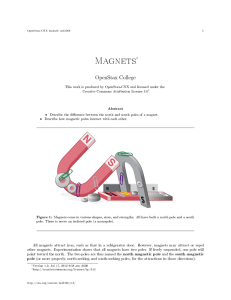
Magnetism and electromagnetic induction Magnets are bipolar
advertisement
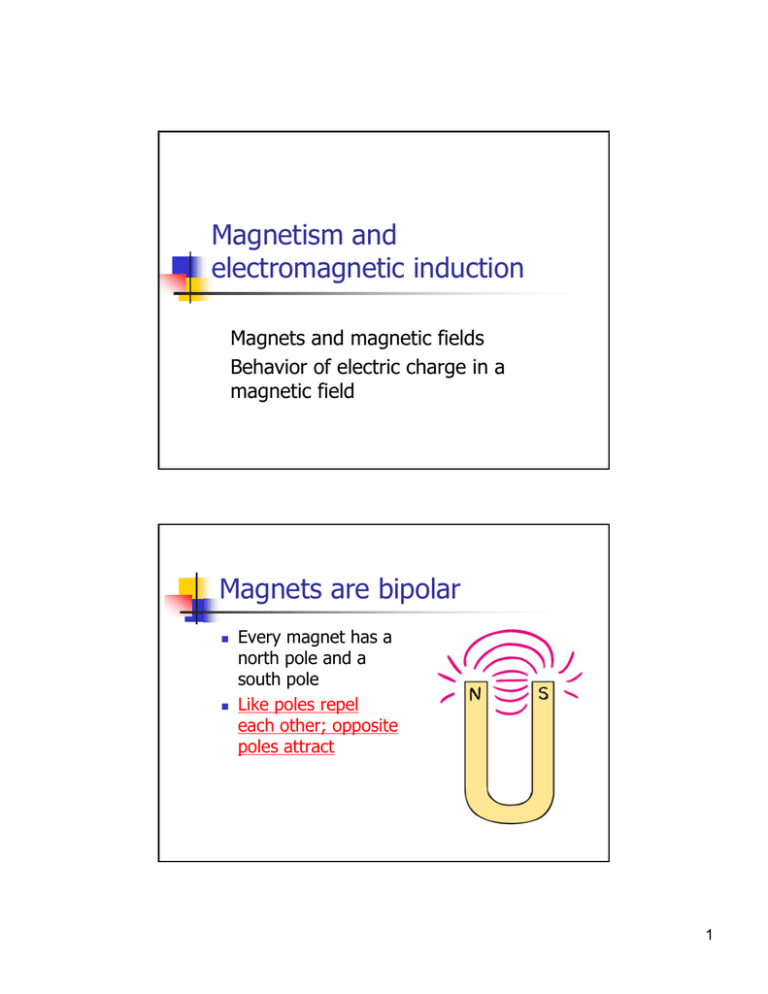
Magnetism and electromagnetic induction Magnets and magnetic fields Behavior of electric charge in a magnetic field Magnets are bipolar Every magnet has a north pole and a south pole Like poles repel each other; opposite poles attract 1 Magnets are bipolar Every magnet has a north pole and a south pole Like poles repel each other; opposite poles attract Breaking a magnet gives you two magnets Magnetic field lines run from north pole to south pole This can be followed with iron dust and a piece of paper demonstration 2 Compasses align with the Earth’s field lines Which way are the forces operating? What is the net force? Why does the needle turn? Demonstration of Earth’s magnetic field Magnetic domains Every magnetic material has “magnetic domains” Random orientation until brought into external magnetic field Domains can then be aligned Shocks will knock them out of alignment 3 Electric currents produce magnetic fields The field is perpendicular to the axis of current flow Field lines surround the wire Different wire configurations give different field configurations Magnetic fields exert force on charge particles, including electric currents Current-carrying wires are deflected by magnets Deflection depends on current direction Current-carrying wires generate their own fields Therefore attract or repel each other 4 Cosmic rays in the Earth’s magnetic field Putting this to work: DC electric motors 5