Electrostatics Worksheet: Circuits, Resistance, Current
advertisement
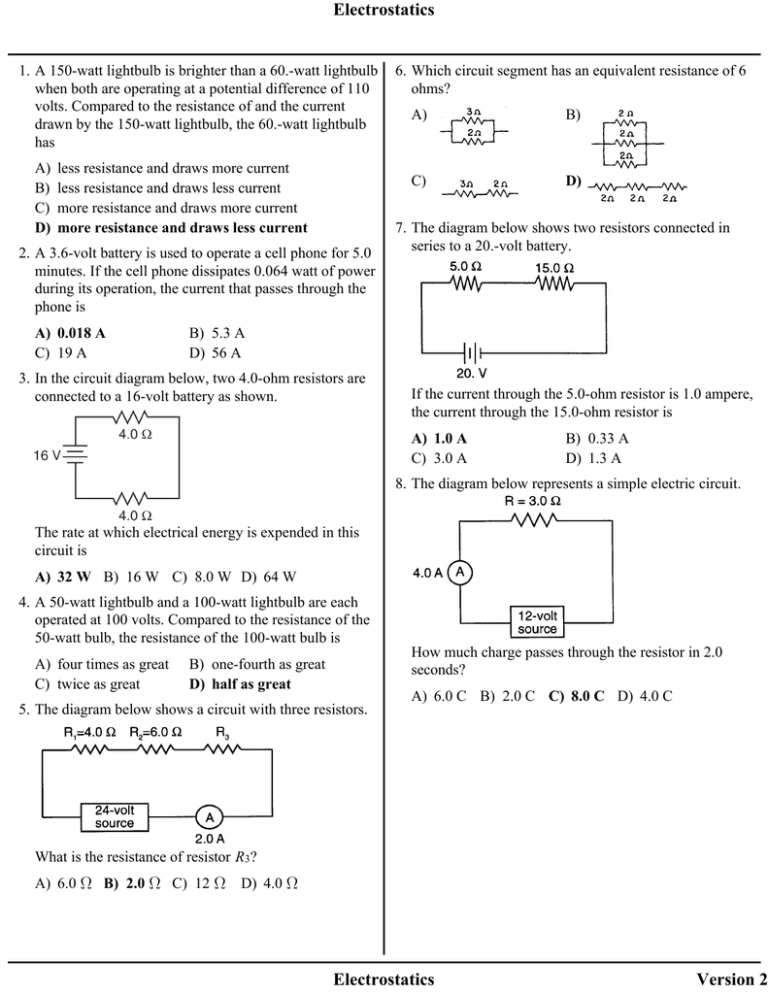
Electrostatics 1. A 150-watt lightbulb is brighter than a 60.-watt lightbulb when both are operating at a potential difference of 110 volts. Compared to the resistance of and the current drawn by the 150-watt lightbulb, the 60.-watt lightbulb has A) B) C) D) less resistance and draws more current less resistance and draws less current more resistance and draws more current more resistance and draws less current 2. A 3.6-volt battery is used to operate a cell phone for 5.0 minutes. If the cell phone dissipates 0.064 watt of power during its operation, the current that passes through the phone is A) 0.018 A C) 19 A 6. Which circuit segment has an equivalent resistance of 6 ohms? A) B) C) D) 7. The diagram below shows two resistors connected in series to a 20.-volt battery. B) 5.3 A D) 56 A 3. In the circuit diagram below, two 4.0-ohm resistors are connected to a 16-volt battery as shown. If the current through the 5.0-ohm resistor is 1.0 ampere, the current through the 15.0-ohm resistor is A) 1.0 A C) 3.0 A B) 0.33 A D) 1.3 A 8. The diagram below represents a simple electric circuit. The rate at which electrical energy is expended in this circuit is A) 32 W B) 16 W C) 8.0 W D) 64 W 4. A 50-watt lightbulb and a 100-watt lightbulb are each operated at 100 volts. Compared to the resistance of the 50-watt bulb, the resistance of the 100-watt bulb is A) four times as great C) twice as great B) one-fourth as great D) half as great 5. The diagram below shows a circuit with three resistors. How much charge passes through the resistor in 2.0 seconds? A) 6.0 C B) 2.0 C C) 8.0 C D) 4.0 C What is the resistance of resistor R3? A) 6.0 B) 2.0 C) 12 D) 4.0 Electrostatics Version 2 Electrostatics 9. The diagram below shows three resistors, R1, R2, and R3, connected to a 12-volt battery. 13. The circuit diagram below represents four resistors connected to a 12-volt source. What is the total current in the circuit? If voltmeter V1 reads 3 volts and voltmeter V2 reads 4 volts, what is the potential drop across resistor R3? A) 12 V B) 5 V C) 0 V D) 4 V 10. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below. A) 24 A C) 8.6 A B) 0.50 A D) 2.0 A 14. Moving 4.0 coulombs of charge through a circuit requires 48 joules of electric energy. What is the potential difference across this circuit? A) 190 V B) 48 V C) 12 V D) 4.0 V 15. In the circuit diagram below, what are the correct readings of voltmeters V1 and V2? The reading of voltmeter V will be A) 5 volts C) 10 volts B) 0.2 volt D) 20 volts 11. The diagram below represents a circuit consisting of two resistors connected to a source of potential difference. A) B) C) D) V1 reads 4.0 V and V2 reads 2.0 V V1 reads 3.0 V and V2 reads 3.0 V V1 reads 2.0 V and V2 reads 4.0 V V1 reads 6.0 V and V2 reads 6.0 V 16. In the diagram below, lamps L1 and L2 are connected to a constant voltage power supply. What is the current through the 20.