Faraday`s Law of Induction

Faraday's Law of Induction
Chapter 31
Put down all diagrams, equations used in the problem, and all of your work.
Directions:
1.
Follow the steps to problem solving
!
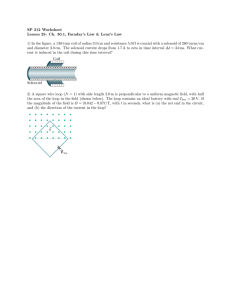
The plane of a rectangular coil of dimensions 5.0 cm by 8.0 cm is perpendicular to the direction of a magnetic field B. If the coil has 75 turns and a total resistance of 8.0 W , at what rate must the magnitude of B change in order to induce a current of 0.10 A in the windings of the coil?
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 1
2.
A long solenoid has n turns per meter and carries a current I = I o
(1 - e a t ), with I o
=30.A and a =1.6 s -1 . Inside the solenoid and coaxial with it is a loop that has a radius R=6.0cm and consists of a total of N turns of fine wire. What emf is induced in the loop by the changing current? Take n=400 turns/m and N=250 turns.
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 2
3.
A long solenoid has 200. turns/cm and carries a current of 1.5 A; Its diameter is 3.0 cm. At its center we place a 100. turn, close packed coil of diameter 2.0 cm. This coil is arranged so that B at the center of the solenoid is parallel to its axis. The current in the solenoid is reduced to zero and then raised to 1.5 A in the other direction at a steady rate over a period of .050 s. What induced emf appears in the coil while the current is being changed? (answer -
4.74`x`10 -2 V)
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 3
4.
A 100. turns of insulated copper wire are wrapped around an iron cylinder of crosssectional area 0.001 m 2 and are connected to a resistor. The total resistance in the circuit is
10.0 W . If the longitudinal magnetic field in the iron changes from 1.00 T in one direction to
1.0 T in the opposite direction, how much charge flows through the circuit? (2.00 x 10 -2 C)
5.
A magnetic field of 0.20 T exists within a solenoid of 500 turns and a diameter of 10.0 cm.
How rapidly (that is, within what period of time) must the field be reduced to zero magnitude if the average magnitude of the induced emf within the coil during this time interval is to be 10. kV? (7.85 x 10 -5 s)
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 4
6.
A bar of mass m and length l moves on two frictionless parallel rails of resistance R in the presence of a uniform magnetic field directed into the paper. The bar is given an initial velocity v o
to the right and is released. Find the velocity of the bar as a function of time.
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 5
7.
A long solenoid of radius R has n turns per unit length and carries a time-varying current that varies sinusoidally as I = I o
cos w t, where I o
is the maximum current and T is the angular frequency of the current source. (a) Determine the electric field outside the solenoid, a distance r from its axis.
(b) What is the electric field inside the solenoid, a distance r from its axis?
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 6
8.
Consider the arrangement shown in the figure at the right.
Assume that R = 6.0
W , l = 1.2 m, and that a uniform 2.5 T magnetic field is directed into the page. At what speed should the bar be moved to produce a current of 0.50 A in the resistor? ( T ch 31 - 18 )
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 7
9.
Right
Use Lenz’s law to answer the following questions concerning the direction of induced currents. a.
What is the direction of the induced current in the resistor R in Figure
31.27a when the bar magnet is moved to the left?
Right
b.
What is the direction of the current induced in the resistor R right after the switch S in the circuit of Figure
31.27b is closed?
Right
c.
What is the direction of the induced current in R when the current I in
Figure 31.27c decreases rapidly to zero?
d.
A copper bar is moved to the right while its axis is maintained perpendicular to a magnetic field, as in figure 31.27d. If the top of the bar becomes positive relative to the bottom, what is the direction of the magnetic field?( T ch 31 - 27 )
Into the paper
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 8
10.
A horizontal wire is free to slide on the vertical rails of a conducting frame as in the figure to the right.
The wire has mass m and length L, and the resistance of the circuit is R. If a uniform magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the frame, what is the terminal velocity of the wire as it falls under the force of gravity?
(Neglect mechanical friction)
AP Hom ework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 9
11.
A thin metal strip is allowed to slide down parallel frictionless rails of negligible resistance connected at the bottom end and elevated to an angle q above the horizontal. A uniform magnetic field B is directed vertically upward throughout the region. The strip has mass m =
35 g, resistance R = 0.20 W , and length between the rails L = 0.3 m. a.
Derive a general expression for the terminal speed of the strip.
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 10
b.
Calculate the terminal speed achieved by the strip sliding along the incline if q = 30.
/ and B = 1.5 T.
c.
Derive a general expression for the speed of the strip at any time t.( T ch 31 - 69 )
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 11
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 12
12.
The current in a solenoid is increasing at a rate of 10 A/s. The cross-sectional area of the solenoid is p cm² and there are 300 turns on its 15 cm length. What is the induced emf which acts to oppose the increasing current?
( T ch 31 - 30 )
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 13
13.
A magnetic field directed into the page changes with time according to B = (0.030t
2 + 1.4)T, where t is in s.
The field has a circular cross-section of radius
R = 2.5 cm. What are the magnitude and direction of the electric field at point P
1
when t = 3.0 s and r
1
= 0.020 m?
( T ch 31 - 33 )
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 14
14.
A circular coil, enclosing an area of 100.0
cm 2 , is made of 200 turns of copper wire as shown in Figure 31.34 of the text. Initially, a
1.1 T uniform magnetic field points perpendicularly upward through the plane of the coil. The direction of the field then reverses so that the final magnetic field has a magnitude of 1.1 T pointing downward through the coil. During the time the field is changing, how much charge flows through the coil if the coil is connected to a 5.0 ohm resistor as shown in figure 31.34 of the text?
( T ch 31 - 38 )
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 15
15.
A 2.0 H inductor carries a steady current of 0.5 A. When a switch in the circuit is opened, the current disappears in 0.010 s. What is the induced emf that appears in the inductor during this time? ( T ch 32 - 1 )
16.
What is the inductance of a 510 turn solenoid that has a radius of 8.0 cm and an overall length of 1.4 m?
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 16
17.
The current in a 0.020 H inductor varies in time as I = 3t 2 - 4t, where I is in A and t is in s.
a.
Calculate the magnitude of the induced emf at t = 1 and t = 5 s.
b.
For what value of t will the induced emf be zero?
18.
A current I = I o sin w t, with I o
= 5.0 A and w /2 p = 60.0 Hz, flows through an inductor whose inductance is 10.0 mH. What is the back emf as a function of time?
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 17
19.
A 50.0 V potential difference is suddenly applied to a coil with L = 50.0 mH and
R = 180.0 ohms. At what rate is the current increasing after .00100s?
20.
In the circuit shown at the right find the following quantities when the switch is just closed and after it has been closed for a long time.
a.
Current i
1
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 18
b.
Current i
2 c.
Total current i d.
Voltage across R
2
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 19
e.
Voltage across inductor L f.
Rate of change in i
2
AP Homework on Faraday's Law of Induction - Page 20