Chapter 3 Alternating Current Circuits I •AC Voltage and Current
advertisement

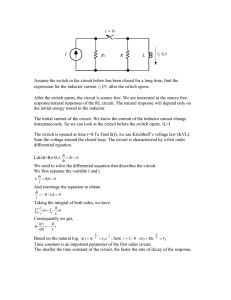
Chapter 3 Alternating Current Circuits I •AC Voltage and Current - Phasors •RMS Voltage and Current •Reactance and Impedance •High Pass and Low Pass filters •RLC Resonance Circuits 1 Waves and Phasors Phasor iy eiωt = ( !1 2 , i 2 eiωt = (0,i) ) ωt x y(t) = A cos(ωt-φ) ω=2πf where f=1/T z =(x,iy) = |z|eiπ/2 = ( cos(π/2), i sin(π/2)= (0,i) z =(x,iy) = |z|eiπ/4 = ( cos(3π/4), isin(3π/4)= ( !1 i , ) 2 2 2 Phase Lag in an AC Circuit In a general AC circuit (RLC) we have to consider that the voltage and current may be out of phase due to the circuit elements. V(t) = Vo sin(ωt) ~ Vo eiωt I(t) = Io sin(ωt-φ) ~ Io ei(ωt-φ) V(t) I(t) φ=π Vo eiωt ωt Io ei(ωt-φ) V(t) I(t) φ=π/2 3 Average and RMS Voltage, Current, Power VAVG = (V ) 2 RMS = 1 1 T T ! V (t ) dt 0 T ! | V (t ) | T 2 dt = 0 (V ) 2 RMS I AVG = 1 T T ! I ( t ) dt 0 T V02 ! sin (" t )!dt = 2 T PAVG = 0 Vo 2 T T ! 1 T T ! I (t )V ( t ) dt 1 + cos(2" t ) 2 0 0 !dt = Vo 2 2 + Vo 2 1 2T 2" T cos(2" t ) 0 Vo 2 1 % 2$ Vo ( == + + ( cos(2" T ) # 1) = '& cos(2" ) # 1*) ! !!!!=!!!VRMS = 2 2T 2" 2 2T 2" !##""##$ 2 Vo 2 Vo 2 1 Vo 2 =0 (I ) 2 RMS (P ) RMS 2 = = 1 T 1 T ! | I (t ) | dt = 2 0 Io 2 2 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!I RMS = T ! | I (t )V (t ) | T 0 2 dt = I 0V0 T Io 2 T ! sin (" t + + ) sin (" t )dt 2 2 0 4 Reactance, Impedance, and Phasors Consider the general RLC circuit with V (t) = V0 e j! t , I(t) = I 0 e j (! t "# ) : dI 1 V (t) = L + IR + $ I(t)dt dt C 1 ( % V (t) = I(t) ' i! L + R + *) Ohm ' s Law Complex (AC) Form & i ! C !###"### $ Re ac tan ce or Complex Im pedance In any AC Circuit the Re sistive, Capacitive, and Inductive elements can be replaces by their Complex Im pedances! Z R =!R!=! X L Z L = i (! L ) = +i! X L 1% 1 ( ZC = ' * = "i! XC i & !C ) Re sistive Re ac tan ce!!!!!!!!!!1 = e+i ! 0 # =!0 Inductive Re ac tan ce!!!!!!!!+i = e+i ! + /2 !!!!!!!# = ++ / 2 !!!!!!Capacitive Re ac tan ce!!!!!"i = e"i ! + /2 !!!!!!! # = "+ / 2 5 Magnitude and Phase 1 & # The total Re ac tan ce can be written as Z = R + i % ! L " ( $ !C ' corresponding to a complex number The magnitude (length) of Z is XL Z XC φ XR | Z | = R 2 + (! L " 1 2 ) !C The phase angle between X R and Z # Z = tan "1 (y / x) = tan "1 cos(# ) = !L " 1 !C R R |Z| 6 Simple RC Circuit - Low pass Filter (1) R V(t) VC ZR VC ZC C ZR VO ZC What is the output voltage V and phase ! looking across the capacitor ? ZC #i / " C VC = Vo ei" t =! Vo ei" t $ voltage divider eq gain = VC / V0 Z R + ZC R # i / "C | VC | = VCVC * (#i / " C)(+i / " C) = Vo = (R # i / " C)(R + i / " C) 1 / "C R + (1 / " C ) 2 2 Vo!