single transistor amplifiers
advertisement

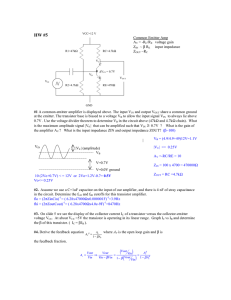
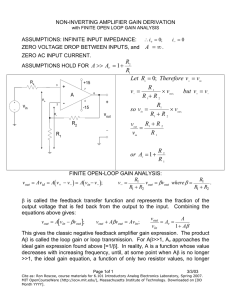
Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 1 3.2 - SINGLE TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Show how to characterize an amplifier 2.) Show the analysis of single transistor amplifiers using resistive loads 3.) Build the amplifier concepts necessary to consider integrated circuit amplifiers Outline • Characterizing an amplifer • BJT Single transistor amplifiers • MOS Single transistor amplifers • Amplifiers with emitter/source degeneration • Summary ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 2 CHARACTERIZING AMPLIFIERS Characterization of Amplifiers Amplifiers will be characterized by the following properties: • Large-signal voltage transfer characteristics (.DC) • Large-signal voltage swing limitations (.DC and .TRAN) • Small-signal, frequency independent performance (.TF) • Gain (.TF) • Input resistance (.TF) • Output resistance (.TF) • Small-signal, frequency response (.AC) • Other properties (.TEMP, .FOUR, etc.) • Noise (.NOISE) • Power dissipation (.OP) • Slew rate (.TRAN) • Etc. ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 3 Types of Single Transistor Amplifiers VCC RC VCC RC vIN RC vOUT VCC VCC vOUT vOUT vIN vOUT vIN RE RE vIN Common Emitter Common Base Common Collector Emitter Degeneration VDD VDD RD VDD RD vIN RD vOUT VDD vOUT vIN vOUT vIN RS RS vIN Common Source vOUT Common Gate ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems Common Drain Source Degeneration STA01 P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 4 Signal Flow in Transistors It is important to recognize that ac signals can only flow into and out of certain transistor terminals. Illustration: C D 180° 180° B 0° 0° G 0° 0° E S STA015 Rules: The collector or drain can never be an input terminal. The base or gate can never be an output terminal. In addition it is important to note polarity reversals on these signal paths. The base-collector or gate-drain path inverts. All other paths are noninverting. (This of course assumes that there are no reactive elements causing phase shifts) ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 5 BJT SINGLE TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS Common Emitter Amplifer Large-Signal: vOUT iC VCC RC vOUT VCC Forward Active Region VCC RC VIN, IB vIN Saturation Region vCE(sat) Common Emitter 0 VCC 0 Small-Signal: IC gm = V t vCE 0 0 Rin i in and VA ro = I C 0.5V iout B E + vin - gmvin ro RC vIN STA02 Rout + rπ 1.0V C vout E βο roR C vout -g m ·ro ·R C iout β o ·ro R in = rπ = and i = r + R gm , Rout = r o + R C , vin = r o + R C in o C (One should also consider the case of a source resistance, RS, in series with the input) ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 6 Example 1 - Common Emitter BJT with Source Resistance Find the small-signal input resistance, Rin, output resistance, Rout, voltage gain, vout/vin, and current gain, iout/iin for the circuit shown. Assume that βo is 100, VA = 100V, and Is = 10fA. E + vin - RS= 10kΩ rπ iout iout ro RL RL= 10kΩ RS=10kΩ 1mA Rout + RC Rout vout Rin iin vin Rin iin + vπ - gmvπ RC= 2.5kΩ C=∞ Solution Small-signal model is: B 5V C C=∞ -5V STA08 vout E STA09 IC 1mA 1+βo V A 100V 101 gm = V = 26mV = 38.5mS, rπ = g = 38.5ms = 2.62kΩ and ro = I = 1mA = 100kΩ t m C R in = R S+rπ = 12.62kΩ, Rout = ro||RC||RL = 1.96kΩ, vout vout v π r π 2.62 -gmRout = = = 12.62 (-38.5·1.96) = -15.66 V/V ⇒ 23.9dB vin v π vin Rin and iout ioutv π gm(ro||RC) iin = v π iin = RL+ro||RC rπ = (7.549mS)(2.62kΩ) = 19.78 A/A The maximum voltage gain (RS → 0, RC → ∞, RL → ∞) is -VA/Vt = -100/0.026 = -3846V/V ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 7 Common Base Amplifer Large-Signal: iC vOUT VCC RC VCC VCC vOUT RL Forward Active Region VIN Saturation Region vIN STA04 0 vCB VCC 0 0 -0.5 0 vIN -0.6 Small-Signal: gmvin Rin i in E B + vin - iout Rout + rπ ro RC C vout B STA05 rπ vout iout -gm β 1 1 Neglecting ro, Rin = g + g ≈ g = β +1 , R out ≈ R C , v ≈ gmRC and i = g +g 1+β = -α π m m o in in m π (One should also consider the case of a source resistance, RS, in series with the input) ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 8 Common Collector (Emitter Follower) Large-Signal: vOUT = vIN -vBE vOUT VCC vIN Forward Active Region VBE ≈ 0.7V vOUT RE 0 STA06 vIN 0 Small-Signal: Rin i in B + vin C vπ + rπ - Rout iout + gmvπ ro RE E vout C STA07 rπ gmRE iout 1 v out Neglecting ro again, Rin = rπ + (1+βο)RE , Rout = 1+β = g , v = 1+g R ≈ 1 and i = -(1+βo) ο m in m E in (One should also consider the case of a source resistance, RS, in series with the input) ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 9 MOS SINGLE TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS Common Source Amplifier Large-Signal: vDS = VGS-VT iD vOUT Cutoff Region Saturation VDD Region vOUT vI VDD RD U T= RD N- V T VDD vO VIN vIN STA10 0 VDD 0 vDS 0 0 VT Triode Region VDD VIN Small-Signal: Rin i in iout G S Rin = ∞, Rout = r + vin - Rout + gmvin rdsRD , ds + R D ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems rds RD vout -g m ·rds·R D vin = r ds + R D D vout S STA11 and iout iin = ∞ P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 10 Common Gate Amplifier Large-Signal: iD Cutoff Region VDD RD vOUT vOUT VDD VDD RD Saturation Region VIN<VT vIN STA12 0 0 vDG VDD VT Triode Region VIN = 0 -VT vIN Small-Signal: gmvin Rin i in iout S + vin G Neglecting rds, 1 Rin = ≈ g , m Rout + rds Rout ≈ RD , ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems RD vout vin ≈ gmRD D vout G STA13 and iout iin = -1 P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 11 Example 2 Find the values of Rin, Rout, and vout/vin of the common gate amplifier including rds. Assume that KN’ = 110µA/V2, VT = 0.7V, λN = 0.04V-1, W/L = 10µm/1µm , ID = 200µA and RD = 20kΩ. Solution First find the model parameters. gm = 2KN’WID = 2·110·10·200 = 663µS L 1 106 and rds = λ I = 0.04·200 = 125kΩ ΝD Using the small-signal model shown we get, vin = (iin-gmvin)rds + iinRD gmvin Rin i in iout S + vin G Rout + rds RD D vout G STA14 vin rds+RD 145kΩ Rin = i = 1+g r = 1+82.9 = 1.728kΩ (Compared to 1.51kΩ if we neglect rds) in m ds Writing a nodal equation at the output gives vout gm+gds 663+8 gmvin + gds(vin-vout) - GDvout → v = g +G = 8+50 = 11.57 V/V in ds D (Compared to 13.26V/V if we neglect rds) Rout = rds||RD = 17.24kΩ (Compared to 20kΩ if we neglect rds) ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 12 Common Drain (Source Follower) Large-Signal: v OUT = v IN - v GS vOUT VDD vIN vOUT Saturation Region vGS RS 0 STA15 vIN 0 Small-Signal: G + vin D Neglecting rds gives, Rin = ∞, Rin + iout vgs - Rout + gmvgs rds RS vout D STA16 RS Rout = RS||(1/gm ) = 1+g R m S ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems S and vout gmRS vin = 1+gmRS < 1 P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 13 AMPLIFIERS WITH EMITTER/SOURCE DEGENERATION Common Emitter with Emitter Degeneration VCC RC Rin iOUT B C + rπ vπ RB ro gmvπ vin vIN Rout + vOUT iIN RB E RC vout RE RE - - STA17 Rin = RB+rπ+(1+βo)RE βοRE Rout = ro 1 + R +R +r + R E||(R B+rπ) ≈ (1+βo)ro B E π vout vin = - RC βoR C ≈ - r +(1+β )R ≈ - R rπ +R B π o E E Rin ro+RC+RE|| 1+β o gm rπro ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems | max. gain P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 14 Common Source with Source Degeneration VDD RD iOUT vOUT Rin + G + vin vgs - iIN vIN RB RG D Rout + gmvgs S rds RD vout RS RS - STA18 Rin = ∞ R out = rds[1 + (gm + gmbs)R S] + R S ≈ rdsgm R S gmRD RD vout vin ≈ - 1+gmRS → - R S max. gain ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems P.E. Allen Single Transistor Amplifiers (6/13/00) Page 15 SUMMARY BJT Single Transistor Amplifiers Small-Signal Performance Common Emitter rπ (Medium) Common Base rπ (Low) 1+β Output Resistance ro (High) ro(1+βo) (Very high) rπ+(1+βo)RE (High) rπ +R S 1+βo (Very low) Voltage Gain -gmRL gmRL 1 Current Gain βo -α -(1+βo) Small-Signal Performance Common Source Common Drain Input Resistance ∞ Output Resistance rdsRD r ds + R D Common Gate rds+RD 1+gmrds rdsRD rds+RD Voltage Gain -g m ·rds·R D r ds + R D gmRD 0.8 Current Gain ∞ -1 ∞ Input Resistance o Common Collector MOS Single Transistor Amplifiers ECE 4430 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems ∞ RS 1+gmRS P.E. Allen