Section 2.2: Projectile Motion and Centripetal Force - Notes
advertisement

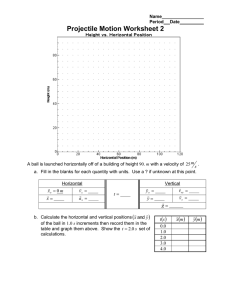
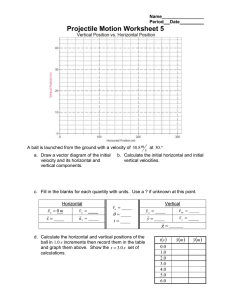
Chapter 3: Forces Date:____________ Section 2.2: Projectile Motion and Centripetal Force - Notes Learning Goals: Explain why objects that are thrown will follow a curved path. Compare circular motion with motion in a straight line. Projectile Motion: Projectile: anything that is _________________ or _______________ through the air Thrown objects don’t always travel in ______________________________ – they ________________ ______________________________. This is because the Earth’s ___________________ causes projectiles to follow a _________________________________. Horizontal Motion: When you throw a ball, the force exerted by your hand ____________ the ball ___________________. After you let go of the ball, ___________________ is accelerating it forward. o The horizontal velocity is ___________________ (ignoring air resistance). Vertical Motion: After you let go of the ball, _________________ pulls it ___________________________. The ball has ____________________ horizontal velocity but _____________________ vertical velocity. Horizontal and Vertical Motion: Gravity exerts an ________________________ force on the ball, changing its direction from only forward to both ___________________________________________________. o Results in the ______________________________ Horizontal and vertical motions are _________________________________________ _____________________________ If you throw a ball as hard as you can from shoulder height in a perfectly horizontal direction, would it take longer to reach the ground than if you dropped a ball from the same height? o A thrown ball and dropped ball will hit the ground ___________________________________. o Both balls travel the same _______________________ distance in the same __________________________________________. o The thrown ball travels a greater ________________________________ distance. Centripetal Acceleration: Centripetal acceleration: acceleration towards the __________________ of a curved or circular path. o In a curve, an object is accelerating because its _________________________ is constantly changing. When an object goes around a curve, the direction of the __________________________ must be towards the _____________________ of the curved path. Centripetal Force: Centripetal force: net force exerted toward the _________________________ of a curved path When a car rounds a curve, a centripetal force must be acting on the car to keep it moving in a __________________________________. In this case, the centripetal force is ________________________ between the tires and the road. If the road is slippery and the frictional force is small, the centripetal force may not be _______________________ to keep the car moving around the curve. o The car will slide in a _____________________________.