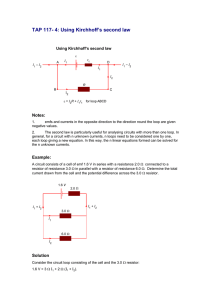
Chapter 2, Solution 3
advertisement
Chapter 2, Solution 3 For silicon, 6.4 x102 -m. A r 2 . Hence, R L A L r2 r2 L 6.4 x102 x 4 x102 0.033953 R x 240 r = 184.3 mm Chapter 2, Solution 10 2 –8A 1 4A i2 i1 3 –6A At node 1, –8–i 1 –6 = 0 or i 1 = –8–6 = –14 A At node 2, –(–8)+i 1 +i 2 –4 = 0 or i 2 = –8–i 1 +4 = –8+14+4 = 10 A Chapter 2, Solution 12 + 30v – loop 2 – 50v + + 40v - + 20v – loop 1 + v1 – + v2 – loop 3 + v3 – For loop 1, –40 –50 +20 + v 1 = 0 or v 1 = 40+50–20 = 70 V For loop 2, –20 +30 –v 2 = 0 or v 2 = 30–20 = 10 V For loop 3, –v 1 +v 2 +v 3 = 0 or v 3 = 70–10 = 60 V Chapter 2, Solution 15 Calculate v and i x in the circuit of Fig. 2.79. 12 + v 10 V + _ + 16 V – – ix + + 4V _ _ Figure 2.79 For Prob. 2.15. Solution For loop 1, –10 + v +4 = 0, v = 6 V For loop 2, –4 + 16 + 3i x =0, i x = –4 A 3 ix Chapter 2, Solution 16 Determine V o in the circuit in Fig. 2.80. 16 14 + 10 V + _ Vo + _ 25 V _ Figure 2.80 For Prob. 2.16. Solution Apply KVL, –10 + (16+14)I + 25 = 0 or 30I = 10–25 = – or I = –15/30 = –500 mA Also, –10 + 16I + V o = 0 or V o = 10 – 16(–0.5) = 10+8 = 18 V Chapter 2, Problem 27. Calculate I o in the circuit of Fig. 2.91. 8 10V + Io 3 6 Figure 2.91 For Prob. 2.27. Solution The 3-ohm resistor is in parallel with the c-ohm resistor and can be replaced by a [(3x6)/(3+6)] = 2-ohm resistor. Therefore, I o = 10/(8+2) = 1 A. Chapter 2, Problem 30. Find R eq for the circuit in Fig. 2.94. 25 180 60 R eq 60 Figure 2.94 For Prob. 2.30. Solution We start by combining the 180-ohm resistor with the 60-ohm resistor which in turn is in parallel with the 60-ohm resistor or = [60(180+60)/(60+180+60)] = 48. Thus, R eq = 25+48 = 73 Ω. Chapter 2, Solution 31 Req 3 2 // 4 //1 3 1 3.5714 1/ 2 1/ 4 1 i 1 = 200/3.5714 = 56 A v 1 = 0.5714xi 1 = 32 V and i 2 = 32/4 = 8 A i 4 = 32/1 = 32 A; i 5 = 32/2 = 16 A; and i 3 = 32+16 = 48 A Chapter 2, Solution 58 The resistance of the bulb is (120)2/60 = 240 40 2A + 90 V - 0.5 A VS 240 + - 1.5 A + 120 V 80 - Once the 160 and 80 resistors are in parallel, they have the same voltage 120V. Hence the current through the 40 resistor is equal to 2 amps. 40(0.5 + 1.5) = 80 volts. Thus v s = 80 + 120 = 200 V.