L G
advertisement

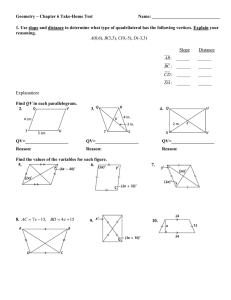
Chapter 7 Study Guide Name:________________________Per:_____ 1) Quadrilateral PLGM is a parallelogram. L a. If 𝑚∠𝑃𝐿𝐺 = 124°, what is the 𝑚∠𝐺𝑀𝑃? Justify. G b. If 𝑚∠𝐿𝑃𝑀 = 56°, what is the 𝑚∠𝑃𝑀𝐺? Justify. R ̅̅̅̅ is 20, what does MP = ? Justify. c. If the length of 𝐿𝐺 P d. If the length of ̅̅̅̅ 𝑃𝑅 is 12, what does PG = ? Justify. M 2) Quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle with diagonals PR and QS. Q a. Name all the parallel segments R b. Name all the right angles. T ̅̅̅̅ is 34, what does QS = ? Justify c. If the length of 𝑃𝑅 P ̅̅̅̅ do you know what QR = ? d. If you know the length of 𝑄𝑃 S 3) Quadrilateral RHMB is a rhombus. H M a. If 𝑚∠𝐻𝑅𝐵 = 70°, what is the 𝑚∠𝐻𝑀𝐵? Justify b. If 𝑚∠𝑀𝐻𝐵 = 55°, what is the measure of 𝑚∠𝑅𝐻𝐵? S ̅̅̅̅ is 25, what does 𝐻𝑅 =? Justify c. If the length of 𝑅𝐵 ̅̅̅̅ is 18, what does 𝑆𝐵 =? Justify d. If the length of 𝐻𝑆 R e. What is the 𝑚∠𝑅𝑆𝐵? Justify B 4) Quadrilateral WXYZ is an isosceles trapezoid. X Y a. If 𝑚∠𝑋𝑊𝑍 = 66°, what is 𝑚∠𝑌𝑍𝑊? Justify b. If 𝑚∠𝑋𝑊𝑍 = 66°, what is 𝑚∠𝑌𝑋𝑊? Justify V c. If the length of ̅̅̅̅̅ 𝑊𝑌 is 10, what does ZX = ? Justify d. If the length of ̅̅̅̅̅ 𝑊𝑋 is 7, what does Zy = ? Justify W Z 5) Quadrilateral ABCD is a kite. a. If 𝑚∠𝐴𝐵𝐶 = 95°, what is 𝑚∠𝐴𝐷𝐶? Justify B b. If 𝑚∠𝐵𝐶𝐸 = 34°, what is 𝑚∠𝐷𝐶𝐸? Justify A C E c. If 𝑚∠𝐵𝐶𝐸 = 34°, what is 𝑚∠𝐸𝐵𝐶? Justify d. If the length of ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 is 16, what does AD = ? Justify ̅̅̅̅ is 25, what does ED = ? Justify e. If the length of 𝐵𝐷 D 6) Calculate the sum of the INTERIOR angles for each of the given regular polygon. Then find the measure of a single angle. a) regular nonagon b) regular 15-gon c) regular 47-gon 7) Determine the measure of the missing angle in each figure. a. b. 8) Use the figure to answer each question. a. What is the sum of the measures for the interior angles of this polygon? b. What is the value of x? c. What is the measure of ∠𝑃𝑇𝑆 ? 9) What type of regular polygon would you have if … a) each interior angle is 156° b) each interior angle is 45° c) sum of exterior angles is 360° 10) If a polygon has 30 sides, what is the sum of the measures of the exterior angles? Justify 11) Calculate the sum of the EXTERIOR angles for each of the given regular polygon. Then find the measure of a single angle. a) regular nonagon c) regular 15-gon d) regular 47-gon 12) Determine if each of the following is a parallelogram. Justify 13) Sketch the following figures & label congruency marks, parallel marks, and right angles as needed. a) Concave Pentagon c) Kite b) Equiangular/Non-Equilateral Hexagon d) Isosceles Trapezoid e) Rhombus 14) List all types of quadrilaterals with the given characteristics. I = Isosceles Trapezoid K = Kite RH = Rhombus a) b) c) d) e) f) P = Parallelogram S = Square R = Rectangle T = Trapezoid The quadrilateral has four right angles. The quadrilateral has four congruent sides. Exactly one pair of opposite sides of the quadrilateral is parallel. Opposite angles of the quadrilateral are congruent. The diagonals of the quadrilateral are congruent. The diagonals of the quadrilateral bisect each other. 15) Find all possible values of x & y where they exist. Diagrams may not be drawn to scale. (Both a and b are trapezoids) b. (Both c and d are kites.) 17) Find the value of the x & y variable in each of the parallelograms Use the statements and the Perpendicular/Parallel Line Theorem to identify the pair of parallel lines in each figure. 19) Solve each of the following by completing the Square a) 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟖𝒙 − 𝟐𝟎 = 𝟎 b) 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟔𝒙 − 𝟏𝟏 = 𝟎 c) 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟑𝒙 + 𝟏 = 𝟎 20) Solve each of the following quadratics (Hint: Check factoring first then use Q.F.) a) 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟏𝟏𝒙 − 𝟒𝟐 = 𝟎 b) 𝟑𝒙𝟐 + 𝟕𝒙 + 𝟐𝟏 = 𝟎 c) (𝟑𝒙 − 𝟓)(𝒙 + 𝟐) = 𝟎 a) 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟔𝒙 − 𝟐 = 𝟎 b) 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟏𝟎𝒙 + 𝟐𝟓 = 𝟎 c) 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟗 = 𝟎 21) Simplify each of the following expressions using addition, subtraction, & multiplication. a) (4𝑚2 + 9𝑚) − (−2𝑚2 + 6) b) (−𝑥 2 − 12) + (4𝑥 2 − 6) c) (2𝑥 + 1)(3𝑥 − 8) 22) Factor each expression a) 2𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 − 9 b) 2𝑝3 + 5𝑝2 + 6𝑝 + 15