Windows NT Scalability Jim Gray Microsoft Research
advertisement

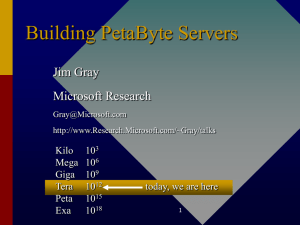
Windows NT Scalability Jim Gray Microsoft Research Gray@Microsoft.com http/www.research.Microsoft.com/~Gray/talks/ Outline • Scalability: What & Why? • Scale UP: NT SMP scalability • Scale OUT: NT Cluster scalability • Key Message: – NT can do the most demanding apps today. – Tomorrow will be even better. What is Scalability? Super Server Server Cluster Server PC Workstation Portable Win Term NetPC Handheld TV • Grow without limits – Capacity – Throughput • Do not add complexity – design – administer – Operate – Use ScaleServer UPCluster & OUT Focus Here • Grow without limits Super Server Server • – SMP: 4, 8, 16, 32 CPUs – 64-bit addressing – Huge storage Cluster Requirements – Auto manage – High availability – Transparency – Programming tools & apps Scalability is Important • Automation benefits growing – ROI of 1 month.... • Slice price going to zero Server – Cyberbrick costs 5k$ • Design, Implement & Manage cost going down – DCOM & Viper make it easy! – NT Clusters are easy! • Billions of clients imply • millions of HUGE servers. Thin clients imply huge servers. Q: Why Does Microsoft Care? A: Billions of clients need millions of servers 2,700 2,400 2,100 1,800 1,500 1,200 900 600 300 0 Servers Shipped per year WindowsNT Server (97-01 are MS estimates) NetWare Unix 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 Expect Microsoft to work hard on Scaleable Windows NT and Scaleable BackOffice. Key technique: INTEGRATION. 1999 2000 2001 Outline • Scalability: What & Why? • Scale UP: NT SMP scalability • Scale OUT: NT Cluster scalability • Key Message: – NT can do the most demanding apps today. – Tomorrow will be even better. How Scaleable is NT?? The Single Node Story • 64 bit file system in NT 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 • 8 node SMP in NT 4.E, 32 node OEM • 64 bit addressing in NT 5 • 1 Terabyte SQL Databases (PetaByte capable) • 10,000 users (TPC-C benchmark) • 100 Million web hits per day (IIS) • 50 GB Exchange mail store next release designed for 16 TB • 50,000 POP3 users on Exchange (1.8 M messages/day) • And, more coming….. Windows NT Server • Scalability Enterprise Edition – 8x SMP support (32x in OEM kit) – Larger process memory (3GB Intel) – Unlimited Virtual Roots in IIS (web) • Transactions – DCOM transactions (Viper TP mon) – Message Queuing (Falcon) • Availability – Clustering (WolfPack) – Web, File, Print,DB … servers fail over. What Happens in 10 Years? 1987: 256 tps $ 14 million computer A dozen people Two rooms of machines 1997: 1,250 tps $ 50 k$ computer One person 1 micro-dollar per transaction (1,000x cheaper) Ready for the next 10 years? NT vs UNIX SMPs • • NT traditionally ran on 1 to 4 cpus – Scales near-linear on them tpmC vs Time UNIX boxes: 32-64 way SMPs 35,000 tpmC vs Time 30,000 – They do 3x more tpmC 25,000 35,000 tpmC vs Time 20,000 30,000 – They cost 10x more. 15,000 25,000 35,000 20,000 10,000 10 way NT machines are available Unix 30,000 15,000 5,000 NT Unix 25,0000 10,000 – They cost more 20,000 5,000 Jan-95 Jan-96 Jan-97 NT 0 15,000 – They are faster 10,000 Jan-95 Jan-96 Jan-97 5,000 My view (shared by many) 0 Jan-95 Jan-96 Jan-97 – Need clusters for availability – Cluster commodity servers to make huge systems tpmC tpmC • h h tpmC h • – a la Tandem, Teradata, VMScluster, IBM Sysplex, IBM SP2 – Clusters reduce need for giant SMPs Transaction Throughput TPC-C • On comparable hardware: NT scales better! • SQL Server & NT Improving 250% per year • NT has best Price Performance (2x cheaper) tpmC on Intel CPUs tpmC vs Intel CPUs NT all 14,000 tpmC 10,000 8,000 h hhhh h 6,000 4,000 2,000 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 tpmC NT UNIX 12,000 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 0 NT Best Unix best h h 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 NT Scales Better Than Solaris • Microsoft SQL 20,000 15,000 tpmC • NT Intel scales to 6x Beats Sybase Solaris UltraSPARC up to 11-way 10,000 5,000 0 0 10 cpus 