the electric charge
advertisement

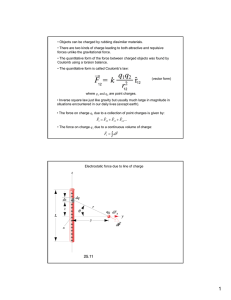
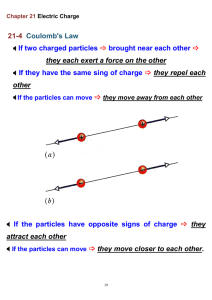
Questions to think about • Why clothes catch hair • How does dust stick to the ceiling • Where the lightings come from electric charge Each object has charge, which is a scalar attribute describing electric interactions of the object with other objects. The SI unit of charge is the coulomb: 1C = 1A ⋅ 1s Fe E The electrostatic force exerted on a particle depends only on the charge q of the particles and the local electric field E, produced by other objects Fe = q ⋅ E E Fe electric field (lines) The SI unit of electric field is the volt per meter. 1V/m = 1N / 1C elementary particles electron mass: 9.1 ⋅ 10-31 kg charge: -1.6 ⋅ 10-19 C proton mass: 1.7 ⋅ 10-27 kg charge: 1.6 ⋅ 10-19 C neutron mass: 1.7 ⋅ 10-27 kg charge: 0 C Coulomb’s law q2 q1 F F r The electrostatic forces between two particles are proportional to charge of each object and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them F= k⋅ q1 ⋅ q 2 r2 Charles Augustin de Coulomb (1596–1650) - French physicist, described electrostatic interaction The proportionality constant k = 9⋅109 Nm2/C2 is called the Coulomb constant. electronic air purifier Gravity is to weak to remove dust particle carried in air by the drag force. A much stronger electrostatic interaction is used to clean air from dust. + - + - + - Charged objects produce electric fields. A power supply removes electrons from the corona wires and places electrons on the collecting plates maintaining a constant electrostatic field. Dust particles acquire charge during a corona discharge and are attracted to the collecting plates. electric potential Electrostatic interaction is conservative. In an electrostatic field, charged particles have electrostatic potential energy. 200 V 300 V Fe Electric potential at a given location is number, such that the electrostatic potential energy of a particle at this location is equal to the product of its charge and the potential. Fe equipotential surfaces The SI unit of potential is the volt: 1V = 1J / 1C Example: An anion with charge 1.6 ⋅ 10-19 C is moved from a location with electric potential of 200 V to a location with electric potential of 100 V. The change in the potential energy of the anion is ∆Ue = (1.6⋅10-19 C) ⋅ 300 V - (1.6⋅10-19 C) ⋅ 200 V = 1.6 ⋅10-17 J Puzzle: What would be the change in potential energy of an electron? electric polarization - - - - - - - - + + + + + + - + + - Van de Graaff generator - In an electric field, charged particles within an object may shift, accumulating different type of charge on opposite sides of the object. The object becomes electrically polarized. An overall neutral object can interact electrically with the objects causing the electrical polarization. lightning storm + 4. When the electric field exceeds certain value (dielectric strength) a violent discharge takes places + + + - - - - - - - + + 1. The air motion in the clouds separates charged particles. + + + 2. The ground becomes charged by induction. + 3. Charge separation results in an electric field.