Q.1] Derive expression for the inductance of a 3
![Q.1] Derive expression for the inductance of a 3](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018083678_1-e4ff1317469347b6cc691fbb93a4b1f5-768x994.png)
SGGS Institute of Engineering and Technology, Vishnupuri, Nanded.
Department of Electrical Engineering
Date: 11/09/2013
Academic year: 2013-14 Assignment:02
Subject: Power System-I Class: Third Year
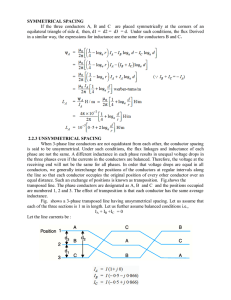
Q.1] Derive expression for the inductance of a 3-phase line with conductors untransposed. What is the significance of imaginary terms in the expressions for inductance? Hence derive the expression for inductance for a completely transposed line.
Q.2] Explain the terms mutual GMD and ‘self GMD’ in the inductance calculation of an over head transmission lines. Find the self GMD of a conductor consisting of seven identical strands each having a radius ‘r’.
Q.3] Which factors govern the capacitance of transmission line?
Derive the capacitance per km to neutral of 3-phase overhead transmission line with unsymmetrical spacing of conductors assuming transposition.
Q.4] How transposition helps in equalizing the capacitance in an unsymmetrical spaced 3-phase overhead transmission line.
Q.5] Write short notes on the following:
I.
Bundled conductor.
II.
Skin effect.
III.
Proximity effect.
IV.
Effect of earth on the capacitance of a transmission line.
Q.6] The reactance of a generator designated X” is given as 0.25 pu based on the generators nameplate rating 18 KV, 500MVA. The base for calculations is 20KV,
100MVA. Find X” on the new base. [Ans: 0.0405 pu]
Q.7] Find the GMR of the each of the unconventional conductors shown in Fig. in terms of the radius ‘r’ of a individual strand.
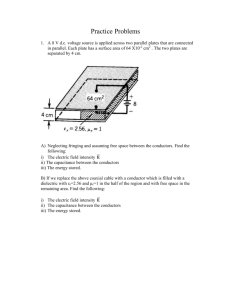
Q.8] A single circuit 3-phase line operating at 50 Hz has a conductor diameter of
5.18 mm. The spacing between the line conductors is given in meters. D ry
=3.2; D yb
=4.0; D br
=5.0. Calculate the inductance and inductive reactance per phase per km.
[Ans: 1.52mH; 0477 Ω]
Q.9] Find the inductive reactance of a 3-phase bundled conductor line with 2 conductors per phase with spacing of 40cm. Phase to phase separation is 7 m in horizontal configuration. All conductors are ACSR with dia. of 3.5cm.
Compare the above value with that of an equivalent single-conductor line.
[Ans: 0.3
Ω/Km ; 0.385
Ω/Km]
Q.10] The three conductors of a 3-phase , 3-wire line are arranged at the corners of a triangle, the sides of which are 1m, 1.3m, 2m . Calculate the inductance and capacitance per km of the line, when the conductors are transposed. The conductors are 1.5 cm diameter. [Ans: 1.0923mH; 0.0107µF]
Q.11] A 100 km double circuit transmission line with 7 stranded copper conductors each strand having 5mm diameter, has 6 conductor arranged in the form shown in
fig. The line is transposed at regular intervals. Evaluate the GMD and GMR and calculate the overall inductance per phase of the line. [ Ans: 0.0717H]
Q.12]Find out the capacitance of a 2-wire, 1-phase line running at a height of ‘h’ meters above the earth.
Calculate the capacitance to neutral in the case of a single phase line whose conductors with radius of 0.25cm are separated by 1.5m and which are lying 7m above the ground. Line length is 50km. [Ans: 0.225µF]
Q.13] Calculate the loop inductance per km of a single phase transmission line comparing of two parallel conductors one meter apart and 1.25 cm in diameter.
Also calculate the reactance of the transmission line if frequency is 50 Hz.
[Ans:0.67 ohm ]
1m
Q.14] A three phase transmission line 100 km long has its conductors of 0.5 cm diameter spaced at the corners of an equilateral trainable 0f 120 cm side. Find the inductance per phase of the system. [Ans: 55.8 mH]
D d= 0.5 cm
D
D= 120 cm
Q.15] A single phase line of 230 V has conductor spacing of 135 cm. The radius of conductor is 0.8 cm.Calculate the loop inductance in mH of the line per km.
[Ans: 2.15 mH]
Q.16] Three conductors of a 3-phase overhead line are arranged in horizontal plane, 6 meter apart. The diameter of each conductor is 1.24 cm. Find the capacitance per 100 km of the line in µF.[Ans: 0.785 µF]
Q.17] There are 6 conductors in a double circuit line. Each conductor has a radius of 12 mm . The six conductors are arranged horizontally. The center to center distance between the conductors is 2 m. The Sequence of conductor are from left to right as follows: a, b, c, a’, b’, c’. Calculate the inductance per km per phase of the system [U.P.S.C. I.E.S. EE-II, 2007] [Ans: 0.546 mH/km]