Physics 2240 Syllabus Scaife/Spring 2012
advertisement

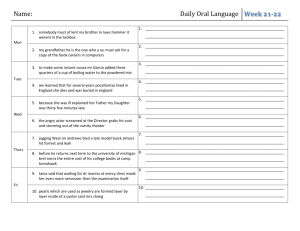
Physics 2240 Syllabus Date Reading Topics Mon 1/23 1.1-­‐1.6 Introduction to Modeling Introduction to SI Units Tues 1/24 4.1-­‐ 4.2 Equilibrium Initial in-­‐class Survey Prelab LAB: Measurement Thurs 1/26 Scaife/Spring 2012 Objectives ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ Define “model” as it relates to physics. List the three basic dimensions of measurement for mechanics. List the three SI base units for mechanics. Match commonly used metric prefixes with powers. Convert units in a tabular format. ⋅ State and explain Newton’s First Law. Identify motion diagrams that depict objects in equilibrium. ⋅ Use the condition of equilibrium to solve for unknown forces. ⋅ Observe measurement error and use the standard deviation to quantify it. ⋅ Linearize data to demonstrate a predicted relationship. ⋅ State the course policy on significant figures. Online Tutorial Homework #1 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight Fri 1/27 4.4-­‐4.6, 5.1 Interactions rd Newton’s 3 Law Free Body Diagrams ⋅ List the four types of interaction studied in this course. ⋅ Represent the forces acting on an object in a free body diagram. rd ⋅ State Newton’s 3 Law and enforce it when drawing free body diagrams. Initial online survey on D2L due at 5pm Mon 1/30 4.3, 5.2 nd Newton’s 2 Law ⋅ Define the unit “Newton” in terms of SI base units. ⋅ Translate free body diagrams into equations. Intro to Mastering Physics AND Homework #1 Due Online by 8 AM Equilibrium Quiz ⋅ Observe the linear relationship between force and acceleration. ⋅ Observe the difference between net force and applied force. Prelab LAB: Force and Acceleration Thurs ⋅ Develop a model of the meaning of the slope and intercept of the line. 2/2 ⋅ Observe the dependence of friction on the normal force. Online Tutorial Homework #2 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight ⋅ Explain the relationship between the friction force and the normal force. Fri Coefficient of Friction ⋅ Define the term “ideal pulley” as it is used in the course. 5.3 2/3 Pulleys ⋅ Draw free body diagrams for systems involving ideal pulleys. Tues 1/31 Mon 2/6 Tues 2/7 Thurs 2/9 Fri 2/10 ⋅ Given a graph of position vs. time for an object moving in 1D: (a) State the direction of motion of the object. (b) Calculate or estimate the object’s velocity. (c) State whether the object is speeding up/slowing down. 2.2-­‐2.3 Velocity and Acceleration ⋅ Given a graph of velocity vs. time for an object moving in 1D: (a) State the direction of motion. (b) Calculate/estimate the object’s acceleration. (c) Calculate/estimate the distance traveled. Homework #2 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Dynamics Quiz Prelab LAB: Graphing Motion ⋅ Predict and observe position and velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to various motions. Online Tutorial Homework #3 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight ⋅ Give examples in which negative acceleration does not yield deceleration. ⋅ State and use the equations of 1D kinematics (see the table on page 38). ⋅ State the value of g, the magnitude of the gravitational acceleration near the 1D Motion with Constant surface of the earth. Acceleration 2.4-­‐2.5 ⋅ Describe the size and direction of the velocity and acceleration of an object thrown or dropped vertically at any point along its trajectory. Freefall ⋅ Use the equations of 1D kinematics to solve for the trajectory of an object thrown or dropped vertically. Physics 2240 Syllabus Mon 2/13 Tues 2/14 3.3 Mon 2/20 Tues 2/21 Thurs 2/23 Fri 2/24 Mon 2/27 Tues 2/28 ⋅ Describe qualitatively the vertical and horizontal motion of a projectile. ⋅ Calculate the trajectory of a projectile. Homework #3 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Thurs 2/16 Fri 2/17 Projectile Motion Scaife/Spring 2012 Prelab Exam Review LAB: Projectile Motion ⋅ Make measurements of the trajectory of a projectile and calculate its initial