Conductor Types & Dimensions: AWG, kcmil Reference
advertisement

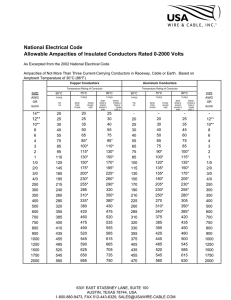
AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES APPROXIMATE DIMENSIONS OF CONDUCTORS Size of Conductor Type of Conductor (AWG or kcmil) 18 RFH-2, FFH-2 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 250 RHH, RHW, RHW-2 300 350 400 500 600 700 750 800 900 1000 1250 1500 1750 2000 18 SF-2, SFF-2 16 14 SF-1, SFF-1 18 RFH-1, XF, XFF 18 TF, TFF, XF, XFF 16 TW, XF, XFF, THHW, THW, 14 THW-2 AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES Diameter (in.) Area (in.2) 0.136 0.148 0.193 0.212 0.236 0.326 0.364 0.412 0.440 0.472 0.582 0.622 0.668 0.720 0.778 0.895 0.950 1.001 1.048 1.133 1.243 1.314 1.348 1.380 1.444 1.502 1.729 1.852 1.966 2.072 0.121 0.133 0.148 0.091 0.106 0.118 0.0145 0.0172 0.0293 0.0353 0.0437 0.0835 0.1041 0.1333 0.1521 0.1750 0.2660 0.3039 0.3505 0.4072 0.4754 0.6291 0.7088 0.7870 0.8626 1.0082 1.2135 1.3561 1.4272 1.4957 1.6377 1.7719 2.3479 2.6938 3.0357 3.3719 0.0115 0.0139 0.0172 0.0065 0.0080 0.0109 0.133 0.0139 AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES APPROXIMATE DIMENSIONS OF CONDUCTORS Size of Conductor Type of Conductor Diameter (in.) Area (in.2) (AWG or kcmil) 12 0.152 0.0181 TW, THHW, THW, THW-2 10 0.176 0.0243 8 0.236 0.0437 RHH, RHW, RHW-2 14 0.163 0.0209 RHH, RHW, RHW-2, XF, XFF 12 0.182 0.0260 RHH, RHW, RHW-2, XF, XFF 10 0.206 0.0333 RHH, RHW, RHW-2 8 0.266 0.0556 6 0.304 0.0726 4 0.352 0.0973 3 0.380 0.1134 2 0.412 0.1333 1 0.492 0.1901 1/0 0.532 0.2223 2/0 0.578 0.2624 3/0 0.630 0.3117 4/0 0.688 0.3718 250 0.765 0.4596 300 0.820 0.5281 TW, THW, THHW, THW-2, 350 0.871 0.5958 RHH, RHW, RHW-2 400 0.918 0.6619 500 1.003 0.7901 600 1.113 0.9729 700 1.184 1.1010 750 1.218 1.1652 800 1.250 1.2272 900 1.314 1.3561 1000 1.372 1.4784 1250 1.539 1.8602 1500 1.662 2.1695 1750 1.776 2.4773 2000 1.882 2.7818 18 0.084 0.0055 TFN, TFFN 16 0.096 0.0072 TFE, PFAH 1 0.422 0.1399 1/0 0.462 0.1676 2/0 0.508 0.2027 TFE, PFA, PFAH, Z 3/0 0.560 0.2463 4/0 0.618 0.3000 Note: Type RHH, RHW, and RHW-2 conductors referenced on this page are without outer an covering. AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES APPROXIMATE DIMENSIONS OF CONDUCTORS Size of Conductor (AWG or kcmil) Diameter (in.) Area (in.2) 14 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 0.111 0.130 0.164 0.236 0.254 0.324 0.352 0.384 0.446 0.0097 0.0133 0.0211 0.0366 0.0507 0.0824 0.0973 0.1158 0.1562 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 0.486 0.532 0.584 0.642 0.1855 0.2223 0.2679 0.3237 250 300 0.711 0.766 0.3970 0.4608 THHN, THWN, THWN-2 350 400 500 600 700 750 800 900 1000 0.817 0.864 0.949 1.051 1.122 1.156 1.188 1.252 1.310 0.5242 0.5863 0.7073 0.8676 0.9887 1.0496 1.1085 1.2311 1.3478 PF, PGFF, PGF, PFF, PTF, PAF, PTFF, PAFF 18 16 0.086 0.098 0.0058 0.0075 PF, PGFF, PGF, PFF, PTF, PAF, PTFF, PAFF, TFE, FEP, PFA, FEPB, PFAH 14 0.113 0.0100 TFE, FEP, PFA, FEPB, PFAH 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 0.132 0.156 0.206 0.244 0.292 0.320 0.352 0.0137 0.0191 0.0333 0.0468 0.0670 0.0804 0.0973 ZF, ZFF 18 16 0.076 0.088 0.0045 0.0061 Type of Conductor THHN, THWN, THWN-2 AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES AREA OF CONDUCTOR TYPES APPROXIMATE DIMENSIONS OF CONDUCTORS Type of Conductor Size of Conductor (AWG or kcmil) Z, ZF, ZFF 14 12 10 8 6 Z 4 3 2 1 14 12 10 8 XHHW, ZW, XHHW-2, XHH 6 4 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 250 300 350 400 500 XHHW, XHHW-2, XHH 600 700 750 800 900 1000 1250 