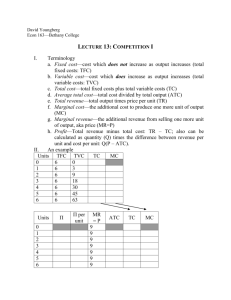
6 # Businesses and Their Costs McGraw-Hill/Irwin
advertisement

6 # Businesses and Their Costs McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. The Business Population • Plant • Factory, farm, mine, store, website, • • LO1 warehouse Firm • Operates one or more plants Industry • Group of firms that produce the same products 6-2 Corporation Advantages • Stocks • Ownership shares of a corporation • Bonds • Liabilities of a corporation • Limited liability LO1 6-3 Principal-Agent Problem • Principals • Stockholders • Agents • Executives LO1 6-4 Economic Costs • The payment that must be made to • • LO2 obtain and retain the services of a resource Explicit costs • Monetary payments Implicit costs • Value of next best use • Self-owned resources • Includes normal profit 6-5 Accounting Profit and Normal Profit • Accounting profit • • LO2 = Revenue – Explicit costs Economic profit = Accounting profit – Implicit costs Economic profit (to summarize) = Total revenue – Economic costs = Total revenue – Explicit costs – Implicit Costs 6-6 Economic Profit LO2 Implicit costs (including a normal profit) Explicit costs Total Revenue Economic (Opportunity) Costs Economic profit Accounting profit Accounting costs (explicit costs only) 6-7 Short Run and Long Run • Short run • Some variable inputs • Fixed plant • Long run • All inputs are variable • Variable plant • Firms enter and exit LO3 6-8 Short-Run Production Relationships • Total product (TP) • Marginal product (MP) Marginal product = Change in total product Change in labor input • Average product (AP) Average product LO3 = Total product Units of labor 6-9 Law of Diminishing Returns • Resources are of equal quality • Technology is fixed • Variable resources are added to fixed • • LO3 resources At some point, marginal product will fall Rationale 6-10 The Law of Diminishing Returns Total, Marginal, and Average Product: The Law of Diminishing Returns LO3 (1) Units of the Variable Resource (Labor) (3) Marginal Product (MP) Change in (2)/ Change in (1) (2) Total Product (TP) 0 0 1 10 10 2 25 15 3 45 20 15.00 4 60 15 15.00 5 70 10 6 75 5 7 75 0 8 70 -5 (4) Average Product (AP), (2)/(1) Increasing marginal returns 10.00 12.50 Diminishin g marginal returns 14.00 Negative marginal returns 8.75 12.50 10.71 6-11 Total Product, TP The Law of Diminishing Returns 30 TP 20 10 0 Marginal Product, MP 1 LO3 20 2 3 Increasing Marginal Returns 4 5 6 7 8 9 Negative Marginal Returns Diminishing Marginal Returns 10 AP 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 MP 6-12 Short-Run Production Costs • Fixed costs (TFC) • Costs do not vary with output • Variable costs (TVC) • Costs vary with output • Total costs (TC) • Sum of TFC and TVC • TC = TFC + TVC LO4 6-13 Per-Unit, or Average, Costs • Average fixed costs • Average variable costs • Average total costs • Marginal costs LO4 AFC = TFC/Q AVC = TVC/Q ATC = TC/Q MC = ΔTC/ΔQ 6-14 Short-Run Production Costs Total, Average, and Marginal Cost Schedules for an Individual Firm in the Short Run Total Cost Data LO4 Average Cost Data Marginal Cost (5) Average Fixed Cost (AFC) AFC = TFC/Q (6) Average Variable Cost (AVC) AVC=TVC/Q (7) Average Total Cost (ATC) ATC = TC/Q 190 $100.00 $90.00 $190.00 $90 170 270 50.00 85.00 135.00 80 100 240 340 33.33 80.00 113.33 70 4 100 300 400 25.00 75.00 100.00 60 5 100 370 470 20.00 74.00 94.00 70 6 100 450 550 16.67 75.00 91.67 80 7 100 540 640 14.29 77.14 91.43 90 8 100 650 750 12.50 81.25 93.75 110 9 100 780 880 11.11 86.67 97.78 130 10 100 930 1030 10.00 93.00 103.00 150 (1) Total Product (Q) (2) Total Fixed Cost (TFC) (3) Total Variable Cost (TVC) (4) Total Cost (TC) TC = TFC + TVC 0 $100 $0 $100 1 100 90 2 100 3 (8) Marginal Cost (MC) MC =ΔTC/ΔQ 6-15 Marginal Cost $200 MC 150 Costs AFC ATC 100 AVC 50 AVC AFC 0 LO4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Q 6-16 Long-Run Production Costs • The firm can change all input • • LO5 amounts, including plant size All costs are variable in the long run Long-run ATC • Different short-run ATCs 6-17 Average Total Costs Firm Size and Costs ATC-1 ATC-5 ATC-2 ATC-3 ATC-4 Output LO5 6-18 Average Total Costs The Long-Run Cost Curve ATC-1 ATC-5 ATC-2 ATC-3 ATC-4 Long-run ATC Output LO4 6-19 Economies and Diseconomies of Scale • Economies of scale • Labor specialization • Managerial specialization • Efficient capital • Other factors • Constant returns to scale LO5 6-20 Economies and Diseconomies of Scale • Diseconomies of scale • Control and coordination problems • Communication problems • Worker alienation • Shirking LO5 6-21 MES and Industry Structure • Minimum efficient scale (MES): • Lowest level of output where longrun average costs are minimized • Can determine the structure of the industry LO5 6-22 Average Total Costs MES and Industry Structure Diseconomies of Scale Constant Returns to Scale Economies of Scale Long-run ATC q1 q2 Output LO5 6-23 Average Total Costs MES and Industry Structure Economies of Scale Diseconomies of Scale Long-run ATC Output LO5 6-24 Average Total Costs MES and Industry Structure Economies Diseconomies of Scale of Scale Long-run ATC Output LO5 6-25