Chapter 6 Selected Answers

CHAPTER 6 ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS SELECTED ANSWERS
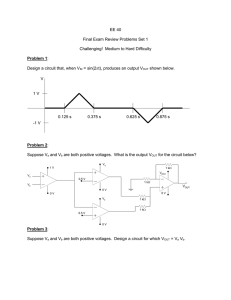
1 . (a) -30 V; (b) -2.5 V; (c) 1.4 V out
= − 10 v in
= − 20 sin 5 t
; (b) v out
= − 10 v in
= − 10 − 5 sin 5 t
5. One possible design is to use a simple inverting op amp circuit with
R f
= 9.1 k Ω and R in
= 5.1 k Ω .
7.
9.
To get a positive output that is smaller than the input, the easiest way is to use inverting amplifier with an inverted voltage supply to give a negative voltage,
where Ω and R in
= 5.1 k Ω
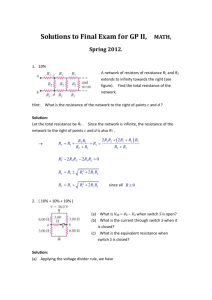
(a) 1.7 V; (b) 3 V; (c) -2.4 V out
= 2 v in
= 8 sin 10 t
; (b) v out
= 2 v in
= 2 + 0 .
5 sin 10 t
13. -2.2
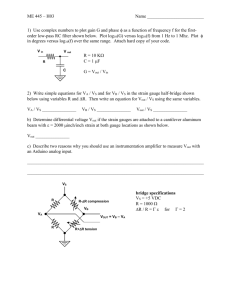
15. One possible solution of many: a non-inverting op amp circuit with the microphone connected to the non-inverting input terminal, the switch connected between the op amp output pin and ground, a feedback resistor R f
= 133 Ω , and a
resistor Ω .
17. V
1
= 21 V
19. v out
( )
; -5.6 V
21. R f
= 236 k Ω and R
1
= 1 k Ω .
23. (a)
2
= R
B
= 1 Ω; (c)
A
is the
25. v out
(0.25 s) = 0.93 V
V
29. R f i
N
∑
= 1 v i
R i
31. Pick Ω . Then v
S
= -0.21 V.
Copyright ©2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
CHAPTER 6 ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS SELECTED ANSWERS
33. One possible solution of many:
35. Set R = 10 k Ω :
Then connect several into:
after f1
= R in
= R =10 k Ω . kV
39. -179
43. R f
= 0, R in
= 100 k Ω , R
2
= 51 Ω .
Copyright ©2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
CHAPTER 6 ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS SELECTED ANSWERS
45. R f
= 120 k Ω and R in
= 200 k Ω , R = 560 Ω .
47. R = 400 Ω , R
1
= 82 Ω .
I I s
49. R = 91 Ω , R
1
= 560 Ω , 467 > R
L
> 67 Ω .
51. (a) –3.7 mV; (b) 28 mV; (c) –3.7 V.
53. v out v in
=
100A
101 + A
; A = 9999.
55. v out
= -16 mV
Copyright ©2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
CHAPTER 6 ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS SELECTED ANSWERS
57. (a)
(b) v out
= 10 5 (-0.00004v
1.99996 sin t
2
- 9.99980×10 -6 v
1
)+5v
2
= 1.00008v
2
- 0.99998v
1
= 0.0005 – v out
= 5 v d
= 10 5 × ( v
2
/ 2 − v a
) =0.99998v
2
-0.99998v
1
= 1.99996 sin t
59. (a)
61. Positive voltage supply, negative voltage supply, inverting input, ground, output
pin.
63. This is a non-inverting op amp circuit, so we expect a gain of 214.
65. For v d
= 6 μ V, where the hand calculations based on the detailed model predict 50 μ V, which is about one order of magnitude larger.
For the same input voltage, PSpice predicts an input current of -1 μ A, whereas the hand calculations predict 99.5
v x
mA = -995 nA (which is reasonably close).
67. (a) Negative saturation begins at V in
V in
= +4.67 V. (b) 40.6 mA.
69.
= –4.72 V, and positive saturation begins at
Copyright ©2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
CHAPTER 6 ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS SELECTED ANSWERS
71. (a)
15
12 V
10
-10
-15
5
0
-5
-2 -1 0
-12 V
1 2
V active
(V)
73.
=
V
1
−
V
2
=
V ref
R
1
R
+
2
R
2
−
R
3
+
R
3
R
Gauge
; (b) V out
= 4.7 k Ω , gain of 5.39 for R = 4.7 k Ω , so R = 11.5 k Ω .
= 0; (c) R = 4.3 k Ω and R
Copyright ©2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.