CAPACITORS IN SERIES AND PARALLEL
advertisement

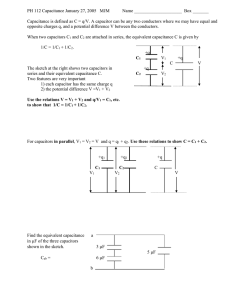
Lesson 10 CAPACITORS IN SERIES AND PARALLEL Lesson 10: Capacitors in Series and Parallel AP Physics B Objectives III.C.3. Capacitors in circuits a) Students should understand the and steady-state behavior of capacitors connected in series or in parallel, so they can: (1) Calculate the equivalent capacitance of a series or parallel combination. (2) Describe how stored charge is divided between capacitors connected in parallel. (3) Determine the ratio of voltages for capacitors connected in series. (4) Calculate the voltage or stored charge, under steady-state conditions, for a capacitor connected to a circuit consisting of a battery and resistors. Student Objectives Students will be able to: 1. Calculate the equivalent capacitance of series and parallel combinations of capacitors. 2. Describe qualitatively the charging and discharging of capacitors. Review of Capacitors C = o A / d capacitance of a capacitor q = C ΔV charge stored on a capacitor Uc = ½ C ΔV2 energy stored in a capacitor Capacitors in Parallel Ceq Ci Derive the relationship for capacitors in parallel from first principles. Hint: = V1 = V2 = V3 Sample Problem 10.1 What is the equivalent capacitance of the circuit below? 6V 2 μF 4 μF Capacitors in Series 1 1 Ceq Ci Derive the relationship for capacitors in series from first principles. Hint: = V1 + V2 + V3 Sample Problem 10.2 What is the equivalent capacitance of the circuit below? C1 = 2 μF 6V C2 = 4 μF Comparisons Resistors Series Parallel Capacitors Charging an RC Circuit Discharging the Capacitor in an RC Circuit