Protein Synthesis
advertisement
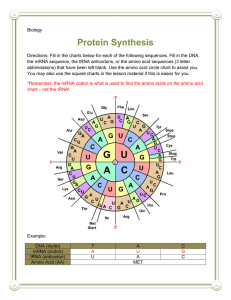
Protein Synthesis Review! What are some functions of proteins? Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms Review! Proteins are polymers, made up of monomers called amino acids There are 20 different types of amino acids Review! What codes for these proteins? DNA contains the sequence of nucleotides that codes for the synthesis of proteins. Problem: DNA is found in the nucleus. Proteins are made at the ribosomes, which are found in the cytoplasm HOW CAN THE INFORMATION FROM THE NUCLEUS GET TO THE RIBOSOME? RNA! – mRNA is used to move information from the DNA to ribosomes This process is called TRANSCRIPTION. Translation The process of converting the information in the nitrogen base sequence of mRNA into a sequence of amino acids which make up proteins Occurs in the RIBOSOMES Translation 1. mRNA attaches and passes through the ribosome. 2. First codon on mRNA moves into position. 3. tRNA (transfer RNA) starts to bring amino acids to the ribosome. Translation 4. tRNA ANTICODON matches up to mRNA codon. 5. mRNA slides through the ribosome to next mRNA codon. Translation 6. New tRNA anticodon matches to next mRNA codon. 7. Amino acids on two tRNAs form a peptide bond with one another. First tRNA floats away to pick up another amino acid for later use Translation 8. Process continues until a stop codon on the mRNA is reached. 9. Result = an amino acid chain is created *Chain of amino acids = polypeptide chain = PROTEIN (more than one polypeptide chain) Protein Synthesis Animation Let’s Review…again! Decode the following If the coding DNA strand contained the following sequence: TAC CGA TTG ACT What would the mRNA strand be? AUG GCU AAC UGA What would the tRNA sequence be? UAC CGA UUG ACU What would the amino acid sequence be? (base it on the mRNA strand!) methionine, alanine, asparagine, “stop”