Long Range Transport Mechanism
advertisement
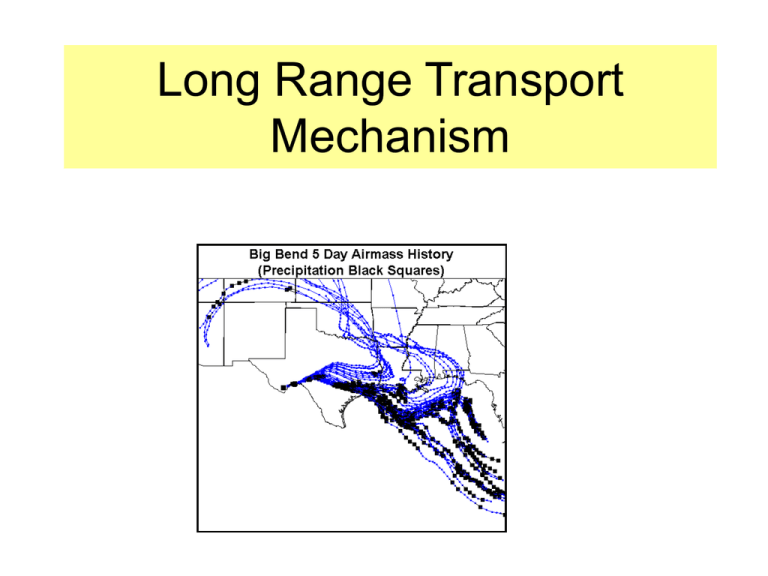
Long Range Transport Mechanism Regional Scale Dispersion Processes Day Time Mixing Random Mixing Vertically distributes pollutants Wind Shear Axial Mixing Horizontally Spreads pollutants Wind Veer Axial Mixing Horizontally redistributes pollutants The three transport processes that shape regional dispersion are wind shear, veer, and eddy motion or random mixing. Homogeneous hazy airmasses are create through shear and veer at night followed by vigorous vertical mixing during the day. Regional Scale Dispersion The degree of of the airmass spreading after a day of transport is independent of the horizontal eddy diffusivity coefficient Airmass History Model Comparison HY-SPLIT Vs. CAPITA Monte Carlo Model HY-SPLIT: NGM wind fields, no mixing Monte Carlo Model: NGM wind fields, mixing At times individual Airmass histories compared very well At times individual Airmass histories compared very poorly Local Flows • Current regional scale models poorly capture local flows – Complex Terrain – Land Water Boundaries – Near source impact • Concentration are due to local and regional contributions Blumenthal et al., 1997 Monte Carlo Transport Animations

