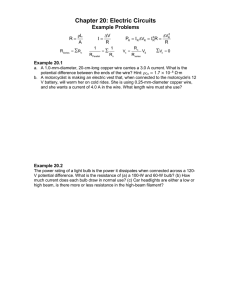
Two copper wires of different diameter are joined in series in a

Q25.1
Two copper wires of different diameter are joined in series in a circuit. A current fl ows in the wire combination.
When the current fl ows from the larger-diameter wire into the smaller-diameter wire,
A. the current increases.
B. the current decreases.
C. the current stays the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
A25.1
Two copper wires of different diameter are joined in series in a circuit. A current fl ows in the wire combination.
When the current fl ows from the larger-diameter wire into the smaller-diameter wire,
A. the current increases.
B. the current decreases.
C. the current stays the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
Q25.2
Two copper wires of different diameter are joined in series in a circuit. A current fl ows in the wire combination.
When the current fl ows from the larger-diameter wire into the smaller-diameter wire,
A. the drift velocity increases.
B. the drift velocity decreases.
C. the drift velocity stays the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
A25.2
Two copper wires of different diameter are joined in series in a circuit. A current fl ows in the wire combination.
When the current fl ows from the larger-diameter wire into the smaller-diameter wire,
A. the drift velocity increases.
B. the drift velocity decreases.
C. the drift velocity stays the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
Q25.3
Electrons in an electric circuit pass through a resistor. Compared to the potential energy of an electron before entering the resistor, the potential energy of an electron after leaving the resistor is
A. greater.
B. less.
C. the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
A25.3
Electrons in an electric circuit pass through a resistor. Compared to the potential energy of an electron before entering the resistor, the potential energy of an electron after leaving the resistor is
A. greater.
B. less.
C. the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
Q25.4
Electrons in an electric circuit pass through a source of emf.
Compared to the potential energy of an electron before entering the source of emf, the potential energy of an electron after leaving the source of emf is
A. greater.
B. less.
C. the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
A25.4
Electrons in an electric circuit pass through a source of emf.
Compared to the potential energy of an electron before entering the source of emf, the potential energy of an electron after leaving the source of emf is
A. greater.
B. less.
C. the same.
D. not enough information given to decide
Q25.5
Two copper wires. First wire is 2 m long and has a radius of 2 mm. The second one is 1 m long and has a radius of 1 mm.
Which one has a higher resistance
A. First wire
B. Second wire.
C. Both have the same resistance.
D. not enough information given to decide
A25.5
Two copper wires. First wire is 2 m long and has a radius of 2 mm. The second one is 1 m long and has a radius of 1 mm.
Which one has a higher resistance
A. First wire
B. Second wire.
C. Both have the same resistance.
D. not enough information given to decide
Q25.6
In the circuit shown, the two bulbs
A and B are identical. The arrow indicates the direction of current fl ow. Compared to bulb A ,
A. bulb B glows more brightly because the current speeds up as it enters lower potential region.
B. bulb B glows less brightly because the bulb A already used up some of the current.
C. bulb B glows just as brightly.
D. answer depends on whether the mobile charges in the wires are positively or negatively charged
A25.6
In the circuit shown, the two bulbs
A and B are identical. The arrow indicates the direction of current fl ow. Compared to bulb A ,
A. bulb B glows more brightly because the current speeds up as it enters lower potential region.
B. bulb B glows less brightly because the bulb A already used up some of the current.
C. bulb B glows just as brightly.
D. answer depends on whether the mobile charges in the wires are positively or negatively charged
Q25.7
In the circuits shown in (a) and (b), all the bulbs are identical and the emf sources are identical and are assumed to be ideal. Which circuit consumes more power
A. (a) B. (b) C. same
D. any of the above, depending on the rated wattage of the bulb.
A25.7
In the circuits shown in (a) and (b), all the bulbs are identical and the emf sources are identical and are assumed to be ideal. Which circuit consumes more power
A. (a) B. (b) C. same
D. any of the above, depending on the rated wattage of the bulb.
Q25.8
In the circuits shown in (a) and (b), all the bulbs are identical and the emf sources are identical and have same internal resistance.
Which circuit consumes more power
A. (a) B. (b) C. same
D. any of the above, depending on the resistance of the bulb.
A25.8
In the circuits shown in (a) and (b), all the bulbs are identical and the emf sources are identical and have same internal resistance.
Which circuit consumes more power
A. (a) B. (b) C. same
D. any of the above, depending on the resistance of the bulb.
Q25.9
An ideal voltmeter
A. has zero resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
B. has zero resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.
C. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
D. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.
A25.9
An ideal voltmeter
A. has zero resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
B. has zero resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.
C. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
D. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.
Q25.10
An ideal ammeter
A. has zero resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
B. has zero resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.
C. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
D. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.
A25.10
An ideal ammeter
A. has zero resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
B. has zero resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.
C. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in parallel with the circuit element being measured.
D. has in fi nite resistance and should be connected in series with the circuit element being measured.