absolute maximum ratings
advertisement

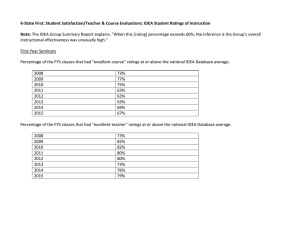
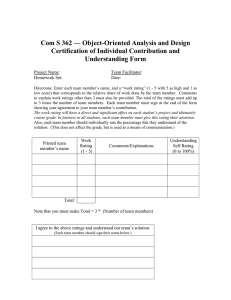
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS BIPOLAR, C-MOS, GaAs, OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICE 1. Definition of Absolute Maximum Rating NJRC defines maximum ratings as the values of voltage, current, temperature, power dissipation etc., which should not be exceeded at any time, otherwise deterioration or destruction of the IC may take place. Maximum values and limits published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. 1.1 Maximum Voltage Ratings Specify the maximum limitation of supply and input voltages. Maximum values and limits published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. 1.2 Maximum Current Ratings Specify the maximum limitation of input and output current. Maximum values and limits published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. 1.3 Maximum Temperature Ratings Specify the maximum limitation of operating and storage temperature. Maximum values and published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. The operating temperature range is the ambient temperature range that IC operates just normally. The electrical characteristics of the ICs specified at 25°C are not guaranteed to apply at the extremes of the operating temperature range. 1.4 Maximum Power Dissipation Rating Specify the maximum limitation of power dissipation. Maximum values and published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. The power dissipation is mentioned following formula. PD = (Tj - Ta) / θja Where PD Tj Ta θja : : : : Power Dissipation Junction Temperature Ambient Temperature Thermal Resistance (W) (°C) (°C) (°C/W) As Tj is normally constant, the maximum power dissipation at a particular ambient temperature is determined by the thermal resistance of the package, which is in turn determined by it's dimensions and materials used in it's manufacture. As a rule the smaller the package, the lower it's maximum power dissipation. Note: Exceeding any of the maximum ratings, even briefly lead to deterioration in IC performance or even destruction. Ver.2007-03-05 -1- ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS STEPPER MOTOR CONTROLLER/DRIVER 1. Definition of Absolute Maximum Rating NJRC defines maximum ratings as the values of voltage, current, temperature, power dissipation etc., which should not be exceeded at any time, otherwise deterioration or destruction of the IC may take place. Maximum values and limits published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. 1.1 Maximum Voltage Ratings Specify the maximum limitation of supply and input voltages. Maximum values and limits published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. 1.2 Maximum Current Ratings Specify the maximum limitation of input and output current. Maximum values and limits published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. 1.3 Maximum Temperature Ratings Specify the maximum limitation of operating and storage temperature. Maximum values and published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. The operating temperature range is the ambient temperature range that IC operates just normally. The electrical characteristics of the ICs specified at 25°C are not guaranteed to apply at the extremes of the operating temperature range. 1.4 Maximum Power Dissipation Rating Specify the maximum limitation of power dissipation. Maximum values and published should be taken into consideration at all times when using or " designing in " NJRC IC's. The power dissipation is mentioned following formula. PD = (Tj - Ta) / θja Where PD Tj Ta θja : : : : Power Dissipation Junction Temperature Ambient Temperature Thermal Resistance (W) (°C) (°C) (°C/ W) As Tj is normally constant, the maximum power dissipation at a particular ambient temperature is determined by the thermal resistance of the package, which is in turn determined by it's dimensions and materials used in it's manufacture. As a rule the smaller the package, the lower it's maximum power dissipation. Note: Exceeding any of the maximum ratings, even briefly lead to deterioration in IC performance or even destruction. -2- Ver.2007-03-05