Introduction to Alternating Current (AC)
advertisement

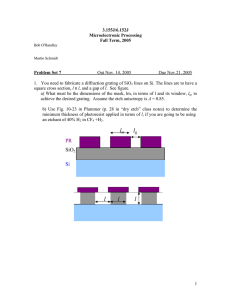
Introduction to Alternating Current (AC) Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen The right-angle triangle C B A Pythagorean Theorem C 2 = A2 + B 2 Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen C = A +B 2 A= C −B 2 B= C −A 2 2 2 2 Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Sin = Opposite side / hypotenuse Cos = Adjacent side / hypotenuse Tan = Opposite side / adjacent side Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Direct Current (dc) – Current flow in only one direction Alternating Current (ac) – Electrical current that rises from zero to a maximum in one direction, falls to zero, then rises to a maximum in the opposite direction and repeats another cycle, the positive and negative alternations being equal. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Why alternating current? Power Transfer – To supply electrical power for lighting, heating, cooling, appliances, and machinery in both home and industry. Information Transfer – To communicate or carry information, such as radio, music, and TV between two points. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Generator and transformer Generator – A device used to convert a mechanical energy input into an electrical energy output. Transformer – A device consisting of two or more coils that are used to couple electric energy from one circuit to another, yet maintain electrical isolation between the two. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen AC power distribution Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Information transfer Communications – Transmission of information between two points. Sound wave – Traveling wave propagated in an elastic medium that travels at a speed of approximately 1133 ft/sec. Transducer – Any device that converts energy from one form to another. Electrical wave – Traveling wave propagated in a conductive medium that is a variation in voltage or current and travels slightly slower than the speed of light. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Wireless Communications – Term describing radio communications that require no wires between two communications points. Electromagnetic (Radio) Waves – A wave that consists of both an electric and a magnetic variation, and travels at the speed of light. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Information transfer Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen AC wave shapes Sine Wave – A wave whose amplitude is the sine of a linear function of time. It is drawn on a graph that plots amplitude against time or radial degrees relative to the angular rotation of an alternator. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen AC waves Amplitude – The magnitude or size an alternation varies from zero. Vector – A quantity that has both magnitude and direction. It is normally represented as a straight line. The length of the line indicates magnitude; the arrowhead on one end indicates direction. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Peak-to-peak value of a sine wave The difference between the maximum positive and minimum negative values of the sine wave. Vpp = 2 × Vpeak Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Root-Mean-Square ( RMS ) value of a sine wave rms = 0.707 × peak RMS value of an ac voltage, current, or power waveform is equal to 0.707 times the peak value. The rms value is the effective or dc value equivalent of the ac wave. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Average value of a sine wave Average Value – The mean value found when the area of a wave above a line is equal to the area of the wave below the line. Average value = 0.637 × peak Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Period and Frequency Period (t) – The time taken for one complete cycle of a periodic or repeating waveform. Frequency (f) – The rate of recurrences of a periodic wave normally within a unit of one second, measured in hertz (cycles per second). t = 1/f f = 1/t Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Wavelength of a sine wave Wavelength ( ) – The distance between two points of corresponding phase equal to the waveform velocity or speed divided by the frequency. = Velocity/Frequency Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Phase relationship Phase – The angular relationship between two waves, normally between current and voltage in an ac circuit. Phase Shift or Angle – The change in phase of a waveform between two points, given in degrees of lead or lag. Phase difference between two waves is normally expressed in degrees. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Square wave Square Wave – A wave that alternates between two fixed values for an equal amount of time. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Duty cycle A term used to describe the amount of ON time versus OFF time. ON time is usually expressed as a percentage. Duty cycle (%) = (Pulse Width (PW))/(Period (t)) × 100% Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Square wave Rise Time – The time it takes a positive edge of a pulse to rise from 10% to 90% of its peak value. Fall Time – The time it takes a negative edge of a pulse to fall from 90% to 10% of its peak value. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Square wave rise and fall times. (a) ideal. (b) actual. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Time-domain and frequency-domain analysis Time-Domain Analysis – A method of representing a waveform by plotting its amplitude versus time. Frequency-Domain Analysis – A method of representing a waveform by plotting its amplitude versus frequency. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Fundamental and Harmonic frequencies Fundamental Frequency – This sine wave is always the lowest frequency and the largest amplitude component of any waveform shape and is used as a reference. Harmonic Frequency – A sine wave that is smaller in amplitude and is some multiple of the fundamental frequency. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Pulses Rectangular (Pulse) Wave – A repeating wave that alternates only between two levels of values and remains at one of these values for a small amount of time relative to the other. Pulse Repetition Frequency – The number of times per second that a pulse is transmitted. Pulse Repetition Time – The time interval between the start of two consecutive pulses. Pulse Width, Pulse Length, or Pulse Duration – The time interval between the leading edge and trailing edge of a pulse at which the amplitude reaches 50% of the peak pulse amplitude. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Triangular wave A repeating wave that has equal positive and negative ramps that have linear rates of change with time. Linear - Relationship between input and output in which the output varies in direct proportion to the time. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Sawtooth wave A repeating waveform that rises from zero to a maximum value linearly, and then falls to zero and repeats. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Other waveforms Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen ac meter Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Current Clamp – A device used in conjunction with an ac ammeter containing a magnetic core in the form of hinged jaws that can be snapped around the current-carrying wire to measure current. Radio-Frequency Probe – A probe used in conjunction with an ac meter to measure high-frequency (RF) signals. High-Voltage Probe – An accessory to the voltmeter that has added multiplier resistors within the probe to divide up the large potential being measured by the probe. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Oscilloscope Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Oscilloscope grid Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Function Generator – A signal generator that can function as a sine, square, rectangular, triangular, or sawtooth wave form generator. Frequency Counter – A meter used to measure the frequency or cycles per second of a periodic wave. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Frequency counter Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen Scopemeter A hand-held, battery-operated instrument that combines a multimeter, oscilloscope, frequency counter, and signal generator in one. Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen End of Alternating Current (AC) Online Resource for ETCH 213 Faculty: B. Allen