Reactance and Resonance
advertisement

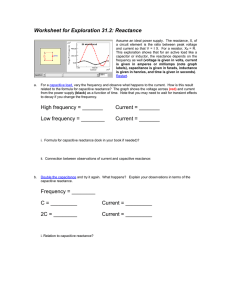
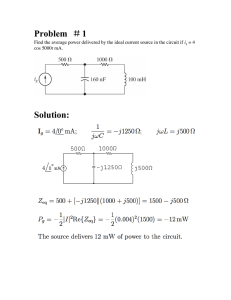
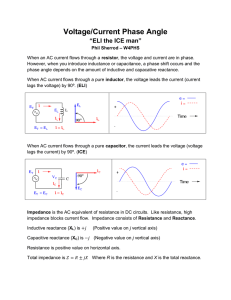
Reactance and Resonance What is Reactance? • The resistance to AC current flow caused by capacitance or inductance. • Measured in ohms • Symbol used is X What is Inductance? • The resistance to AC current flow caused by resistance, reactance or any combination of the two • Measured in ohms • Symbol used is Z What is Capacitive Reactance? When a circuit containing a capacitor is first energized, the voltage across the capacitor is zero but the current is high. As time passes, the voltage increases, current goes to zero. Capacitive Reactance As the frequency of the applied signal increases, capacitive reactance decreases As the frequency of the applied signal decreases, capacitive reactance increases What is Inductive Reactance? When a circuit containing a inductor is first energized, the current across the inductor is zero but the voltage is high. As time passes, the current increases, voltage goes to zero. Inductive Reactance As the frequency of the applied signal increases, inductive reactance increases As the frequency of the applied signal decreases, inductive reactance decreases Resonance Maximum power transfer occurs when the source and load impedances are equal. Demonstration: Use LC tuner to match source to load impedance. Resonance Most transmitter have a 50 ohm characteristic impedance. The use of a transmatch will match the load to the source impedance. Pi & T networks. Impedance Matching Caution: Using an impedance transformer at high power can result in core saturation, creating harmonics and causing signal distortion. RF impedance transformers are often used to equalize impedances of source and load to maximize the transfer of power. Source = Load