velocity. ⋅ Predict the effect that a change in initial conditions will have on the trajectory. EXAM 1 5.4 Topics: Newton’s Laws, 1-­‐D Motion ⋅ Describe the role of centripetal acceleration in circular motion. ⋅ Explain how inertia causes passengers in a turning car to seemingly experience Circular Motion and Centripetal centrifugal forces. Acceleration ⋅ Relate centripetal acceleration, speed and radius for an object in circular motion. ⋅ Relate the period, speed and radius of uniform circular motion. Homework #4 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Prelab Projectile Motion Quiz FORMAL LAB: Drag ⋅ Observe that drag can be linearly dependent or quadratically dependent on velocity. Online Tutorial Homework #4 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight Circular Motion Problems ⋅ Identify the two requirements for accomplishing work. ⋅ Give the SI units of work and express them in SI base units. 6.1-­‐6.2, Work and Kinetic Energy ⋅ Explain the significance of the “dot product” in the equation for work. 1.10 ⋅ Define kinetic energy and relate it to work. ⋅ Explain the significance of negative work. Homework #5 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Circular Motion Quiz Formal Lab Report from Drag Due at Start of Class ⋅ Define mechanical advantage. Thurs Prelab LAB: S imple M achines ⋅ Observe the relationship between mechanical advantage and work. 3/1 ⋅ Design pulley systems to give a desired mechanical advantage. Online Tutorial Homework #5 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight Fri 3/2 Mon 3/5 Tues 3/6 7.1 Gravitational Potential Energy ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ Describe conceptually what is meant by potential energy. Relate changes in potential energy to work. Calculate gravitational potential energy. Explain what is meant by the “zero level” of gravitational potential energy. ⋅ Define mechanical energy in terms of KE and PE. ⋅ Calculate elastic potential energy. ⋅ Draw initial state/final state diagrams involving KE, gravitational PE and elastic Mechanical Energy 7.2-­‐7.4 PE. Elastic Potential Energy ⋅ Define “conservative” and solve problems involving both PE and non-­‐ conservative work. Homework #6 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM -­‐-­‐ Exam Review Physics 2240 Syllabus Thurs 3/8 Fri 3/9 Mon 3/12 Prelab LAB: Springs EXAM 2 8.1 Momentum and Impulse Scaife/Spring 2012 ⋅ Verify Hooke’s Law for a vertical mass-­‐on-­‐spring. ⋅ Verify approximate energy conservation in the system. ⋅ Allow for the kinetic energy of an oscillating spring. Topics: Projectiles, Circular Motion, Work & Energy ⋅ Define momentum and impulse. ⋅ Use the concept of impulse to define the average force applied. Homework #7 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Mechanical Energy Quiz ⋅ Show that the momentum of one participant in a collision is not conserved. Prelab LAB: Collisions Thurs ⋅ Show that the total momentum of all participants in a collision is conserved. 3/15 Online Tutorial Homework #6 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight ⋅ Explain why it is common to analyze a group of colliding objects as a single system. Fri 8.2-­‐8.3 Collisions and Explosions ⋅ Set up the equation of momentum conservation for a 2D collision or explosion. 3/16 ⋅ Describe the energy change in a perfectly inelastic collision or an explosion. Tues 3/13 SPRING BREAK 3/19-­‐3/23 Mon 3/26 Tues 3/27 ⋅ Write and solve the equations that govern a 1D elastic collision. ⋅ Explain the rule of conservation of relative velocity for a 1D elastic collision. Homework #8 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM -­‐-­‐ Momentum Quiz 8.4 Elastic Collisions Prelab LAB: 2D Collisions Thurs ⋅ Show that vector momentum is conserved in a 2D collision. 