South Korea, North Korea
advertisement

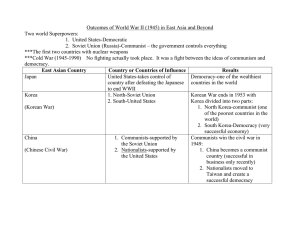
South Korea, North Korea and Japan The main physical features of Japan and the Koreas are rugged mountains. Korea • Korean peninsula includes both North and South Korea. • Much of the peninsula is covered by mountains. • Has some large plains • Most of Korea’s rivers flow westward and pour into the Yellow Sea. The main physical features of Japan and the Koreas are rugged mountains. Japan • Four large islands, 3,000 smaller islands • Major islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu • Mountains cover 75 percent of the country. • Largest mountain range is called the Japanese Alps. • Fuji is Japan’s tallest mountain and has become a symbol of Japan. Most of the lowlands in Japan are densely populated with more than 20,000 people per square mile Inventive methods are used to maximize space. Houses are small and are built very close together with narrow streets. There are sound walls built around housing to block traffic noise. Stores are constructed on the tops of roofs to increase available land for farming. Malls are located underground as well. Most of the people live in apartments. For entertainment, people will go to driving ranges or batting cages, which are screened in. Resources of Japan and the Koreas • One of the world’s strongest fishing economies Japan • A fishery is a place where lots of fish and other seafood can be caught. • Not very rich in mineral resources ----------North • Large deposits of coal, iron, and other minerals Korea • Hydroelectric power -----------South • Increasing Hydroelectric and Nuclearpower Korea• Mineral resources are meager; some coal and lead Religions of Korean People (based on 2004 census report) History of the Koreas http://seoulistic.com/travel-to-korea/80-amazing-pictures-of-korea-by-photographers/ • Korea Initially a unified state with a rich history • Attacked by the Japanese in the late 1500s- then rebuilt • Then attacked again by the Mongols in the 1620 and 1630s • So, then decided to turn inward and not get involved in the affairs of others… take up an ISOLATIONIST policy! • Korea’s nickname is the Hermit Kingdom. • During this time Korea experiences much peace, until… Country Time 10th century B.C. Go-Joseon 1st century B.C. Three kingdoms (Shilla, Baekje and Goguryeo) 668 – 935 A.D. Shilla (south: 668-935) Balhae (north: 698-926) 935 - 1392 Goryeo Dynasty 1392 – 1910 Joseon Dynasty 1910 - 1945 Japanese rule 1948 Established Republic of Korea in South 1950-1953 Korean war 1961 Military coup 1988 Seoul Olympics Japan Annexes Korea ("the Hermit Kingdom") 22 August 1910 San Francisco Chronicle article about the annexation of Korea by Japan Japanese Rule Japan annexed Korea by force in 1910. Japan in 1938 outlawed use of Korean language in an attempt to eradicate Korean national identity. Country Time 10th century B.C. Go-Joseon 1st century B.C. Three kingdoms (Shilla, Baekje and Goguryeo) 668 – 935 A.D. Shilla (south: 668-935) Balhae (north: 698-926) 935 - 1392 Goryeo Dynasty 1392 – 1910 Joseon Dynasty 1910 - 1945 Japanese rule Deep lament and resentment toward invaders prevailed in Korean literature and music, along with attempts to grapple with new, modern forms. Divided Peninsula • In 1945 at Postdam conference US (Truman), USSR (Stalin) and UK (Churchil) decided to divide Korean peninsula at 38th parallel without consulting Koreans. Country Time 10th century B.C. Go-Joseon 1st century B.C. Three kingdoms (Shilla, Baekje and Goguryeo) 668 – 935 A.D. Shilla (south: 668-935) Balhae (north: 698-926) 935 - 1392 Goryeo Dynasty 1392 – 1910 Joseon Dynasty 1910 - 1945 Japanese rule 1948 Established Republic of Korea in South 1950-1953 Korean war 1961 Military coup 1988 Seoul Olympics Korean War • North Korea invaded south by launching surprise attack on 6/25/50. • United Nations forces led by US defended South. • Many Koreans lost or separated from family members in both south and north. Country Time 10th centry B.C. Go-Joseon 1st centry B.C. Three kingdoms (Shilla, Baekje and Goguryeo) 668 – 935 A.D. Shilla (south: 668-935) Balhae (north: 698-926) 935 - 1392 Goryeo Dynasty 1392 – 1910 Joseon Dynasty 1910 - 1945 Japanese rule 1948 Established Republic of Korea in South 1950-1953 Korean war 1961 Military coup 1988 Seoul Olympics RESULTS • North Korea: Communist government. • South Korea: a democratic government. • Effects of the Korean War started still linger today. Inside North Korea • National Geographic, Lisa Ling A new documentary… Secret State of North Korea • PBS Frontline • Secret footage under Kim Jong-Un’s rule In the North… The KIM Dynasty • • • Kim Il-Sung Kim Jong-Il