Student Academic Services Intended Learning Outcomes
advertisement

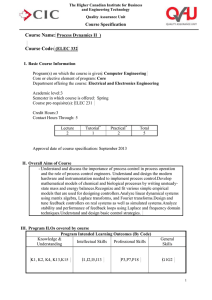
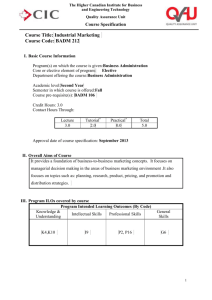
Student Academic Services Intended Learning Outcomes What are Intended Learning Outcomes? Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) define what a learner will have acquired and will be able to do upon successfully completing their studies. ILOs are expressed from the students’ perspective and are measurable, achievable and assessable. Why should we write Intended Learning Outcomes? ILOs are the cornerstone of every session, course, programme, module, or unit of study. ILOs allow learners to see what they are aiming for at all times and the value of the appropriately aligned assessments. The Quality Assurance Agency Understanding Assessment guide (2011) illustrates the relationship between ILOs, assessment and learning activities/resources and the order in which they should be considered, “Stage 1: Decide on the intended learning outcomes. What should the students be able to do on completion of the course (and what underpinning knowledge and understanding will they need in order to do it) that they could not do when they started? Stage 2: Devise the assessment task(s). If you have written precise learning outcomes this should be easy because the assessment should be whether or not they can satisfactorily demonstrate achievement of the outcomes. Stage 3: Devise the learning activities necessary (including formative assessment tasks) to enable the students to satisfactorily undertake the assessment task(s). These stages should be conducted iteratively, with each stage informing the others to ensure coherence.” This approach is called constructive alignment. Author: Nichola Hayes There are a lot of references for constructive alignment, but the work of Prof. John Biggs provides a good overview of its value. http://youtu.be/iMZA80XpP6Y [Part of theTeaching Teaching & Understanding Understanding series – video length: 8 mins] It is due to educational theorists such as Biggs and the Quality Assurance Agency that ILOs are a key element of any HEI programme of study. The Quality Code for Higher Education (2012) ensures equality and parity across the UK HE sector and Part B stipulates HEIs must demonstrate: “Learning and teaching activities and associated resources provide every student with an equal and effective opportunity to achieve the intended learning outcomes.” How to write Intended Learning Outcomes? Intended Learning Outcomes should be written using what is often referred to as, active verbs (something students can do to demonstrate the results of their learning). In this context passive verbs would be ‘appreciate’ or ‘show awareness’ – they make it difficult for the student to understand what is needed; and difficult for staff to assess. A commonly seen passive verb used for writing ILOs is ‘understand’. The UoL Learning and Teaching website highlights the pitfalls of using ‘understand’. “...take the following example: Understand how to drive a car. This could mean several different things. • Move, steer and stop a car. • Understand the mechanics of how to drive a car but not actually be able to drive one.” Consider the first of these, Move, steer and stop a car. 5 February 2013 In order to measure/observe how well the learner can do these things we can use active verbs to write the following ILOs: Labour Market Studies Analyse and critique theories of workplace and work-related learning Reproduce the manoeuvres required to perform a three-point turn safely. Discuss the stopping distances required when driving a car at 30mph, 50mph and 70mph. Biological Sciences Explain how chromosomes are inherited through mitosis and meiosis and how genetic variation is generated Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives is a good starting point for developing learning outcomes. The taxonomy identifies six different levels of learning: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. There are several resources that list the active verbs you might consider for each of Bloom’s levels of learning. For example, Can your ILOs be measured/observed? Are all of your ILOs addressed by your assessments? Can the learner achieve ALL of the ILOs? • • Level of Learning Knowledge Active Verbs • Define • Reproduce • Arrange Comprehension • • • Discuss Explain Classify Application • • • Demonstrate Operate Solve Analysis • • • Differentiate Analyse Calculate • • • Predict Assess Construct • • • Assess Critique Predict Synthesis Evaluation Measurable/Observable ILO Examples Archaeology Demonstrate a knowledge of basic Greek grammar and syntax Mathematics Construct basic VBA computer programs for the numerical solution of basic problems Intended Learning Outcomes - Quick Check References & Resources Biggs, J. & Tang, C., 2007. Teaching for Quality Learning at rd University (3 ed.), Buckingham: Society for Research into Higher Education/ Open University Press. [eBook available from UoL Library] Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education. 2012. B3: Learning and teaching Quality Code for Higher Education. [online] Available at: <http://www.qaa.ac.uk/Publications/InformationAndGuidan ce/Documents/Quality-Code-B3.pdf> [Accessed 03 February 2013] Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education. 2011. Understanding assessment: its role in safeguarding academic standards and quality in higher education. [online] Available at: <http://www.qaa.ac.uk/Publications/InformationAndGuidan ce/Documents/UnderstandingAssessment.pdf> [Accessed 03 February 2013] University of Leicester. Learning and Teaching. [online] Available at: <http://www.le.ac.uk/teaching/learningoutcomesunderstan d.html> [Accessed 03 February 2013] Cox, D. & Matthews, L., 2010. PGCert Module A Handout. University of Leicester. Bloom’s Taxonomy - Active Verb Lists http://www.indstate.edu/academicaffairs/assessment/isu_a ssessment_handbook/verbs_for_writing_student_learning_ outcomes.pdf http://apps.medialab.uwindsor.ca/ctl/downloads/2007/Geri %20Van%20Gyn%20%20Verbs%20for%20Learning%20Outcomes.pdf ILO Guides Race, P. How to Design Learning Outcomes. [online] Available at: <http://www.glyndwr.ac.uk/pd/newi_mod3/mod3/papers/ Race%20Designing%20LO.pdf > [Accessed 03 February 2013] Baume, D. (2009) Writing and Using Good Learning Outcomes. [online] Available at: http://www.leedsmet.ac.uk/staff/files/Learning_Outcomes. pdf [Accessed 03 February 2013]