3/29 Online Tutorial Homework #7 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight ⋅ Define “radian” and “rigid body”. ⋅ Describe the analogy between rotation and 1D motion. Fri 9.1-­‐9.3 Angular Kinematics 3/30 ⋅ Define angular position, velocity and acceleration and state the units of each. ⋅ Relate linear movement to angular movement. Mon 4/2 Tues 4/3 9.4 Rotational Energy ⋅ Define moment of inertia. ⋅ Determine the relationship between translational and rotational kinetic energy for an object of known moment of inertia that is rolling without slipping. Homework #9 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM -­‐-­‐ Collisions Quiz Prelab LAB: Angular Dynamics Thurs ⋅ Demonstrate the dependence of angular velocity on radius of mass. 4/5 Online Tutorial Homework #8 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight Fri NO CLASS—April Break 4/6 Mon 4/9 NO CLASS – April Break Tues 4/10 Homework #10 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM ⋅ Identify the two requirements for producing torque about a given axis of rotation. ⋅ Define perpendicular force as it relates to torque. ⋅ Calculate the torque produced by a given force about a known axis. Prelab LAB: Torque and Statics ⋅ Identify the two conditions necessary for equilibrium of a rigid body. ⋅ Given a statics problem, choose an advantageous axis of rotation and set up the equations of force and torque balance. Thurs NO CLASS – Engineering Expo 4/12 Physics 2240 Syllabus Fri 4/13 Mon 4/13 Tues 4/17 Thur 4/19 Fri 4/20 Mon 4/23 Tues 4/24 Thurs 4/26 Fri 4/27 Mon 4/30 Tues 5/1 -­‐-­‐ Exam Review EXAM 3 Topics: Energy, Momentum, Rotational Kinematics 10.4 FORMAL LAB: Moment of Prelab Inertia Homework #11 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Fixed-­‐Axis Rotation, nd 10.2 ⋅ Use the analog of Newton’s 2 Law for rotation. Statics Quiz ⋅ Decompose an arbitrary motion of a rigid body into rotation about the center of mass plus translation of the center of mass. 10.3 Rotation and Translation ⋅ Apply the constraint of rolling without slipping to relate the rotational and linear dynamics of a rigid body. ⋅ Calculate the center of mass for a system of discrete masses. ⋅ Calculate the moment of inertia for a system of discrete masses. 9.4-­‐9.6 Computing Moments of Inertia ⋅ Set up the integral to define the moment of inertia or CM of a simple object. ⋅ Use the Parallel Axis Theorem to define the moment of inertia of a composite object or object in asymmetric rotation. Homework #12 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Rotational Dynamics Quiz Formal Lab Report from Moment of Inertia Due at Start of Class LAB: Mechanical Advantage in Rotation Online Tutorial Homework #9 on Mastering Physics Due by Midnight ⋅ Define the angular momentum of a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis. ⋅ Define the angular momentum of a point particle and give an observational 10.5-­‐10.6 Angular Momentum justification for this concept. ⋅ Analyze rotational collisions. ⋅ Define and relate period, frequency and angular frequency. ⋅ Define amplitude. 13.1-­‐13.2 Simple Harmonic Motion ⋅ Draw analogies between simple harmonic and circular motion. ⋅ Relate the angular frequency of the harmonic motion of a mass-­‐on-­‐spring to the spring constant and mass. Homework #13 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM -­‐-­‐ Exam Review Prelab Thurs Describing Harmonic Motion 15.1-­‐15.3 5/3 and Waves Fri 5/4 Scaife/Spring 2012 EXAM 4 ⋅ Use sine and cosine functions with phase to describe oscillations and waves. Rotational Dynamics, Angular Momentum ⋅ Explain why the pendulum only yields SHM if the amplitude of oscillations is small. 13.5 The Simple Pendulum ⋅ Relate the angular frequency of pendulum motion to the length of the pendulum and the strength of gravity. Tues ⋅ Explain the phase shift between position, velocity and acceleration in SHM. Prelab LAB: Pendulums 5/8 ⋅ Determine the moment of inertia of a physical pendulum. Homework #14 on Mastering Physics Due Online by 8 AM Thurs Online Tutorial Homework #10 on Lon Capa Due by 8 AM 5/10 Review, -­‐-­‐ Final in-­‐class Survey Final Exam Review Activity Fri 5/11 Final online survey on D2L Due by 5 pm Mon 5/7 FINAL EXAM: Monday, May 14 5:00 PM – 6:52 PM