Kim Jong- Un World's most secretive society Decades of this rigid state-controlled system have led to stagnation and a leadership dependent on the cult of personality. North Korea has traditionally enjoyed the support of its powerful neighbor China, but in recent years Chinese leaders appear to have become increasingly frustrated and embarrassed by Pyongyang The Kim’s are known for their crazy behavior and claims… The 32-year-old reportedly used anti-aircraft fire to execute his defense chief for disrespectful behavior, including napping during a military rally attended by the leader. Other strange Facts: AAbtmRO#image=1 http://www.msn.com/en-us/news/photos/15-strange-facts-about-the-kim-dynasty/ss- Modern Korea • Korea (South Korea) is a developed country • Has one of the world's fastest growing economies • 2009 Korean GDP ranked No.12 in the world. 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2008 Has Become a Strong DEMOCRACY Korean Wave (Hallyu): Korean Cultural Export, since early 1990s • Korean movies, TV dramas, and pop-music are very popular around the world; rapidly spreading beyond Asian countries • Korea is among the world’s top ten cultural exporters “Wonder Girls” “Girls’ Generation” “DBSK” “Super Junior” “Psy” …and K-Pop miss A EXO Korean Food Cooked rice, main dish, and side dishes 3-12 side dishes Kimchi fermented pickled vegetable with or without hot pepper, hundreds of variations Common elements of cooking soy sauce soy-bean paste (dyon-jang similar to miso) hot-pepper paste (go-chu-jang) sesame oil Lots of vegetables Bulgogi Bibimbap Kimbap I. Myth of the creation of Japan Video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PIQ9Ea7WDSI A. According to an ancient Japanese legend, the islands were formed by gods, Izanagi and Izanami. Izanagi lowered a jeweled spear into the sea. The salt water dripped from the spear and hardened to form islands. The gods then descended from heaven to live on the island and created the rest of the world. The gods had had three children. Amaterasu was the Sun goddess and is related to the Japanese Imperial Family. Although Japan does not have a lot of land, it has been able to influence the world. Currently, Japan has one of the leading economies in the world, leading in electronics and automobile production. Japan also has one of the highest educated populations. B. What insight into Japanese Culture might this story give you??? II.Isolation • Throughout Japanese history, Japan had stayed isolated from foreigners – Just like China & Korea Not completely cut off though! • Japan is similar to what culture? •- cultural diffusion from China examples: » Character writing (Kana), » Confucianism, » Zen Buddhism » Daoism III. Religion A. There are two many religions in Japan, Shinto and Buddhism. The majority of people follow a combination of the religions and Confucianism. 92 million – Buddhist 85 million – Shinto 120 million - Confucianism B. Confucianism is based the five basic relationships with a superior and inferior person. The superior is expected to lead a moral life and to guide the inferior person. C. Shinto or “the way of the gods” is an indigenous religion in Japan. The basic belief is that spirits or kami live in everything and control the forces of nature. One could win the favor of the gods through prayer and offerings at shrines marked with Torii gates. There are over 2 million gods. Indigenous – Created and remaining within one nation Shinto is made up of four relationships: -Tradition and family -Love of nature -Physical cleanliness -Matsuri – Worship and honor of the spirits Torii Gates When Buddhism reached Japan, it had already split into different sects. The commoners practice a form of Buddhism where anyone could enter paradise through faith. The samurai practiced Zen Buddhism from China. Zen Buddhism emphasizes meditation and self – discipline as a way to reach salvation. It offered a way for the samurai to develop the mental and physical self-control that their lives demanded. Zen Buddhism's central theories are that human life is full of suffering due to illness, death and the loss of loved ones. By getting rid of desires and attachments, one can achieve a state of enlightenment and escape suffering and the circle of reincarnations. It is said that one can achieve self-enlightenment through meditation and self discipline. The discipline and practical approach of Zen made it the Buddhism of the medieval Japanese military class. Samurai would spend time meditating in a garden to achieve enlightenment. The garden created an environment that created a particular mood based upon the display of elements. Zen Garden Rocks can symbolize the