aka (info. text) Purpose: to convey knowledge about a topic from someone
advertisement

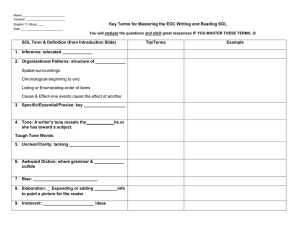
aka (info. text) Purpose: to convey knowledge about a topic from someone credible about that information to someone less knowledgeable about the topic • Facts, statistics, true information • Explains or gives the audience information on a specific topic • Examples: Textbooks, cookbooks, informational brochures, etc. 1. Clear Purpose • What is the author trying to inform or explain? • Three different kinds of purposes when addressing an audience: – To inform – To argue/persuade – To entertain • What type of evidence does the author use? Is this 2. Credible Author • Do you trust the author? • Have they had life experience about the topic? • Are they educated? 3. Intended Audience • Who is the author talking to or writing for? • What can you assume about the audience? • Is the audience educated? How old is the audience? 4. Specific Word Choice (aka Diction) • Denotation – literal or dictionary meaning • Denotative: “Animals are killed for food.” • Connotation – figurative or associated meaning – Connotative: “The Falcon’s basketball team slaughtered WWS.” 4. Specific Word Choice (aka Diction) • What words really jump out and are important? • Does the author need to define certain words for the audience? • How does this diction contribute to the tone or emotional feeling of the text? 5. Tone • Tone: the authors attitude towards the topic • Expressed through diction • Two categories of tone: subjective or objective. • Objective tone is “impartial” • Does not show feelings, and is neither for or against a topic • Unbiased or neutral • Does not use pronouns such as “I and You” • Examples: Textbooks, some newspaper articles • Subjective tone =personal and biased • Characteristic of narrative writing • Author writes to evoke an emotion within the audience • Author uses words that describe feelings, experiences, or thoughts • Example: Stories or Poems