Representing Thousandths
advertisement

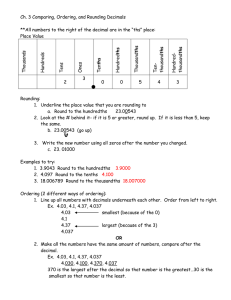
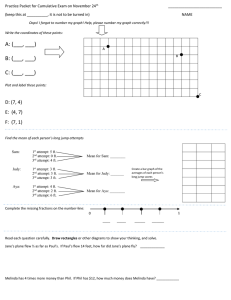
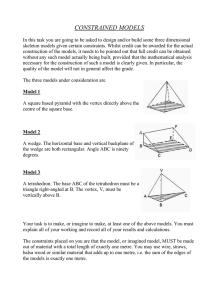
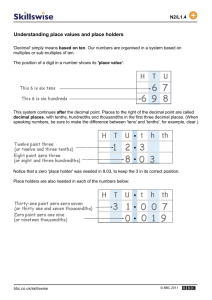
Representing Thousandths Visualizing Thousandths Materials • • overhead transparency of a 10x10 grid (attached) overhead projector Activity Display an overhead transparency of a 10x10 grid. Explain that the grid represents one whole and ask students to point to sections of the grid that represent different quantities of tenths and hundredths (e.g., 1 tenth, 7 tenths, 20 hundredths, 92 hundredths). Next, ask students to imagine what one thousandth of the grid would look like. Discuss how a thousandth is one-tenth of a hundredth (a small square). Help students to understand this idea by using an overhead marker (preferably with a fine tip) to divide a small square into ten sections. Alternatively, place 10 toothpick pieces, cut to the length of a small square, lengthwise in the square to divide it into 10 parts. Discuss how one thousandth is a small quantity compared to the whole grid. Note: Base-ten materials provide another powerful way to visualize thousandths. Start with a cube of 10 flats to represent the whole. One flat represents a tenth, a rod represents a hundredth, and a unit cube represents a thousandth. Decimal Numbers – Grade 4 to Grade 6 1 © Queen's Printer for Ontario, 2006 Representing Thousandths Thinking about a Thousandth Materials • • • • • overhead transparency of a 10x10 Grid (attached) overhead projector copies of 10x10 Grids (6 grids on a page) – 2 pages per pair of students scissors – for each pair of students tape – 1 roll per pair of students Activity Display an overhead transparency of a 10x10 Grid. Cover nine columns of the grid with a sheet of paper so that only one column is visible on the screen. Ask students to imagine that the column represents the whole and to explain the relationship between a small square and the column (i.e., a small square is one tenth of the column). Have students come to the overhead projector and indicate what 3 tenths, 5 tenths, and 9 tenths would look like. Next, reveal the entire 10x10 grid and tell the students that the entire grid now represents one whole. Again, ask them to explain the relationship between a small square and the entire grid. (A small square is one hundredth of the grid.) Have students indicate on the overhead transparency different numbers of hundredths (e.g., 3 hundredths, 20 hundredths, 89 hundredths). Arrange students in pairs. Provide students with copies of 10x10 Grids, scissors, and tape and explain that they are to work with their partner to create a model that represents one whole in which one small square represents a thousandth. Students should discover that 10 grids taped together in any configuration form a whole that is composed of 1000 small squares and that each square is one thousandth of the whole. A Possible Model for Thousandths Have students share their models with the class and ask them to explain the relationship between a small square and one whole. Record 0.325 on the board and instruct pairs of students to shade part of their model to show the decimal number. Record other decimal numbers on the board and have students discuss with their partner how their model could be shaded to show the numbers. Decimal Numbers – Grade 4 to Grade 6 2 © Queen's Printer for Ontario, 2006 Representing Thousandths Thousandths on a Metre Stick Materials • metre stick (calibrated in centimetres and millimetres) Activity Tape a metre stick to the board. Ensure that students are close enough to the metre stick to see the centimetre markings and numbers. Discuss how one metre is divided into 10 decimetres, 100 centimetres, and 1000 millimetres. Ask the following questions and have students explain their answers: – “What fraction is a decimetre of a metre?” [one tenth] – “What fraction is a centimetre of a metre?” [one hundredth] – “What fraction is a millimetre of a metre?” [one thousandth] Draw a line segment that extends from 0 to 8 cm below the metre stick on the board. Ask: – “What is the length of the line segment in centimetres? in millimetres?” – “What fraction is the line segment of the metre?” Have students explain why the line segment can be described as 8 hundredths of a metre and 80 thousandths of a metre. Record these amounts as decimal numbers and have students explain why 0.08 (8 hundredths) and 0.080 (80 thousandths) represent the same quantity. Continue by drawing other line segments below the metre stick and asking students to identify the number of hundredths and thousandths that each line segment is of one metre. Decimal Numbers – Grade 4 to Grade 6 3 © Queen's Printer for Ontario, 2006 Representing Thousandths Thousandths on a Number Line Materials • metre stick (calibrated in centimetres and millimetres) Activity On the board, draw a line that is 1 m long. Label 0 and 1 at opposite ends. 0 1 Explain that the length of the line is one metre. Clarify that a metre is composed of 1000 millimetres and that each millimetre is one thousandth of a metre. On the board, record a decimal number expressed as thousandths (e.g., 0.564) and ask students to estimate the location of the decimal number on the number line. Invite a few students to indicate their estimates on the number line and have them explain their thinking. For example, students might explain that 0.564 would be located slightly to the right of the midway point between 0 and 1 1 1 because 564 thousandths is close to 5 tenths ( ) or 56 hundredths (close to ). 2 2 Ask students to use a metre stick to check estimated positions of numbers on the line segment. Two students could hold the metre stick directly below the number line and a third student could indicate how the markings on the metre stick can be used to locate the position of the decimal number (e.g., 0.564 would be located 4 millimetres to the right of the 56 centimetre mark). Repeat by having students estimate the location of other thousandths (e.g., 0.764, 0.911, 0.005). For each number, ask students to explain how they made their estimate and to check their estimates using the metre stick. Decimal Numbers – Grade 4 to Grade 6 4 © Queen's Printer for Ontario, 2006 10x10 Grid Decimal Numbers – Grade 4 to Grade 6 5 © Queen's Printer for Ontario, 2006 10x10 Grids Decimal Numbers – Grade 4 to Grade 6 6 © Queen's Printer for Ontario, 2006