20 New News: SUN is Waking Up • Sybase on 4x Sun UltraSPARC • • – 4x250Mhz 57$/tpmC @ 11.6 ktpmC – 6x300Mhz 69$/tpmC @ 14.6 ktpmC Microsoft & Unisys – 4x200Mhz 43$/tpmC @ 10.7 ktpmC – 6x200Mhz 40$/tpmC @ 12.2 ktpmC SUN: – 10% better performance – 20% higher unit price New News: HPUX is New Leader • Sybase on HP 8x SMP scales to 40 ktpmC! • Price/Performance is flat (no diseconomy) Sybase & HP tpmC vs CPUs HP + Sybase $/tpmC vs tpmC 45000 40000 35000 $/tmpC tpmC 30000 25000 20000 15000 10000 5000 $140 $120 $100 $80 $60 $40 $20 $0 0 10000 20000 0 0 5 10 cpus 15 20 tpmC 30000 40000 Sun/Solaris More Competitive TPC Price/tpmC • Competitive prices • no premium 50 45 40 except on CPUs 38 37 34 33 35 29 30 24 25 21 20 20 15 Oracle on UltraSPARC, 31 k tpmC HP-Sybase 39K tpmC SUN & Sybase 11.6 ktpmC Microsoft, HP, 9.1 k tpmc 16 12 10 10 11 9 6 7 6 8 9 6 5 5 0 processor disk software net total/10 Only NT Has Economy of Scale • NT is 2x less • 25.0 20.0 Microsoft/NT tpmC/k$ • expensive 40$/tpmC vs 110$/tpmC Only NT has economy of scale Unix has dis-economy of scale Transactions/k$ by vendor 15.0 Oracle/Unix Sybase/Unix 10.0 Informix/Unix DB2/Unix 5.0 0.0 0 10,000 20,000 tpmC 30,000 40,000 TPC-D Decision Support Benchmark • NT has good performance and price/performance. TPC D 100 GB results 3,000 Price/Perf ($/QthD) 2,500 More Througput 2,000 NT 1,500 NT 1,000 Lower price NT 500 0 200 400 600 800 Performance 1000 1200 1400 1600 • • • Scaleup To Big Databases? NT 4 and SQL Server 6.5 – DBs up to 1 Billion records, – 100 GB – Covers most (80%) data warehouses SQL Server 7.0 – Designed for Terabytes • Hundreds of disks per server. • SMP parallel search – Data Mining and Multi-Media TerraServer is good MM example Satellite photos of Earth (1 TB) Dayton-Hudson Sales records (300GB) Human Genome (3GB) Manhattan phone book (15MB) Excel spreadsheet Database Scaleup: TerraServer™ • • • • • • • Demo NT and SQL Server scalability Stress test SQL Server 7.0 Requirements – 1 TB – Unencumbered (put on www) – Interesting to everyone everywhere – And not offensive to anyone anywhere Loaded – 1.1 M place names from Encarta World Atlas – 1 M Sq Km from USGS (1 meter resolution) – 2 M Sq Km from Russian Space agency (2 m) Will be on web (world’s largest atlas) Sell images with commerce server. USGS CRDA: 3 TB more coming. TerraServer System • • • • • • DEC Alpha 4100 (4x smp) + 324 StorageWorks Drives (1.4 TB) RAID 5 Protected SQL Server 7.0 USGS 1-meter data (30% of US) Russian Space data Two meter resolution SPIN-2 images (2 M km2 2% of earth) Demo http://msrlab/terraserver Manageability Windows NT 5.0 and Windows 98 • Active Directory tracks all objects in net • Integration with IE 4. –Web-centric user interface • Management Console –Component architecture • Zero Admin Kit and Systems Management Server • PlugNPlay, Instant On, Remote Boot,.. • Hydra and Intelli-Mirroring Thin Client Support TSO comes to NT lower per-client costs Net PC Windows NT Server with “Hydra” Server Existing, Desktop PC MS-DOS, UNIX, Mac clients Dedicated Windows terminal Windows NT 5.0 IntelliMirror™ • Extends CMU Coda File System ideas • Files and settings mirrored on • • • • client and server Great for disconnected users Facilitates roaming Easy to replace PCs Optimizes network performance Best of PC and centralized computing advantages Outline • Scalability: What & Why? • Scale UP: NT SMP scalability • Scale OUT: NT Cluster scalability • Key Message: – NT can do the most demanding apps today. – Tomorrow will be even better. • • • • Scale OUT Clusters Have Advantages Fault tolerance: – Spare modules mask failures Modular growth without limits – Grow by adding small modules Parallel data search – Use multiple processors and disks Clients and servers made from the same stuff – Inexpensive: built with commodity CyberBricks How scaleable is NT?? The Cluster Story • 16-node Tandem Cluster • – 64 cpus – 2 TB of disk – Decision support 45-node Compaq Cluster – 140 cpus – 14 GB DRAM – 4 TB RAID disk – OLTP (Debit Credit) • 1 B tpd (14 k tps) microsoft.com • • • • 90m