dt di L = dt di L =
advertisement

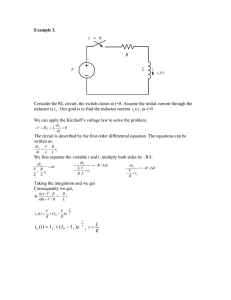
R=20 Ω V=10 V The switch in the circuit is closed at t=0. L=10 H " = !L di dt What is the initial current in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed (at t=0+) ? A) 0 A B) 0.5 A C)1.0 A D) 2 A E) None of these. 1 R=20 Ω V=10 V The switch in the circuit is closed at t=0. L=10 H " = !L di dt What is the initial current in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed (at t=0+) ? A) 0 A B) 0.5 A C)1.0 A D) 2 A E) None of these. 2 CAPA #13 is due Friday New online participation survey is still up! Reading: 34.3-5 _________________________ Last: Inductors in circuits Today: Inductors, and AC circuits Next: Maxwell's equations, putting it all together! 3 1 Clicker Question The switch in the circuit below is closed at t=0. What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed ? R=20 Ω V=10 V L=10 H A) 0 A/s B) 0.5A/s C)1A/s D) 10A/s E) None of these. Hints: What is the initial current through the circuit? Given that - what is the initial voltage across the inductor? 4 Clicker Question The switch in the circuit below is closed at t=0. V = 10V Before t=0, V=? V=? R=20 Ω L = 10H What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed ? A) 0 A/s B) 0.5A/s C)1A/s D) 10A/s E) None of these. Hints: What is the initial current through the circuit? Given that - what is the initial voltage across the inductor? V=0 " = !L di dt 5 Clicker Question The switch in the circuit below is closed at t=0. R=20 Ω Before t=0, V=? V=0 V = 10V L = 10H What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed ? A) 0 A/s B) 0.5A/s C)1A/s D) 10A/s E) None of these. Hints: What is the initial current through the circuit? Given that - what is the initial voltage across the inductor? V=0 6 2 Clicker Question The switch in the circuit below is closed at t=0. V=10 V = 10V V=10! V=0 R=20 Ω L = 10H What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed ? A) 0 A/s B) 0.5A/s C)1A/s D) 10A/s E) None of these. Hints: What is the initial current through the circuit? Given that - what is the initial voltage across the inductor? V=0 7 Clicker Question The switch in the circuit below is closed at t=0. V=10 V = 10V R=20 Ω At t=0+, V=? L = 10 What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed ? A) 0 A/s B) 0.5A/s C)1A/s D) 10A/s E) None of these. Hints: What is the initial current through the circuit? Given that - what is the initial voltage across the inductor? V=0 di " = !L dt 8 Clicker Question The switch in the circuit below is closed at t=0. V=10 R = 20! V = 10V V=10!! (briefly) L = 10H What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed ? A) 0 A/s B) 0.5A/s C)1A/s D) 10A/s E) None of these. Hints: What is the initial current through the circuit? Given that - what is the initial voltage across the inductor? V=0 9 3 Clicker Question The switch in the circuit below is closed at t=0. V=10 R = 20! V = 10V V=10!! (briefly) L = 10H What is the initial rate of change of current di/dt in the inductor, immediately after the switch is closed ? A) 0 A/s B) 0.5A/s C)1A/s D) 10A/s E) None of these. Hints: What is the initial current through the circuit? Given that - what is the initial voltage across the inductor? V=0 " = !L di dt Answer: I(initial)=0, so it must still be 0. Thus, ΔV(across R)=0 V(across inductor) = V(batt!) , but also V(inductor) = L di/dt. So at t=0+, di/dt = V(batt)/L = 10V/10H = 1 A/s. 10 Clicker Question An LR circuit is shown below. Initially the switch is open. At time t=0, the switch is closed. What is the current thru the inductor L immediately after the switch is closed (time = 0+)? R1 = 10Ω V = 10V L = 10H R2 = 10Ω A) Zero B) 1 A C) 0.5A D) None of these. 11 Clicker Question An LR circuit is shown below. Initially the switch is open. At time t=0, the switch is closed. R1 = 10Ω V = 10V L = 10H R2 = 10Ω After a long time, what is the current from the battery? A) 0A B) 0.5A C) 1.0A D) 2.0A E) None of these. 12 4 AC Circuits The Voltage in your wall sockets at home is AC. AC stands for Alternating Current, but would perhaps more appropriately be called Alternating Voltage. Alternating = Sinusoidal with time 13 V (t ) = V peak sin(!t ) " = 2!f = 2! T ω is the radial frequency (radians / second) f is the frequency in (cycles / second = Hertz) T is the period in (seconds), i.e. time for one cycle 14 In the United States of America f = 60 cycles/second or Hertz T = (1 / 60) seconds Vpeak = 170 Volts One might be interested in something like the average Voltage. But, the average V(t) = 0. 15 5 Vrms = V (root mean square) = V2 Time Average of Voltage squared. Vrms = V p sin 2 (!t ) = V p 1 / 2 = V p / 2 Time Average of sin2 or cos2 over many cycles = 1/2 Vrms = 170V / 2 = 120 Volts This is how we refer to the US Standard Voltage. 16 The term “AC Voltage” or “VAC” means Vrms = V peak / 2 The term “AC Current” [somewhat redundant] means irms = i peak / 2 RMS values of AC Voltage and Current are always implied if not explicitly stated otherwise. This is because the old DC formulas involving V, i, R, P (power) all hold for AC circuits if we use the RMS values. 17 Example: AC Voltage across a resistor V (t ) = V p sin(!t ) VAC ~ R i (t ) = V V p sin(!t ) = = i peak sin(!t ) R R P(t ) = iV = i peakV p sin 2 (!t ) Instantaneous Power is oscillating from zero to maximum. 18 6 We might be interested in the average (over time) power delivered to the resistor. P(t ) = iV = i peakV peak sin 2 (!t ) 1 < P(t ) >= i peakV peak < sin 2 (!t ) >= i peakV peak 2 & 1 #& 1 # < P(t ) >= $ i peak !$ V peak ! % 2 "% 2 " Pave = irmsVrms Same form as before, but now RMS values. 19 CT 33.35 A 100 W light bulb is attached to a wall plug. (120 VAC, 60 Hz) What is the peak power output to the bulb? A) 100 W B) Sqrt[2]*100 W = 141 W C) 200 W D) Other 21 CT 33.36 A 600 Watt hairdryer is attached to 120 VAC circuit. What is the peak current through the hairdryer (to within 5%)? A: 0 A B) 5 A E) Other C) 7 A D) 10 A P = IV, which means P(ave) = I(rms)* V(rms) 600 W = I(rms) * 120 V => I(rms) = 600/120 = 5 A. But I(peak) = I(rms)*Sqrt[2] = 5*1.4, about 7. 22 7 CT 33.37 The instantaneous power consumed by my De-luxe Toaster Oven looks like this as a function of time: 23 CT 33.38 1200 W Which of the following is correct? P ave V rms I rms A: 1200 W 120 V 10 A (=1200/120) B: 1200 W 170 V 7 A (=1200/170) C: 600 W 120 V 5 A (= 600/120) D: 600 W 170 V 3.5 A (=600/170) E: None of the above is right. 24 CT 33.39 What is "T" in the picture (in the USA)? A: 1/30 s B: 1/60 s C: 1/120 s D: Other 25 8