Pre-Lab 4 - Paws.wcu.edu.
advertisement
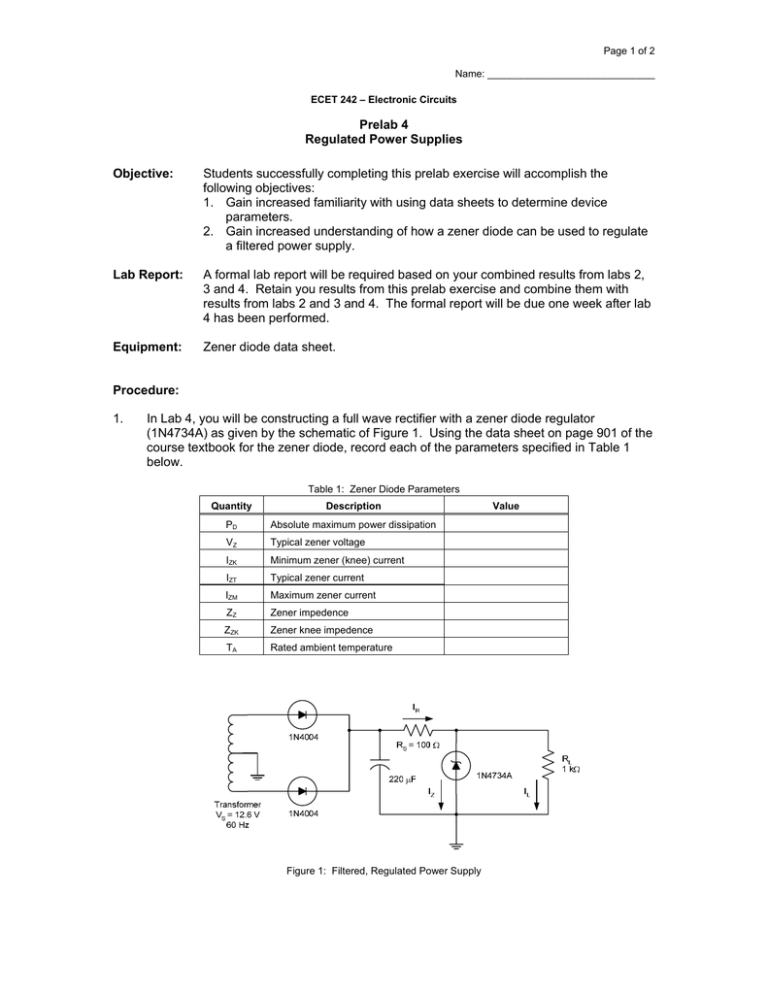
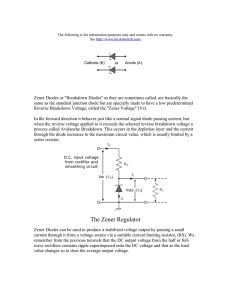
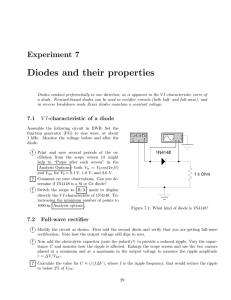
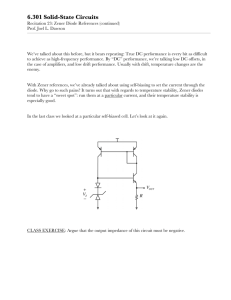
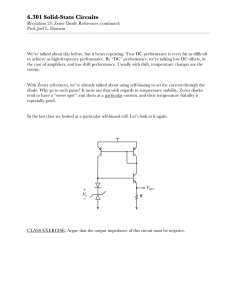
Page 1 of 2 Name: ______________________________ ECET 242 – Electronic Circuits Prelab 4 Regulated Power Supplies Objective: Students successfully completing this prelab exercise will accomplish the following objectives: 1. Gain increased familiarity with using data sheets to determine device parameters. 2. Gain increased understanding of how a zener diode can be used to regulate a filtered power supply. Lab Report: A formal lab report will be required based on your combined results from labs 2, 3 and 4. Retain you results from this prelab exercise and combine them with results from labs 2 and 3 and 4. The formal report will be due one week after lab 4 has been performed. Equipment: Zener diode data sheet. Procedure: 1. In Lab 4, you will be constructing a full wave rectifier with a zener diode regulator (1N4734A) as given by the schematic of Figure 1. Using the data sheet on page 901 of the course textbook for the zener diode, record each of the parameters specified in Table 1 below. Table 1: Zener Diode Parameters Quantity Description PD Absolute maximum power dissipation VZ Typical zener voltage IZK Minimum zener (knee) current IZT Typical zener current IZM Maximum zener current ZZ Zener impedence ZZK Zener knee impedence TA Rated ambient temperature Figure 1: Filtered, Regulated Power Supply Value Page 2 of 2 Examine the schematic for a full wave rectifier with a zener diode regulator shown in Figure 1. Using the parameters for a zener diode obtained in the previous step, determine the quantities which follow. a. Peak secondary voltage, VS(P). b. Peak capacitor voltage, VC(P). c. Series resistor current, IR. d. Capacitor ripple voltage, VRPP. e. Capacitor percent ripple, %VRPP = (VRPP / VC(P)) x 100%. f. DC output voltage, Vdc. g. Load current, IL. h. Zener current, IZ. i. Output ripple voltage, VRPP(Out). j. Output percent ripple, %VRPP(Out) = (VRPP(Out) / Vdc) x 100%. 2. Remove the load resistance and determine the zener current, IZ. Will the zener diode be safe with this current? 3. If the load resistance is shorted out (RL = 0 Ω), determine each of the following quantities. a. Total circuit current, IR. b. Load current, IL. c. 4. Zener current, IZ. A zener diode will regulate voltage as long as the zener current is greater than or equal to the rated zener knee current, IZK. For the circuit of Figure 1, assume the zener current is equal to IZK. With the 1 kΩ load resistor replaced, determine each of the following quantities. a. Total circuit current, IR. b. Load current, IL. c. 5. Minimum allowable load resistance, RL(Min). Calculate the output ripple and percent output ripple for RL = 470 Ω, and for the minimum allowable load resistance. Record your results in Table 2 below. Does percent output ripple increase, decrease or remain the same as resistance is decreased? Is the change large or small? Table 2: Output Ripple for Various Loads Load Resistance (Ω) RL(Min) 470 Ω 1 kΩ Output Ripple (mV) Percent Output Ripple (%)