. A scavenger eats plants and dead animals. Plants are dependent on animals to assist in the process of pollination. Pollinators are animals that assist in this process by helping to move pollen from one flower to another, in order for fertilisation to take place. Examples of pollinators include bees, wasps, birds, small mammals, etc. For example, bees are attracted to flowers and feed from their nectar. Bees then transfer pollen from other flowers to the flower they are feeding on. The pollen sticks to their legs. Bees Transfer Pollen Many flowering plants depend on bees to pollinate them so that fertilization can take place. Bees depend on the flowers to provide them with nectar. Without each other, bees and flowers could not survive. Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 13 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth So we can see that plants and animals depend on each other in order to survive. Animals also help plants by dispersing their seeds. The animals that eat the seeds move away and excrete the seeds, which grow into new plants. Sometimes seeds stick to the animals’ fur and in this way, the seeds are transferred to different places. Squirrel Eating Seeds 2) Between Living and Non-Living Things Non-living things found in an ecosystem include air (for oxygen and carbon-dioxide), water and soil. Plants need the water in the soil and carbon dioxide in the air for photosynthesis. Earthworms are living creatures that depend on the soil for their habitat (non-living). They live in rich, moist soil which is essential to stop their skin from becoming dry. The earthworms excrete droppings into the soil, which makes it fertile for other animals and plants. When they dig tunnels, they also put air into the soil. Many birds build nests from reeds (non-living) to raise their young. Bird Building Nest Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 14 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth So we can see that plants and animals which are living things are dependent on other living things as well as non-living things, in order to survive. A symbiotic relationship is when two organisms of different species i.e. either a plant and an animal, or two different animal species, interact in long-term relationships. In these relationships at least one of the organisms benefits, for example, an oxpecker and a buffalo. The bird eats parasites off the buffalo and at the same time, the buffalo is cleaned. The Oxpecker and Buffalo In some symbiotic relationships, both organisms benefit. In other symbiotic relationships, only one organism benefits, for example, barnacles growing on a mussel. The barnacles have a habitat and the mussel is not harmed. Barnacles Attached to Mussels Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 15 Natural Science & Technology: Grade 5 Life and Living: Plants and Animals on Earth In other symbiotic relationships called parasitism, one organism benefits and the other is harmed, for example, a tick that feeds off an animal. Tick Feeding off a Dog Version 1: September 2015 © Copyright My Cyberwall 2015 www.mycyberwall.co.za 16