Introduction to Hematology MLAB 1415- Hematology Keri Brophy-Martinez
advertisement

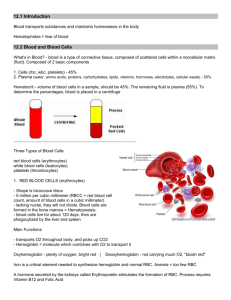
MLAB 1415- Hematology Keri Brophy-Martinez Introduction to Hematology Terms Hematology Study of formed cellular blood elements: the white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets Hemostasis Arrest of bleeding by the formation of a barrier to blood loss Maintenance of an adequate number of cells to carry out the functions of the organism Hematopoiesis Dynamic formation and development of blood cells, normally in the bone marrow Process responsible for the replacement of circulating blood cells Functions of the Hematology lab Confirm a physician’s clinical impression of a possible hematological disorder Establish a diagnosis or rule out a diagnosis Detect an unsuspected disorder Monitor the effects of radiation or chemotherapy Blood Composition Plasma: 55% Constituents of Plasma Water (92%) Solutes(8%) Albumins Globulins Fibrinogen Others ( electrolytes, hormones, vitamins, lipids, salts, enzymes and carbohydrates) Functions of Plasma Transport medium for nutrients & metabolites Immune Defense Coagulation Blood Composition Cellular Elements Leukocytes: 1% White Blood Cell= WBC Granulocytes- fight infection Lymphocytes- cellular and humoral immunity Monocytes- phagocytosis of foreign substances and dead or dying cells Platelets: 1% Thrombocytes Help to maintain hemostasis by plugging capillaries and forming clots Actually a fragment of cytoplasm from megakaryocyte Erythrocytes: 43% Red Blood Cell= RBC Transports oxygen (O2) to tissues and excrete carbon dioxide (CO2) from tissues RBC’s do not have a nucleus A B&H C&E D F G I J Erythrocytes (RBCs) Lymphocytes Segmented neutrophil Eosinophil Monocyte Platelets Neutrophilic band Basophil 55% 45% proteins, albumins, globulins, fibrinogen, electrolytes, hormones, nutrients, and respiratory gases Blood Composition Plasma: liquid portion of blood from an anticoagulated tubes Serum: liquid portion of blood from a clotted specimen Reference ranges Differ according to age, race, sex and geographic location Established by individual facilities in order to account for patient population Refer to inside covers of textbook to review various reference ranges Overview: Laboratory testing Complete Blood Count= CBC Quantifies the white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC) , hemoglobin, hematocrit and platelets. Calculates the RBC indices WBC Differential: enumeration of the types of WBC’s, RBC morphology, platelets