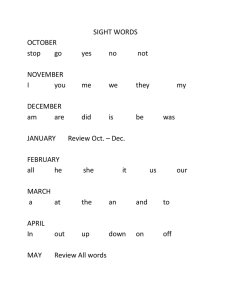
Solved examples on synchronous machines
advertisement

09‐Dec‐14 46 A 3-phase, wye-connected, round-rotor synchronous generator rated at 10 kVA, 230 V has a synchronous reactance of 1.2 Ω per phase and an armature resistance of 0.5 Ω per phase. Calculate the percent voltage regulation at full-load with 0.8 lagging power factor. 47 1 09‐Dec‐14 The phasor diagram is shown in Figure from which: 48 Substituting: We get: Then 49 2 09‐Dec‐14 Repeat the previous problem for the case of 0.8 leading power factor, other data remaining unchanged. 50 Notice: The voltage regulation at full-load with 0.8 leading power factor is negative 51 3 09‐Dec‐14 For the generator of example (2), determine the power factor such that the voltage regulation is zero on full-load. 52 53 4 09‐Dec‐14 A 3-phase, round-rotor synchronous generator is rated 150 MW, 0.85 power factor, 12.6 kV, 60 Hz, and 1800 rpm. Each winding has a line-to-neutral resistance of 1.535 Ω. The data for the no-load magnetization curve are: The short-circuit armature-current test gives a straight line through the origin and through rated armature current at 700-A field current. 54 a) b) c) d) Determine the unsaturated synchronous impedance per phase. Determine the saturated synchronous impedance per phase. Draw a phasor diagram and determine the voltage regulation for the condition of rated load and 0.85 power factor lagging. Repeat part (c) for rated load and 0.85 pf leading. 55 5 09‐Dec‐14 The saturation curve and the short-circuit test data are plotted 56 Calculate From the rated current: Fig.: ab- 57 6 09‐Dec‐14 =cos-1 0.85 = -31.8°. The phasor diagram is shown in Fig 58 For = +31.8°, Fig. (b) gives the phasor diagram. 59 7 09‐Dec‐14 A 3600 rpm, 60 Hz, 13.8 kV synchronous generator has a synchronous reactance of 20Ω. The generator is operating at rated voltage and speed with the per phase excitation voltage Ef=11.5kV and the torque angle δ=15° Calculate (a) stator current, (b) power factor, and (c) total output power. 60 a) b) c) 61 8 09‐Dec‐14 For the synchronous generator of example (5), determine (a) the maximum power that can be converted from mechanical to electrical form without loss of synchronism if the field current is unchanged and (b) the value of current Is for this condition 62 a) Since δ=90°: b) 63 9