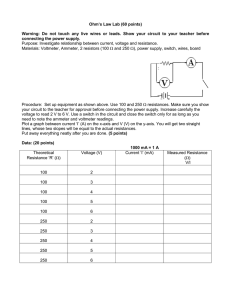
Ammeter & Voltmeter Setup: Reading Electrical Meters
advertisement

Setting Up and Reading the Ammeter 1 Setting Up an Ammeter • The ammeter is used to measure electrical current in a circuit. • In order to connect an ammeter to a circuit you must break the circuit and insert the meter. The ammeter is hooked up in series. 2 3 • The negative terminal (-) of the ammeter is connected to the positive terminal of the battery. Negative Terminal 4 • The ammeter has three positive terminals labelled 50, 500 and 5. • This indicates that the ammeter can measure current using three different scales – 0 to 50 mA (milliamperes), 0 to 500 mA, and 0 to 5A. • Since 1000 mA = 1A, the last scale is the highest scale. 5 Increments on AMMETER 500 mA scale by 10 mA 50 mA scale by 1 mA 5 A scale by 0.1 A NOTE: 1 mA = 0.001 A or 1/1000 A 6 50 500 5 7 50 500 5 8 50 500 5 9 50 500 5 10 50 500 5 11 50 500 5 12 Setting Up and Reading the Voltmeter 13 Setting Up a Voltmeter • The voltmeter is used to measure electrical potential (voltage) in a circuit.3 • In order to connect a voltmeter to a circuit you connect the meter to either side of the circuit component. The voltmeter is hooked up in parallel. 14 15 • The negative terminal (-) of the ammeter is connected to the positive terminal of the battery. Negative Terminal 16 • The voltmeter has three positive terminals labelled 3, 15 and 300. This indicates that the voltmeter can measure voltage using three different scales – 0 to 3V, 15V and 0 to 300 V. 17 Increments on VOLTMETER 300 V scale by 10 V 3 V scale by 0.1 V 15 V scale by 0.5 V 18 3 15 300 19 3 15 300 20 3 15 300 21 3 15 300 22 3 15 300 23 3 15 300 24