= 1 / " RC 1 + (1 / " RC ) 2 VC R φ Vo 1/ωC X ### Y ### #" $ !## #" $ =Z #$ !#" =1 #$ !## !#" 2 2 % 1/" C ( % ( #i / " C R + i / "C R / "C Phase : VC = ( )( )=' 2 # i ' 2 2* 2* R # i / "C R + i / "C & R + (1 / " C ) ) & R + (1 / " C ) ) %Y ( % #R / " C ( % #1 ( % 1 ( +C = tan #1 ' * = tan #1 ' = tan #1 ( #" RC ) = cot #1 ' = tan #1 ' #, /2 * 2 2 * & X) &1/" C ) & " RC ) & " RC *) At !!" = 1 / RC!!!+C = tan #1 (1) # , / 2 = , / 4 # , / 2 = #, / 4 7 Simple RC Circuit - Low pass Filter (2) 1 1 !!"!!| VC | = Vo = 0.707 Vo RC 2 1 !!!! fbreak = # RC !##"2## $ Break!Frequency!occurs!when!!!!! break = | VC | = 1 1 + (! RC ) 2 Vo break frequency ln(0.707) fb fb φ=−π/4 8 Simple RC Circuit - High Pass Filter C V(t) ZC Vout ZR V(t) R What is the output voltage VR and phase ! R looking across the resistor ? " ZR % R j( t VR = $ Vo!e = !Vo!e j( t ' (R ) j / ( C) # Z R + ZC & | VR | = VRVR* = gain = VR / VO = 2 R Vo = (R ) j / ( C)(R + j / ( C) R R + (1 / ( C ) 2 2 Vo = ( RC 1 + (( RC ) 2 Vo ( RC 1 + (( RC ) R θ 1/ωC 2 " % " % R2 R / (C 1 % )1 " Y % )1 " Phase : VR = $ 2 + j !!!!!*!! ! = tan = tan $# '& $# ' R 2' $ 2 2' X ( RC & # R + (1 / ( C ) & # R + (1 / ( C ) & At !!( = 1 / RC!!!! R = tan )1 (1) = + / 4 9 Simple RC Circuit - High Pass Filter (2) | VR | = ! RC 1 + (! RC ) 2 Vo 1 fbreak = " RC !##"2## $ !!!!!!| VR | = 1 Vo = 0.707 Vo 2 break frequency ln(0.707) fb fb φ=π/4 10 Differentiator and Integrator Connection R V(t) V(t) R C ! i dt C !#"#$ VR = R dq / dt VC = !# #"## $ differentiator RC<<T 1/T <<1/RC f << 1/RC f < fbreak fbreak 1 int egrator RC>>T 1/T >>1/RC f >>1/RC f > fbreak fbreak 11 Band Pass or Notch Filter ωHI= ωLO= 12 RLC Circuit spring damping mass 13 Resonance Condition and Q-factor ZL=ZC at ω0 Q = |ZL|/R = |ZC|/R ωο 14 Power in AC Circuits 15 Decibel Scale DECIBEL SCALE When measuring power gain and scale. voltage gain in an amplifier or circuit we often use the dcibel Power P db = 10 log(Pout/Pin) Voltage V db = 20 log 10 (Vout /Vin) = 20 log 10 (gain) Sound Power • Near total silence - 0 dB • A whisper - 15 dB • Normal conversation - 60 dB • A lawnmower - 90 dB • A car horn - 110 dB • A rock concert or a jet engine - 120 dB • A gunshot or firecracker - 140 dB Vdb at the Break Frequency At the breaking frequency the gain Vout/Vin drops by a factor of 1/ 2 . This is called the -3 db point. Can you jusify this rema rk? 16