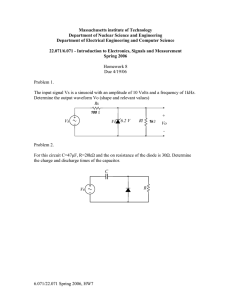
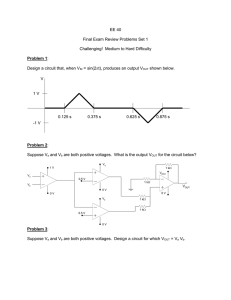
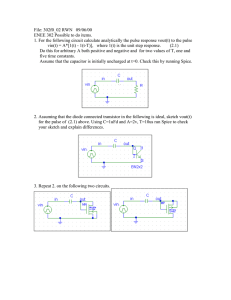
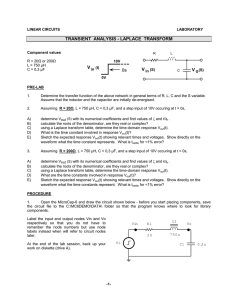
Qu. 1. Using the following formula, calculate the voltage in the
advertisement

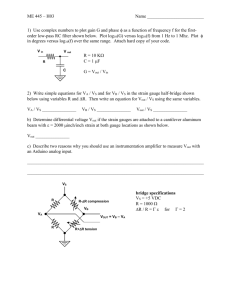
+12v Qu. 1. Using the following formula, calculate the voltage in the potential divider at the point ‘Vout.’ Vout = V x R1 100Ω R2 R1 + R2 Vout R2 300Ω 0v Qu. 2. The variable resistor shown in the diagram is set at exactly half way. +5v Vout What is the voltage present at Vout? 0v +10v Qu. 3. The following thermistor has a resistance of 30kohms at 20°C. What would be the output voltage at Vout with a temperature of 20°C? R1 20kΩ Vout R2 Thermistor 0v Qu. 4. The following potential divider has been connected to produce a voltage at Vout of 6 volts. A voltmeter with a resistance of 10kohms is connected between Vout and 0v. What will be the reading on the meter and why? +12v +12v R1 10kΩ R1 10kΩ Vout Vout R2 10kΩ R2 10kΩ 0v V 0v +10v Qu. 5. What are the voltages present at V1 and V2? R1 100Ω V1 R2 200Ω V2 R3 200Ω PTD- 96 0v (10kΩ) Answers to WS1.2 Q1/ 9 volts Q2/ 2.5 volts Q3/ 6 volts Q4/ 4 volts, because the meter will act as a resistor and combined with R2, would give a total resistance of 5 Kohms, instead of 10 Kohms. Q5/ V1 = 8 volts V2 = 4 volts