sky, earth, islands, or mountains. Early History • Small clans • Early Rulers- Tenno Clan: In district of Yamato never very strong but never overthrown • During middle ages, landowners became very powerful and Japan settled into its own feudal type system – Rice Tax • Nobles (Daimyos) rise in power… protected by warriors (Samurai) Tokugawa Shogun -Military leader of Japan during the Middle Ages -Used to be a temporary title but now became a permanent title -Emperor power declines (figure head) Tokugawa= Isolate! • Shogun makes decision to keep Japan isolated from invaders! Bushido • Japanese Samurai code of warrior • Similar to European Knights » code of Chivalry Harakiri (seppuku) • seppuku “selfdisembowelment” • hara-kiri, “belly-cutting” – the honorable method of taking one’s own life practiced by men of the samurai (military) class in feudal Japan. • it was an effective way to demonstrate the courage, self-control, and strong resolve of the samurai and to prove sincerity of purpose. Watch segments of the following videos. In what ways does Japanese history explain these current issues in Japanese society? • Marathon Monkshttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S06oMxdt40A • Sumo Scandalhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Tlb5XjeKlk End of Isolation- Perry visits Japan • During the 19th Century, The “West wanted to begin trading with China and Japan • Japan had refused as did China but in 1853, they had persuasion • 1853: US Commodore Matthew Perry brings fleet to Japan with a letter from the US presidents asking Japan to open up its ports- claims he will come back with a bigger fleet if demands are not met 1854 Treaty of Kanagawa • two ports open to US • By 1860, Japan opened ports to others. How would the Japanese feel about being forced to do this? • -upset at shogun • -realized they were weak and Tokugawa Shogun realized time was over • -Japan looks to new emperor Mutsuhito for pride and nationalism • -Chose name “Meji” which means enlightened ruler –o“if you can’t beat the west, be the west” • Meiji = Modernization/ Industrialization • Made Japan a modern economic and World power by creating industry Modernized Japan • • • • • Schools modeled after US Army of Germany Navy of Britain Germany’s government Industrialize like west 1870- 1914 – Build factories – Build railroads Conclusion • With modernization came more money and more POWER • Japan by 1894- felt equal with West wanted to show their power to the world • Began to follow Western footsteps of imperialism What is imperialism? • taking over a territory of a weaker nation by a stronger nation ( Bully effect) and use them for resources Sino- Japanese War 1876 • Japan vs. China –oLike western countries, Japan forced Korea to open up ports but China protested both agreed not to fight but China sent in troops and Japan responded and defeated China easily » Got control of Taiwan and other islands • This left Russia realizing Japan was a major power in Asia and challenged their supremacy Russo-Japanese War 1904-1905 • Both wanted control of Manchuria • Japan offered to recognize Russian rights in Manchuria if Russia stayed out of Korea • O They did not and war started • O Japan wins and US negotiated treaty between both countries – Japan gains complete control of Korea » Annexation of Korea WWI- Japan fought with Allies (US, Russia, Great Britain and France) • 1914-1918 • Win war but get nothing for help in winning war • Disappointed and relationship with West declines 1918-1938 • -Japan continues to imperialize in order to obtain more resources and power. They had faced major depression during the 1920’s due to a major earthquake and depression in West • REMEMBER Japan needs resources and is not a self sufficient country based on geography WWII • During WWII Japan aligns with axis powers of Germany and Italy. They share betrayal of others. Japan and Italy were left out of WWI treaty December 7th, 1941 Pearl Harbor Attack Why did they do this? • Japan wanted dominance in Pacific and only powerful nation with any interest in Pacific Ocean. They figured if they took out harbors in Pear Harbor which contained submarines, carriers, and destroyers, US would not be able to help other nations in Pacific because it would be too far away o Successful attack except for one thing: Japan did not count on Air-craft carriers not being at Pearl Harbor » These would later allow US to attack Japan (island hopping) and eventually drop the A-bomb Results • A-bomb dropped on Nagasaki and Hiroshima and Japan is rebuilt by US – Emperor is no longer seen as divine – Creation of a Mixed Economy like US – -Rebuilt into Economic power of technology