lecture-6-eric

Lecture 6
Introduction to Bipolar Transistors
Q point analysis
DC Operating point analysis and modeling
Some Resources
Semiconductor Applets http://jas.eng.buffalo.edu/
Marc E. Herniter: Schematic Capture with
Cadence PSpice (2nd Edition)
NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
• An npn BJT consists of a thin layer of p-type material between two layers of n-type material as shown in the figure.
Lecture 5
The npn BJT.
EE171
• In most cases the base-emitter junction is forward biased and the base-collector junction is reverse biased (active region).
Lecture 5
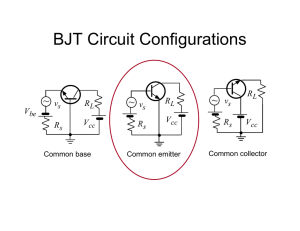
An npn transistor with variable biasing sources (common-emitter configuration).
EE171
• The emitter is heavily doped compared with the base. Most of the current is due to electrons moving from the emitter.
• Base current consists of holes crossing from the base into the emitter and of holes that recombine with electrons in the base.
Lecture 5 EE171
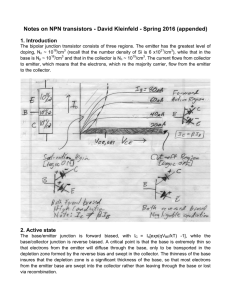
Common-Emitter Characteristics
• Input characteristic is similar to the forward bias characteristic of a pn junction.
• In the output characteristics, the collector current is independent of V
CE.
Lecture 5
Common-emitter characteristics of a typical npn BJT.
EE171
Secondary Effects
• Base-width Modulation
• Collector Breakdown
• Leakage Current
Lecture 5 EE171
Base-width Modulation:
• As V
CE gets larger, depletion region of collector extends farther into the base. This means less recombination at the base and hence less base current.
• In case of a constant base current, the emitter current should increase to maintain this constant base current.
• That is why in reality, collector current would increase with increasing V
CE
(next slide).
Lecture 5 EE171
Early Voltage:
• The straight line extension of collector current curves all meet at a point on the negative V
CE axis.
The voltage amplitude at the intersection is called the Early voltage.
Lecture 5
Common-emitter characteristics displaying exaggerated secondary effects.
EE171
Collector Breakdown:
• There are two main reasons for collector breakdown:
-Avalanche Breakdown
-Punch-through
Lecture 5 EE171
Leakage Current
• The reason for this current is reverse leakage current of the collector junction.
• At room temperature, the leakage current is extremely small, but, as the temperature increases so does the leakage current.
Lecture 5 EE171
Load-line analysis
Lecture 5
Load-line analysis of the amplifier
EE171
Lets study Example 4.2 of the book to understand the analysis.
Lecture 5
Load-line analysis for Example 4.2.
EE171
Lecture 5
Load-line analysis for Example 4.2.
EE171
Input-output waveforms
Lecture 5
Voltage waveforms for the amplifier of Example 4.2.
EE171
Lets study Example 4.2 of the book to understand the analysis.
Lecture 5
Load-line analysis for Example 4.2.
EE171
Lecture 5
Load-line analysis for Example 4.2.
EE171
Distortion
• Distortion occurs in BJT amplifiers due to nonlinearity of the input characteristic and non-uniform spacing of the output characteristic.
Output of the amplifier of Example 4.2 for v in
( t ) = 1.2 sin(2000 p t ) showing gross distortion.
Lecture 5 EE171
Clipping occurs if the BJT swing reaches saturation or cutoff.
Amplification occurs in the active region. Clipping occurs when the instantaneous operating point enters saturation or cutoff. In saturation, v
CE
< 0.2 V.
Lecture 5 EE171