Lecture 11 Op Amp Circuits 2

Lecture 11 Op Amp Circuits 2
10-‐21-‐11
• Mean = 80
Midterm Grades
• Standard Devia=on = 14
66 80 94
Grading
• Midterm 1 15% (10-‐14-‐11)
• Midterm 2 15% (11-‐4-‐11)
• Final Exam 30% (12-‐8-‐11 noon-‐ 3 pm)
• Homework 20% (Homework 4 due Monday)
• Quizzes 20% (lowest quiz grade dropped,
quiz 3 on Monday)
If you are not going to be able to take the midterms and the final exam on these dates you should take this class at a later date!
So What’s So Good About Feedback?
• With lots of feedback the feedback network determines the gain and the gain of the amplifier is not important
– Passive components are rela=vely stable
– Ac=ve components are less stable – they dri] & are more sensi=ve to the environment (temp, etc.
• Impact of noise is reduced (see next slide).
So What’s So Good About Feedback?
Reference: Intersil Ap Note on Feedback, Op Amps and Compensa=on
(posted on EE 101 website under “Reference Documents.”)
Summing Amplifier
• Summing Amplifier is an op amp circuit that combines several inputs and produces an output that is the weighted sum of the inputs.
6
Summing Amplifier Example
Calculate v o
and i o
in the op amp mixer circuit shown below.
7
Differen=al Amplifier with Op Amp
• Difference amplifier is a device that amplifies the difference between two inputs but rejects any signals common to the two inputs (common mode interference) .
Analysis: Apply KCL at both nodes a & b and solve for v o
.
Reject common mode
8
Common Mode Interference
Differen=al
• Common mode is applied to both inputs, e.g. between a cable shield and two internal wires.
• Differen=al amp rejects common mode signals.
• Check Op Amp spec sheet for
CMRR = A
D
/A
CM
Common
~
Gnd
~
-
+
5.4 Cascaded Op Amp (1)
• It is a head-‐to-‐tail arrangement of two or more op amp circuits such that the output to one is the input of the next.
€ €
A = v o v
1
= A
1
A
2
A
3
10
€
Cascaded Op Amps
• Find v o
and i o
in the circuit shown below
– Recognize cascaded, non-‐inver=ng amps
(signal applied to non-‐ inver=ng input)
– Determine gain of each stage and use cascaded gain to find v o
– Use knowledge of va and vb and then Ohm’s Law across 10 k
Ω
resistor
Ans: 350mV, 25μA
11
5.4 Cascaded Op Amp (3)
If v
1
= 1V and v
2
= 2V, find v o
in the op amp circuit shown below.
Ans: 8 2/3 V
12
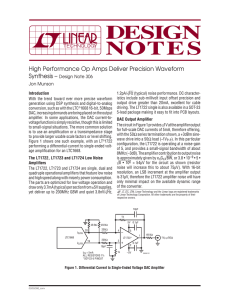
DAC Applica=on
• Digital-‐to Analog Converter (DAC) : it is a device which transforms digital signals into analog form.
Four-‐bit DCA: (a) block diagram (b) binary weighted ladder type
Summing Amplifier where
V
1
– MSB, V
4
– LSB
V
1
to V
4
are either 0 or 1 V
13
DAC Circuit Example
For the circuit shown below, calculate v o
if v
1
= 0V, v
2
=1V and v
3
= 1V.
Ans:-‐0.75V
14