1500 1750 2000 18 16 KF-2, KFF-2 14 12 10 18 16 KF-1, KFF-1 14 12 10 Diameter (in.) 0.103 0.122 0.156 0.196 0.234 0.282 0.330 0.362 0.402 0.133 0.152 0.176 0.236 0.274 0.322 0.350 0.382 0.442 0.482 0.528 0.580 0.638 0.705 0.760 0.811 0.858 0.943 1.053 1.124 1.158 1.190 1.254 1.312 1.479 1.602 1.716 1.822 0.063 0.075 0.090 0.109 0.133 0.057 0.069 0.084 0.103 0.127 Area (in.2) 0.0083 0.0117 0.0191 0.0302 0.0430 0.0625 0.0855 0.1029 0.1269 0.0139 0.0181 0.0243 0.0437 0.0590 0.0814 0.0962 0.1146 0.1534 0.1825 0.2190 0.2642 0.3197 0.3904 0.4536 0.5166 0.5782 0.6984 0.8709 0.9923 1.0532 1.1122 1.2351 1.3519 1.7180 2.0157 2.3127 2.6073 0.0031 0.0044 0.0064 0.0093 0.0139 0.0026 0.0037 0.0055 0.0083 0.0127 CONDUIT FILL EXAMPLES Conduit fill is generally based on 40% of the cross-sectional area of the conduit. Sections of conduit 24” or less in length may be filled to 60%. APPROXIMATE DIMENSIONS OF COMPACT CONDUCTORS BARE THHW AND THW Size of CONDUCTORS THHN CONDUCTORS Conductor CONDUCTOR App. Diameter App. Diameter (AWG or (in.) Area (in.2) (in.) Area (in.2) kcmil) Diameter (in.) 8 0.134 0.255 0.0510 — — 6 0.169 0.290 0.0660 0.240 0.0452 4 0.213 0.335 0.0881 0.305 0.0730 2 0.268 0.390 0.1194 0.360 0.1017 1 0.299 0.465 0.1698 0.415 0.1352 1/0 0.336 0.500 0.1963 0.450 0.1590 2/0 0.376 0.545 0.2332 0.495 0.1924 3/0 0.423 0.590 0.2733 0.540 0.2290 4/0 0.475 0.645 0.3267 0.595 0.2780 250 0.520 0.725 0.4128 0.670 0.3525 300 0.570 0.775 0.4717 0.720 0.4071 350 0.616 0.820 0.5281 0.770 0.4656 400 0.659 0.865 0.5876 0.815 0.5216 500 0.736 0.940 0.6939 0.885 0.6151 600 0.813 1.050 0.8659 0.985 0.7620 700 0.877 1.110 0.9676 1.050 0.8659 750 0.908 1.150 1.0386 1.075 0.9076 XHHW CONDUCTORS App. Diameter (in.) Area (in.2) 0.224 0.0394 0.260 0.0530 0.305 0.0730 0.360 0.1017 0.415 0.1352 0.450 0.1590 0.490 0.1885 0.540 0.2290 0.590 0.2733 0.660 0.3421 0.715 0.4015 0.760 0.4536 0.800 0.5026 0.880 0.6082 0.980 0.7542 1.050 0.8659 1.090 0.9331 To find the number of conductors allowed in a conduit: 1 2 ex. 1 2 ex. Find the available area in square inches of the raceway. Divide the available area of the conduit by the area of the conductors. Chapter 9, Table 1 of the NEC provides us with the maximum percentage of fill allowed for raceways. Chapter 9, Table 4 provides us with the area of raceways, and Chapter 9, Table 5 of the NEC gives us the area of conductors. A section of 1 in. EMT, 18” long would be allowed to contain how many 8 AWG XHHW conductors? .519 (60% area of 1 in. EMT) = 11.8 = 12, 8 AWG, XHHW conductors are allowed in this raceway .0437 (area of 8 AWG XHHW) Round up only where the fraction is .8 or larger and all of the conductors are the same size. A 1-1/4 in. rigid metal conduit 30 ft. long contains 12, 10 AWG, THWN conductors; how many 12 AWG, THHN conductors may be added? 1 .610 (40% area of 1-1/4 in. RMC) − (.0211 × 12) (area of 10 AWG, THWN) = .3568 (remaining area) 2 .3568 (remaining area) = 26.8 = 26, 12 AWG, THHN conductors are allowed in this raceway .0133 (area of 12 AWG, THHN) Note: The provision that allows the next higher number of conductors to be installed in the raceway where the calculation results in a decimal of .8 or larger may only be used where all of the conductors in the raceway are the same size. Tables found in Annex C of the NEC can only be used where there are more than three conductors in the raceway, all of the conductors are the same size and type, and the raceway is longer than 24”. (The following tables are based on 40% conduit fill.) CONDUIT FILL EXAMPLES 40% CONDUIT FILL (EMT)