-ohm resistor? If lamp L1 burns out, the brightness of L2 will A) 0.25 A C) 12 A A) increase C) remain the same B) 6.0 A D) 4.0 A B) decrease 12. Circuit A has four 3.0-ohm resistors connected in series with a 24-volt battery, and circuit B has two 3.0-ohm resistors connected in series with a 24-volt battery. Compared to the total potential drop across circuit A, the total potential drop across circuit B is A) one-half as great C) the same B) twice as great D) four times as great Electrostatics Version 2 Electrostatics 17. Which circuit has the smallest equivalent resistance? A) 20. The diagram below represents currents in a segment of an electric circuit. B) What is the reading of ammeter A? A) 1 A C) B) 3 A C) 4 A D) 2 A D) 18. Three identical lamps are connected in parallel with each other. If the resistance of each lamp is X ohms, what is the equivalent resistance of this parallel combination? A) B) C) D) 19. Three resistors, 4 ohms, 6 ohms, and 8 ohms, are connected in parallel in an electric circuit. The equivalent resistance of the circuit is A) B) C) D) 18 between 10 and 18 between 4 and 8 less than 4 Electrostatics Version 2 Electrostatics 21. In which circuit would current flow through resistor R 1, but not through resistor R 2 while switch S is open? A) B) C) D) 22. In the circuit diagram shown below, ammeter A1 reads 10. amperes. 25. In the circuit diagram shown below, what is the current through the 4.0-ohm resistor? A) 1.0 ampere C) 3.0 amperes What is the reading of ammeter A2? B) 0.33 ampere D) 48 amperes 26. The diagram below shows currents in a segment of an electric circuit. A) 6.0 A B) 10. A C) 4.0 A D) 20. A Base your answers to questions 23 and 24 on the diagram below, which shows two resistors and three ammeters connected to a voltage source. 23. What is the current reading of ammeter A1 ? A) 10.0 A C) 3.0 A What is the reading of ammeter A? B) 6.0 A D) 4.0 A A) 1 A 24. What is the potential difference across the source? A) 120 V B) 60. V C) 220 V D) 440 V B) 5 A C) 9 A D) 15 A 27. Conductivity in metallic solids is due to the presence of free A) electrons C) neutrons Electrostatics B) nuclei D) protons Version 2 Electrostatics 28. Compared to insulators, metals are better conductors of electricity because metals contain more free A) electrons C) negative ions B) protons D) positive ions 29. An MP3 player draws a current of 0.120 ampere from a 3.00-volt battery. What is the total charge that passes through the player in 900. seconds? A) 324 C C) 5.40 C A) B) 108 C D) 1.80 C 30. The current in a wire is 4.0 amperes. The time required for electrons to pass a certain point in the wire is A) 1.0 s 33. A copper wire is part of a complete circuit through which current flows. Which graph best represents the relationship between the wire's length and its resistance? B) B) 0.25 s C) 0.50 s D) 4.0 s 31. What is the current in a wire if 3.4 × 1019 electrons pass by a point in this wire every 60. seconds? 1.8 × 10 –18 A A) C) 9.1 × 10 –2 A C) 3.1 × 10 –11 A B) D) 11 A 32. A manufacturer recommends that the longer the extension cord used with an electric drill, the thicker (heavier gauge) the extension cord should be. This recommendation is made because the resistance of a wire varies A) directly with length and inversely with cross-sectional area B) directly with both length and cross-sectional area C) inversely with length and directly with cross-sectional area D) inversely with both length and cross-sectional area D) 34. If the length of a copper wire is reduced by half, then the resistance of the wire will be A) quartered C) doubled B) quadrupled D) halved 35. Which change decreases the resistance of a piece of copper wire? A) B) C) D) decreasing the wire’s temperature increasing the wire’s length increasing the wire’s resistivity decreasing the wire’s diameter 36. A circuit consists of a resistor and a battery. Increasing the voltage of the battery while keeping