MAGNETIC FORCE ON CURRENT CARRYING WIRES
Lesson 5
MAGNETIC FORCE ON
CURRENT CARRYING
WIRES
Announcements
Magnetism HW #4 due today
HW #5 due MONDAY
Waves HW # 6 (Diffraction) due WED
– R: Ch. 17 pp. 555 562 & pp. 567 571
– Q: 5
– P: 7, 10, 14, 28, 29
Electricity packet due MONDAY
Optics/Waves/Modern packet due
WEDNESDAY
AP Physics B Learning Objectives
III.D.3. Fields of long current-carrying wires
Students should understand the magnetic field produced by a long straight current-carrying wire, so they can: a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the field at a point in the vicinity of such a wire.
b) Use superposition to determine the magnetic field produced by two long wires.
c) Calculate the force of attraction or repulsion between two long current-carrying wires.
Student Learning Objectives
Students will be able to
1.
2.
Calculate the magnitude of the force current-carrying wires exert on one another.
Determine whether the force between current-carrying wires is attractive or repulsive.
Magnetic Force on Current-
Carrying Wire
F = I L B sin
– I: current in Amps
– L: length in meters
– B: magnetic field in Tesla
– : angle between current and field
Derive this!
Solution:
F = q v B sin θ
I = q/t q = I t v = L/t
F = ( I t ) (L/t) B sin θ
F = I L B sin θ
Sample Problem: What is the force on a 100 m long wire bearing a 30 A current flowing north if the wire is in a downward-directed magnetic field of 400 mT?
Sample Problem: What is the magnetic field strength if the current in the wire is 15 A and the force is downward and has a magnitude of 40 N/m? What is the direction of the current?
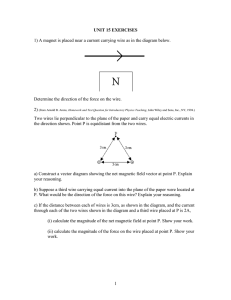
Sample problem 5.3:
What is the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on a 100 m long wire that passes through point P which bears a current of
50 amps in the same direction?
I
2
= 50.0 A P
3.0 m
I
1
= 13.0 A