Strategic Planning Update for Educational Effectiveness Review:
advertisement
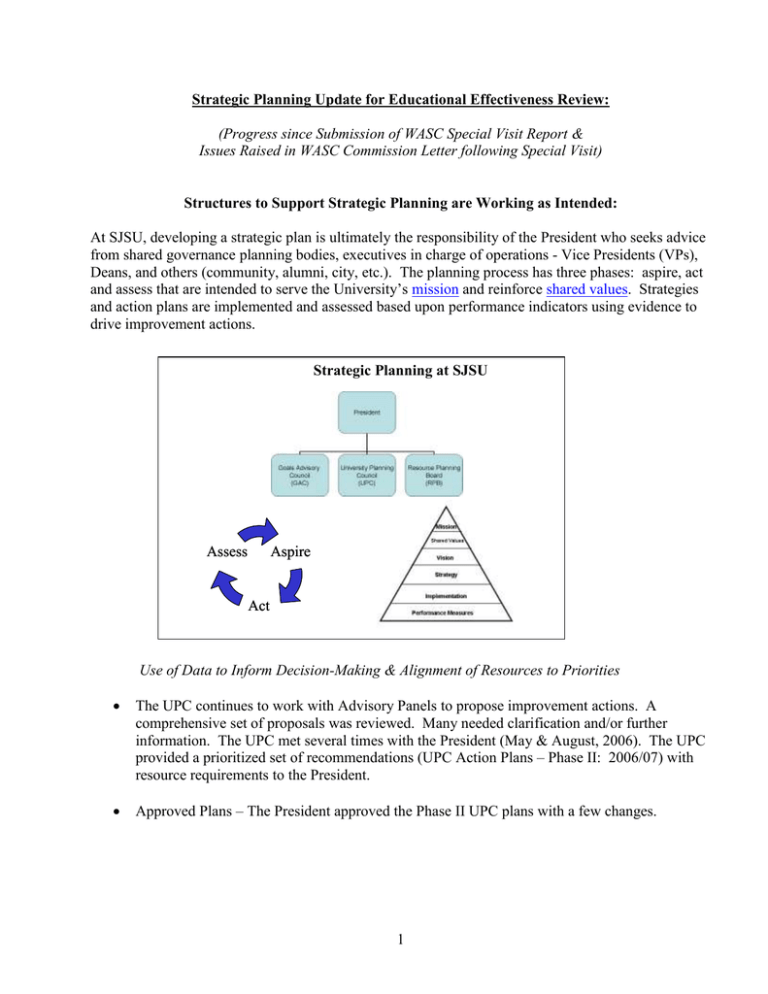
Strategic Planning Update for Educational Effectiveness Review: (Progress since Submission of WASC Special Visit Report & Issues Raised in WASC Commission Letter following Special Visit) Structures to Support Strategic Planning are Working as Intended: At SJSU, developing a strategic plan is ultimately the responsibility of the President who seeks advice from shared governance planning bodies, executives in charge of operations - Vice Presidents (VPs), Deans, and others (community, alumni, city, etc.). The planning process has three phases: aspire, act and assess that are intended to serve the University’s mission and reinforce shared values. Strategies and action plans are implemented and assessed based upon performance indicators using evidence to drive improvement actions. Strategic Planning at SJSU Assess Aspire Act Use of Data to Inform Decision-Making & Alignment of Resources to Priorities The UPC continues to work with Advisory Panels to propose improvement actions. A comprehensive set of proposals was reviewed. Many needed clarification and/or further information. The UPC met several times with the President (May & August, 2006). The UPC provided a prioritized set of recommendations (UPC Action Plans – Phase II: 2006/07) with resource requirements to the President. Approved Plans – The President approved the Phase II UPC plans with a few changes. 1 Alignment of Resources to Strategic Goals $ Allocated $2,500,000 Enhancing Academic Quality $2,000,000 Enriching the Student Experience $1,500,000 Improving Campus Work Environment & Infrastructure $1,000,000 Strengthening Community Alliances $500,000 $0 2005/06 2006/07 President continues working with Deans and VPs for feedback and input (held 4 retreats: (i) President’s Staff; (ii) Deans; (iii) IE Summer Retreat Deans & VPs; (iv) AAMT) on strategic direction. Results of these working sessions include: o Articulation of hallmarks of SJSU educational experience (multicultural and global experiences; innovation and creativity; and integrative learning); o Changes to Advising plan – create an electronic HUB of information, pay faculty to advise during summer, and provide faculty advising training. o Enrollment Management – devised process to cascade FTES targeting from University level through colleges and departments; and o Planning for the second Achieving Greater Expectations Institute: Inclusive Excellence as a Pathway to Vision 2010. Assessment – the strategic planning process is undergoing assessment at various levels. The first level involves assessing the various planning bodies in terms of their effectiveness. The second level involves assessing the strategic planning process and how all of the planning bodies work together. The third level involves assessing the performance of the institution in achieving goals. o Strategic Planning Bodies GAC – conducted survey at completion of vision & goal setting in Spring 2005. UPC – assessment of achievement of milestones (performance to plan) scheduled for Fall 2006. RPB – assess clarity and achievement of purpose (decision-making regarding effective use of resources and communication to achieve transparency). A referral was made to the Senate for an assessment of this planning body in Fall 2006. o Strategic Planning Process An assessment is planned