4.3. Effective or RMS Value
advertisement
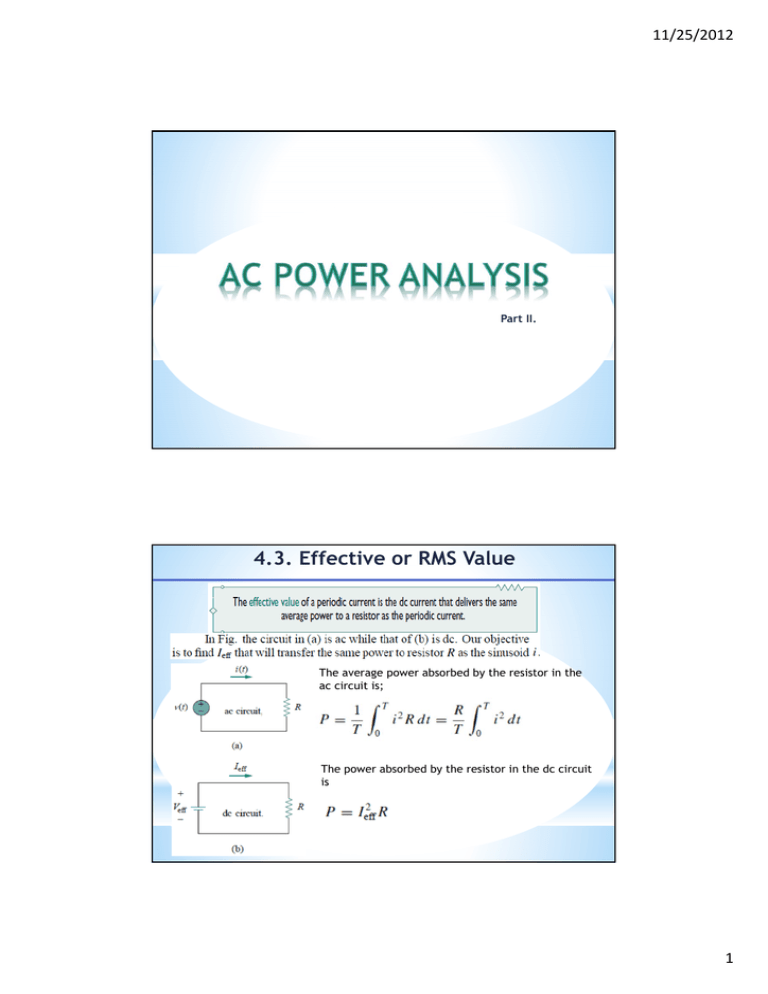
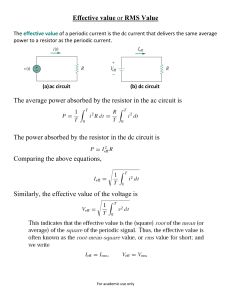
11/25/2012 Part II. 4.3. Effective or RMS Value The average power absorbed by the resistor in the ac circuit is; The power absorbed by the resistor in the dc circuit is 1 11/25/2012 4.3. Effective or RMS Value Equating these equations; The effective value of the voltage is found in the same way as current; This indicates that the effective value is the (square) root of the mean (or average) of the square of the periodic signal. Thus, the effective value is often known as the root-mean-square value, or rms value for short; and we write 4.3. Effective or RMS Value To find rms value of x(t), we first find its square then find the mean of that. and 2 11/25/2012 4.3. Effective or RMS Value The average power can be written in terms of the rms values; Similarly, the average power by a resistor R in; Example 4.7. Determine the rms value of the current waveform in figure. If the current is passed through a 2 Ω resistor, find the average power absorbed by the resistor. Solution: 3 11/25/2012 Example 4.7. Example 4.8. The waveform shown in figure is a half-wave rectified sine wave. Find the rms value and the amount of average power dissipated in a 10Ω resistor. Solution: 4 11/25/2012 Example 4.8. Example 4.8. 5 11/25/2012 4.4. Apparent Power and Power Factor İf the voltage and current at the terminals of a circuit are; 4.4. Apparent Power and Power Factor The power factor is; The power factor angle; 6 11/25/2012 4.4. Apparent Power and Power Factor The value of pf ranges between zero to unity. For a purely resistive load, the voltage and current are in phase, so that 0 and pf=1. This implies that apparent power is equal to the average power. For a purely reactive load, 90 and pf=0. In this case the average power is zero. In between these two extreme cases pf is said to be leading or lagging. Leading power factor means that current leads voltage, which implies a capacitive load. Lagging power factor means that current lags voltage, implying an inductive current. Example 4.9. Solution: 7 11/25/2012 Example 4.9. Example 4.10. Determine the power factor of the entire circuit of Figure as seen by the source. Calculate the average power delivered by the source. Solution: 8 11/25/2012 Example 4.10. 9