Ohm`s law relates current (I) to voltage (V) as: Ohmic circuits have
advertisement

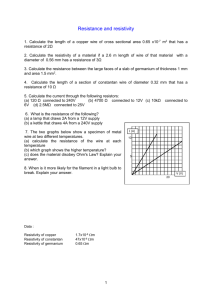
1 Created by Boundless Ohm's law relates current (I) to voltage (V) as: A , where R is radiancy B , where R is radical C , where R is resistance D , where R is reaction 2 Created by Boundless Ohmic circuits have current­voltage plots that are A linear and pass through the origin B linear and do not pass through the origin C not linear and pass through the origin D not linear and do not pass through the origin 3 Created by Boundless When a superconductor is placed in a weak external magnetic field and A warmed above its transition temperature, the magnetic field is attracted B cooled below its transition temperature, the magnetic field is attracted C warmed above its transition temperature, the magnetic field is ejected D 4 cooled below its transition temperature, the magnetic field is ejected Created by Boundless When cooled below a critical temperature, superconductor will exhibit A zero electrical resistance and expel magnetic field B non­zero electrical resistance and attract magnetic field C zero electrical resistance and attract magnetic field D non­zero electrical resistance and expel magnetic field 5 Created by Boundless Resistance and resistivity describe the extent to which an object or material A changes in volume in response to an electric current B impedes the heat flow C changes in volume in response to a temperature change D impedes the flow of electric current 6 Created by Boundless Resistivity is an A depends on the shape of an object B intrinsic property of a material C extrinsic property of a material D depends on the mass of an object 7 Created by Boundless The resistance of an object depends on A All of these answers B the material C the length D the cross­sectional area of a resistor 8 Created by Boundless Resistivity and resistance depend on temperature with the dependence being 9 A linear B nonlinear C nonlinear for small temperature changes and linear for large D linear for small temperature changes and nonlinear for large Created by Boundless Over temperature changes of 100 ºC or less, resistivity (ρ) varies with temperature change (ΔT) as: A , where ρ0 is the original resistivity and α is the temperature coefficient of resistivity B , where ρ0 is the original resistivity and α is the temperature coefficient of resistivity C , where ρ0 is the original resistivity and α is the temperature coefficient of resistivity D , where ρ0 is the original resistivity and α is the temperature coefficient of resistivity