that will include broad input from all of the planning bodies, President’s Staff, Senate, faculty, staff and students. Planning for this activity is expected to begin before the end of Fall 2006. o SJSU Institution – Vision 2010 Progress Report is a balanced scorecard of performance indicators related to our students, academic programs, resources (finance, facilities, people) external accountability requirements and strategic goals. Performance is assessed against specified target levels to determine if performance is on target, and to determine improvement actions if appropriate. 2 Structures Contributing to Improvements in Student Success & Institutional Learning: Use of Data to Inform Decision-Making & Alignment of Resources to Priorities The SJSU Strategic Plan is a living document that is organized around goals, actions and indicators. Dashboard Indicators for Student Success At SJSU, we are implementing promising, new business practices. We have developed a balanced scorecard of key performance measures, and we call it our Vision 2010 Progress Report which relates to our strategic direction. We are implementing new business intelligence software called Cognos to gain access to our performance data in new ways that will inform decisions designed to foster continuous improvement. We are still building our quality improvement infrastructure. Our Vision 2010 Progress Report has key measures related to several areas including: Our Students, Our Academic Programs, Our Resources, Our Strategic Goals and Our External Accountability. For the most part, the scorecard is based upon an analysis that is comparative - a look at historical information, compared to current and projected performance, relative to peer organizations. Performance thresholds are set to categorize performance as on target, cautionary or off target. The performance level is graphically represented as green or yellow or red on the dashboard/scorecard. Scorecards are reports, and dashboards are the graphical representation of performance data. Performance data is easily analyzed by several dimensions simultaneously (which is called a cube analysis) with the ability to drill down and aggregate information quickly. Cognos is business intelligence software for performance management and financial reporting that is adding value by layering the data to integrate reporting, analysis and dashboards with an easy user interface. The inverted triangle (in the graphic shown above) indicates that value is added to the data as we work from the Data Source (which is the most narrowly defined and complex to manage layer) up to the Metadata layer where we determine relationships among the data. However, this layer is still pretty complex and technical. At the Academy layer there are packaged reports that are simplified for users to easily access the data. As you move up through the layers, complexity is removed using various frameworks and tools. Cognos is accessed via our intranet using a web-based interface. Each query is a hit against the CMS database and thus we’ve implemented a data warehousing solution. By using packages of (admissions, enrollment, and progress to graduation) data, we are able to conduct cube analysis and display that information on a dashboard or scorecard. We’ve made progress and our immediate next steps will include: training, refinement of threshold levels, and integrating non-CMS data. 3

