Lecture 9 A
advertisement

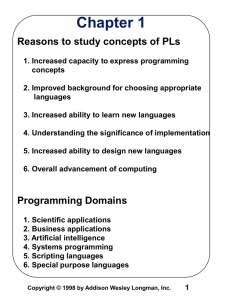
Slide 9.1 9 MACHINE LEARNING: SYMBOL-BASED 9.0 Introduction 9.5 Knowledge and Learning 9.1 A Framework for Symbol-based Learning 9.6 Unsupervised Learning 9.7 Reinforcement Learning 9.8 Epilogue and References 9.9 Exercises 9.2 Version Space Search 9.3 The ID3 Decision Tree Induction Algorithm 9.4 Inductive Bias and Learnability Slide 9.2 Figure 9.1: A general model of the learning process. A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.3 Figure 9.2: Examples and near misses for the concept “arch.” A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.4 Figure 9.3: Generalization of descriptions to include multiple examples. (continued on next slide) A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.5 Figure 9.3: Generalization of descriptions to include multiple examples. (continued from previous slide) A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger a near miss. In 9.4c we add constraints to 9.4a so that it can’t match with 9.4b. Figure 9.4: Specialization of a description to exclude Slide 9.6 © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.7 Figure 9.5: A concept space. A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.8 Defining specific to general search, for hypothesis set S as: A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.9 In this algorithm, negative instances lead to the specialization of candidate concepts; the algorithm uses positive instances to eliminate overly specialized concepts. A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.10 Figure 9.6: The role of negative examples in preventing overgeneralization. A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.11 Figure 9.7: Specific to general search of the version space learning the concept “ball.” A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.12 The algorithm specializes G and generalizes S until they converge on the target concept. The algorithm is defined: A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.13 Figure 9.8: General to specific search of the version space learning the concept “ball.” A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.14 Figure 9.9: The candidate elimination algorithm learning the concept “red ball.” A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.15 Figure 9.10: Converging boundaries of the G and S sets in the candidate elimination algorithm. A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.16 Figure 9.11: A portion of LEX’s hierarchy of symbols. A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley Slide 9.17 Figure 9.12: A version space for OP2, adapted from Mitchell et al. (1983). A R T I F I C I A L I N T E L L I G E N C E: Structure and Strategies for Complex Problem Solving, 4th Edition George F. Luger © 2002 Addison Wesley