hits/day – 17m page views – #4 site on Internet 900k visitors per day Not cheap – Data Centers – Bandwidth – 27 people on content – 22 people on systems • • • Production – Windows NT.4 and IIS.3 • 20 HTTP, • 3 download, • 3 FTP • 5 SQL 6.5 • Index Server + 3 search Stagers – Site Server for content – DCOM Publishing wizard Network – 6 DS3 – 4 TB/day download capacity Replicas in UK and Japan Tandem 2 Ton • 2 TB SQL database • 1.2 TB user data • 16 node cluster • 64 cpus, 480 disks • Decision support parallel data-mining • Will be Wolf Pack aware • Demoed at DB Expo in • ServerNet™ interconnect Billion Transactions per Day Project • Built a 45-node Windows NT Cluster (with help from Intel & Compaq) • • • • • • > 900 disks All off-the-shelf parts Using SQL Server & DTC distributed transactions DCOM & ODBC clients on 20 front-end nodes DebitCredit Transaction Each server node has 1/20 th of the DB Each server node does 1/20 th of the work 15% of the transactions are “distributed” Billion Transactions Per Day Hardware • 45 nodes (Compaq Proliant) • Clustered with 100 Mbps Switched Ethernet • 140 cpu, 13 GB, 3 TB (RAID 1, 5). Type Workflow MTS SQL Server Distributed Transaction Coordinator TOTAL nodes CPUs DRAM ctlrs disks 20 Compaq Proliant 2500 20 Compaq Proliant 5000 5 Compaq Proliant 5000 45 20x 20x 20x 20x RAID space 20x 2 128 1 1 2 GB 20x 20x 20x 20x 4 512 4 20x 36x4.2GB 7x9.1GB 130 GB 5x 5x 5x 5x 5x 4 256 1 3 8 GB 140 13 GB 105 895 3 TB Local Debit Credit Driver Thread DebitCredit Driver DebitCredit Component Database 1 2 4 3 Run 5 6 Init 8 9 Loop 10 7 DebitCredit 11 12 13 14 DebitCredit Distributed Debit Credit Same DTC Database1 Database2 18 11 DebitCredit 21 UpdateAcct 22 23 12 DTC 19 13 20 14 25 15 16 17 24 25 26 27 28 29 26 27 28 Distributed Debit Credit Different DTC Database1 Database2 20 23 11 DebitCredit 24 UpdateAcct 25 12 DTC1 13 21 14 22 15 16 17 19 18 26 27 27 30 30 31 31 34 35 34 28 29 33 32 DTC2 1.2 B tpd • 1 B tpd ran for 24 hrs. • Out-of-the-box software • Off-the-shelf hardware • AMAZING! •Sized for 30 days •Linear growth •5 micro-dollars per transaction • • 1 billion tpd = 11,574 tps ~ 700,000 tpm (transactions/minute) ATT Millions of Transactions Per Day – 185 million calls per peak day (worldwide) 1,000. 900. 800. Visa ~20 million tpd 100. 700. 600. – 400 million customers 500. 10. 400. – 250K ATMs worldwide 300. 1. 200. – 7 billion transactions 100. 0. 0.1 (card+cheque) in 1994 1 Btpd Visa ATT BofA NYSE New York Stock Exchange – 600,000 tpd Bank of America – 20 million tpd checks cleared (more than any other bank) – 1.4 million tpd ATM transactions Worldwide Airlines Reservations: 250 Mtpd Mtpd • How Much Is 1 Billion Tpd? • • • 37 1 B tpd: So What? • Shows what is possible, easy to build • • – Grows without limits Shows scaleup of DTC, MTS, SQL… Shows (again) that shared-nothing clusters scale • Next task: make it easy. – auto partition data – auto partition application – auto manage & operate Cluster Server: High Availability • Multiple servers form one system • Industry standard APIs and hardware • Server application and tools support – IIS web server – File and Print servers – IP and NetName failover – Transaction and Queue Server failover – SQL Server, Enterprise edition • Tight integration with Windows NT -- its easy! • Two-Node clusters now (2 to 20 cpus) • 16 node soon (2 to 192 cpus). WolfPack Cluster IIS & SQL Failover Demo Browser Alice Betty Web site Web site Database Database Web site files Database files Summary • SMP Scale UP: OK but limited • Cluster Scale OUT: OK and unlimited • Manageability: • • • – fault tolerance OK & easy! – more needed CyberBricks work Manual Federation now Automatic in future Scalability Research Problems • Automatic everything • Scaleable applications • • • • • – Parallel programming with clusters – Harvesting cluster resources Data and process placement – auto load balance – dealing with scale (thousands of nodes) High-performance DCOM – active messages meet ORBs? Process pairs, other FT concepts? Real time: instant failover Geographic (WAN) failover