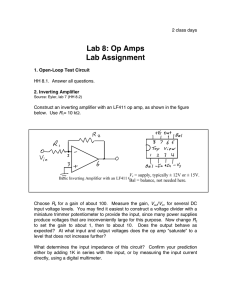
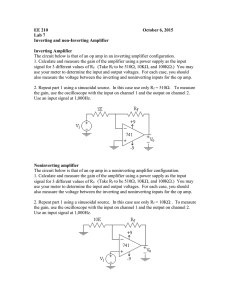
Electrical Engineering
advertisement

Electrical Engineering Electrical Engineering Chapter: Operational Amplifiers / Operationsverstärker Michael E. Auer Source of figures: Alexander/Sadiku: Fundamentals of Electric Circuits, McGraw-Hill Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering OpAmp Basics (1) Michael E.Auer It is an electronic unit that behaves like a voltage-controlled voltage source. It is an active circuit element designed to perform amplification and mathematical operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, differentiation and integration. 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering OpAmp Basics (2) A typical op amp: (a) pin configuration, (b) circuit symbol , (b) device (c) Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering OpAmp Basics (3) The equivalent circuit Of the non-ideal op amp Op Amp output: vo as a function of Vd A – Open Loop Voltage Gain vd = v2 – v1 Michael E.Auer vo = A·vd = A(v2 –v1) 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering OpAmp Basics (4) Typical ranges for op amp parameters Michael E.Auer Parameter Typical range Ideal values Open-loop gain, A 105 to 108 ∞ Input resistance, Ri 105 to 1013 Ω ∞Ω Output resistance, Ro 1 to 50 Ω 0Ω Supply voltage, VCC 5 to 15 V 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering OpAmp Example Circuit Michael E.Auer Simulation model 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Definition of the Ideal OpAmp An ideal op amp has the following characteristics: • Infinite open-loop gain, A ≈ ∞ Vd = 0 • Infinite input resistance, Ri ≈ ∞ i1 = i2 = 0 • Zero output resistance, Ro ≈ 0 Ideal Voltage source Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Inverting Amplifier Basic Circuit Inverting amplifier reverses the polarity of the input signal while amplifying it vo = − AV = − Rf R1 vi Rf R1 Voltage gain Rin = R1 Rout = 0 Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Inverting Amplifier Equivalent Circuit Polarity ! Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Inverting Amplifier Example (1) Refer to the op amp below. If vi = 0.5V, calculate: (a) The voltage gain, (b) the output voltage, vo and (c) the current in the 10kΩ resistor. Answer: (a) – 2.5; (b) -1.25V; (c) 50μA Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Inverting Amplifier Example (2) Determine the voltage vo in the circuit below. Answer: vo = 3∙va – 12 = -6V Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinv. Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Noninverting Amplifier Basic Circuit Non-inverting amplifier is designed to produce positive voltage gain Rf ⋅ vi vo = 1 + R1 AV = 1 + Rf R1 positive ! Rin = ∞ Rout = 0 Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Noninverting Amplifier Example Calculate the voltage vo in the circuit below. Answer: vo = 7V Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Unity Gain Amplifier (Voltage Follower) Special noninverting amplifier with: Rf = 0 ; R1 = ∞ Application as buffer amplifier to isolate one circuit from another Voltage follower Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Summing Amplifier Basic Circuit Summing Amplifier is an op amp circuit that combines several inputs and produces an output that is the weighted sum of the inputs. Rf Rf Rf vo = − v1 + v2 + v3 R2 R3 R1 if R1 = R2 = R3 : Rf Rf Rf vo = − v1 + v2 + v3 R1 R1 R1 Rf vo = − ⋅ (v1 + v2 + v3 ) R1 Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Summing Amplifier Example Calculate the voltage vo and the current io. Answer: vo = -8V; io = - 4.8mA Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Difference Amplifier Basic Circuit Difference amplifier is a device that amplifies the difference between two inputs but rejects any signals common to the two inputs. vo = R2 (1 + R1 / R2 ) R v2 − 2 v1 R1 (1 + R3 / R4 ) R1 vo = v2 − v1 if Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 R2 R3 = =1 R1 R4 EE05 Electrical Engineering Instrumentation Amplifier Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Cascaded OpAmps It is an arrangement of two or more op amp circuits such that the output to one is the input of the next. vo = A ⋅ v1 Michael E.Auer with 20.09.2013 A = A1 ⋅ A2 ⋅ A3 EE05 Electrical Engineering Two-stage Amplifier Example Determine R1 to R5 so that vo = -5v1+3v2 and Rin = 10kΩ. R4 R5 R2 Answer: R1 = R3 = 10kΩ R4 = 30kΩ R2 = R5 = 50kΩ Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Cascaded OpAmps Example Find vo and io in the circuit shown below. Answer: 350mV, 25μA Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Application: DAC Digital-to Analog Converter (DAC) : it is a device which transforms digital signals into analog form. Four-bit DCA: (a) block diagram (b) binary weighted ladder type − V0 = Rf R1 V1 + Rf R2 V2 + Rf R3 V3 + Rf R4 V4 where V1 – MSB, V4 – LSB V1 to V4 are either 0 or 1 V Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Chapter Content Basics of Op Amps / OV Grundlagen Ideal Op Amp / Idealer OV Inverting Amplifier / Invertierender Verstärker Noninverting Amplifier / Nichtinvertierender Verstärker Summing Amplifier / Summierer Verstärker Difference Amplifier / Differenzverstärker Cascaded Op Amp Circuits / Zusammenschaltung von OVs Summary / Zusammenfassung Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05 Electrical Engineering Summary • • • • • • • • • • The OpAmp is a high gain amplifier that has high input resistance and low output resistance. An ideal OpAmp has an infinite input resistance, a zero output resistance, and an infinite gain. For an ideal OpAmp, the current into each of its two input terminals is zero, and the voltage across its input terminals is negligibly small. In an inverting amplifier, the output is a negative multiple of the input. In a noninverting amplifier, the output is a positive multiple of the input. In a voltage follower, the output follows the input. In a summing amplifier, the output is the weighted sum of the inputs. In a difference amplifier, the output is proportional to the difference of the two inputs. OpAmp circuits may be cascaded without changing their input-output relationships. Typical applications of the OpAmp considered in this chapter include the DAC and the instrumentation amplifier. Michael E.Auer 20.09.2013 EE05