the temperature of the circuit constant would result in an increase in A) B) C) D) Electrostatics neither current nor resistance current, only resistance, only both current and resistance Version 2 Electrostatics 37. A complete circuit is left on for several minutes, causing the connecting copper wire to become hot. As the temperature of the wire increases, the electrical resistance of the wire A) decreases C) remains the same B) increases A) halved C) quartered 38. An incandescent light bulb is supplied with a constant potential difference of 120 volts. As the filament of the bulb heats up, its resistance A) B) C) D) increases and the current through it decreases decreases and the current through it decreases decreases and the current through it increases increases and the current through it increases 39. If the diameter of a wire were decreased, its electrical resistance would A) decrease C) remain the same 45. An electric circuit consists of a variable resistor connected to a source of constant potential difference. If the resistance of the resistor is doubled, the current through the resistor is B) increase B) doubled D) quadrupled 46. In a simple electric circuit, a 24-ohm resistor is connected across a 6.0-volt battery. What is the current in the circuit? A) 4.0 A C) 1.0 A B) 140 A D) 0.25 A 47. What is the minimum equipment needed to determine the power dissipated in a resistor of unknown value? A) B) C) D) a voltmeter and an ammeter, only an ammeter, only a voltmeter, only a voltmeter, an ammeter, and a stopwatch 40. The electrical resistance of a metallic conductor is inversely proportional to its A) B) C) D) temperature cross-sectional area resistivity length 41. If a wire of cross-sectional area equal to A has a resistance of R, then another wire of the same material with a cross-sectional area equal to 2A will have a resistance of A) R B) 2R C) R/2 D) R/4 42. At 20°C, four conducting wires made of different materials have the same length and the same diameter. Which wire has the least resistance? A) nichrome C) gold B) tungsten D) aluminum 43. A 0.686-meter-long wire has a cross-sectional area of 8.23 ×10 –6 meter 2 and a resistance of 0.125 ohm at 20° Celsius. This wire could be made of A) aluminum C) tungsten B) copper D) nichrome 44. Pieces of aluminum, copper, gold, and silver wire each have the same length and the same cross-sectional area. Which wire has the lowest resistance at 20°C? A) silver C) copper B) aluminum D) gold Electrostatics Version 2 Electrostatics 48. The resistance of a circuit remains constant. Which graph best represents the relationship between the current in the circuit and the potential difference provided by the battery? 49. Which graph best represents the relationship between the power expended by a resistor that obeys Ohm's Law and the potential difference applied to the resistor? A) A) B) B) C) C) D) D) 50. A length of copper wire and a 1.00-meter-long silver wire have the same cross-sectional area and resistance at 20°C. Calculate the length of the copper wire. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Electrostatics Version 2 Answer Key Electricity practice test 1. D 37. B 2. A 38. A 3. A 39. B 4. D 40. B 5. B 41. C 6. D 42. C 7. A 43. D 8. C 44. A 9. B 45. A 10. C 46. D 11. D 47. A 12. C 48. C 13. B 49. D 14. C 50. 15. D 16. C 17. D 18. B 19. D 20. D 21. B 22. A 23. B 24. A 25. C 26. C 27. A 28. A 29. B 30. A 31. C 32. A 33. D 34. D 35. A 36. B Electrostatics Version 2