COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT 11 COURSE OUTLINE
advertisement
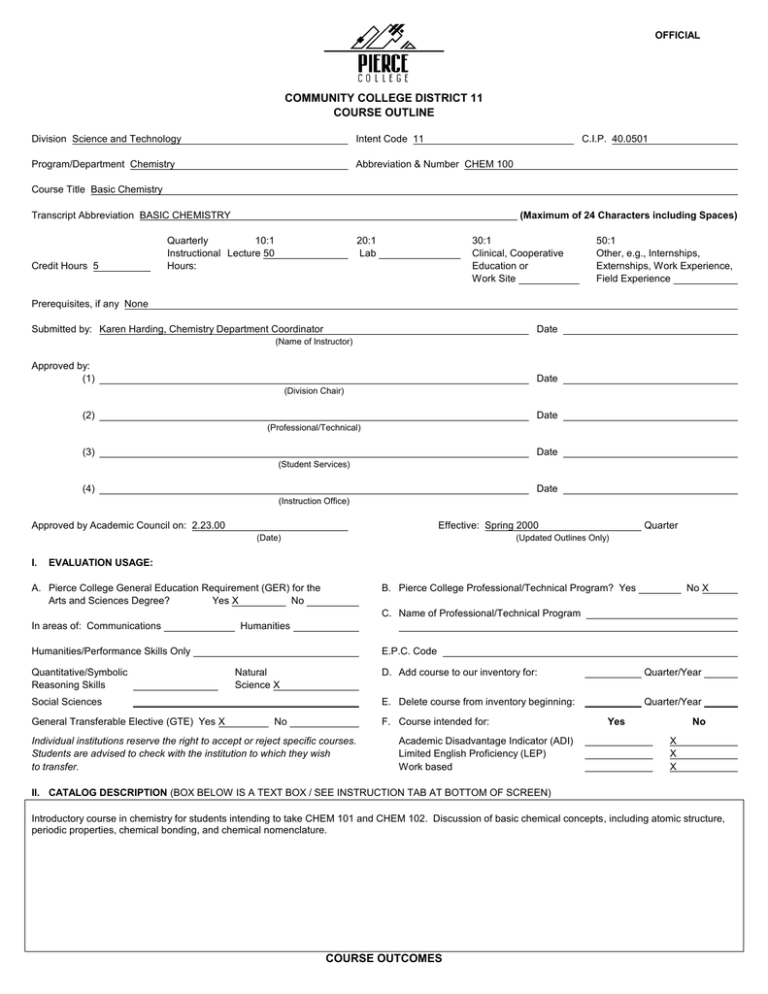
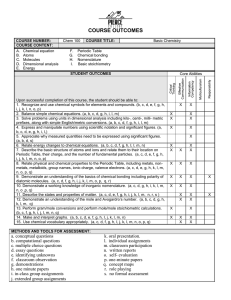
OFFICIAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT 11 COURSE OUTLINE Division Science and Technology Intent Code 11 C.I.P. 40.0501 Program/Department Chemistry Abbreviation & Number CHEM 100 Course Title Basic Chemistry Transcript Abbreviation BASIC CHEMISTRY Credit Hours 5 (Maximum of 24 Characters including Spaces) Quarterly 10:1 Instructional Lecture 50 Hours: 20:1 Lab 30:1 Clinical, Cooperative Education or Work Site 50:1 Other, e.g., Internships, Externships, Work Experience, Field Experience Prerequisites, if any None Submitted by: Karen Harding, Chemistry Department Coordinator Date (Name of Instructor) Approved by: (1) Date (Division Chair) (2) Date (Professional/Technical) (3) Date (Student Services) (4) Date (Instruction Office) Approved by Academic Council on: 2.23.00 Effective: Spring 2000 (Date) I. Quarter (Updated Outlines Only) EVALUATION USAGE: A. Pierce College General Education Requirement (GER) for the Arts and Sciences Degree? Yes X No B. Pierce College Professional/Technical Program? Yes No X C. Name of Professional/Technical Program In areas of: Communications Humanities Humanities/Performance Skills Only Quantitative/Symbolic Reasoning Skills E.P.C. Code Natural Science X Social Sciences General Transferable Elective (GTE) Yes X No D. Add course to our inventory for: Quarter/Year E. Delete course from inventory beginning: Quarter/Year F. Course intended for: Individual institutions reserve the right to accept or reject specific courses. Students are advised to check with the institution to which they wish to transfer. Academic Disadvantage Indicator (ADI) Limited English Proficiency (LEP) Work based Yes No X X X II. CATALOG DESCRIPTION (BOX BELOW IS A TEXT BOX / SEE INSTRUCTION TAB AT BOTTOM OF SCREEN) Introductory course in chemistry for students intending to take CHEM 101 and CHEM 102. Discussion of basic chemical concepts, including atomic structure, periodic properties, chemical bonding, and chemical nomenclature. COURSE OUTCOMES COURSE NUMBER: COURSE CONTENT: A. Chemical equation B. Atoms C. Molecules D. Dimensional analysis E. Energy Chem 100 COURSE TITLE: Basic Chemistry F. Periodic Table G. Chemical bonding H. Nomenclature I. Basic stoichiometry Core Abilities STUDENT OUTCOMES Indicate the desirable results that can be expected to occur from the course experience. These are usually expressed in measurable and observable terms. 1. Recognize and use chemical symbols for elements and compounds. (b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, n, o, p) 2. Balance simple chemical equations. (a, b, c, d, g, h, i, l, m) 3. Solve problems using units in dimensional analysis including kilo-, centi-, milli- metric prefixes, along with simple English/metric conversions. (a, b, c, d, f, g, h, i, l, m) 4. Express and manipulate numbers using scientific notation and significant figures. (a, b, c, d, e, g, h, i, l,) 5. Appreciate why measured quantities need to be expressed using significant figures. (a, b, d, s) 6. Relate energy changes to chemical equations. (a, b, c, d, f, g, h, I, l, m, n) 7. Describe the basic structure of atoms and ions and relate them to their location on Periodic Table, their charge, and the number of fundamental particles. (a, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, o, p) 8. Relate physical and chemical properties to the Periodic Table, including metals, nonmetals, metalloids, group names, ionic charge, valence electrons. (a, c, d, e, g, h, k, l, m, n, o, p, q) 9. Demonstrate an understanding of the basics of chemical bonding including polarity of diatomic molecules. (a, c, d, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, o, p, q, r) 10. Demonstrate a working knowledge of inorganic nomenclature. (a, c, d, g, h, i, k, l, m, n, o ,p, q) 11. Describe the states and properties of matter. (a, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k, l, m, n, r, s ) 12. Demonstrate an understanding of the mole and Avogadro’s number. (a, b, c, d, g, h, k, l, m, q) 13. Perform gram/mole conversions and perform mole/mole stoichiometric calculations. (b, c, f, g, h, i, j, l, m, n, q) 14. Make and interpret graphs. (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, I, j, k, l, m, n) 15. Use chemical vocabulary appropriately. (a, c, d, f, g, h, I, j, k, l, m, n, o, p, q) METHODS AND TOOLS FOR ASSESSMENT: a. conceptual questions b. computational questions c. multiple choice questions d. essay questions e. identifying unknowns f. classroom observation g. demonstrations h. one minute papers i. in-class group assignments j. extended group assignments k. oral presentation. l. individual assignments m. classroom participation n. written reports o. self- evaluation p. one-minute papers q. concept maps r. role playing s. no formal assessment X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X