Kids Discover Solar System Magazine Worksheet, the First
advertisement

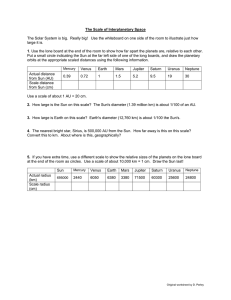
Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Name ______________________________________________________________ Kids Discover Solar System Magazine Worksheet, the First 1. Planets circle. The Moon circles Earth. Earth circles the Sun. Everything in the Solar System circles the Sun. Another term for “circles” is… a. rotation. b. revolution. c. spinning. d. turning 2. Spinning, circling, crashing – why don’t all the planets and moons and asteroids just stay put? a. Weak atomic force b. Strong atomic force c. Magnetism d. Gravity 3. The Sun has ______________% of the mass of the Solar System. (Enter a number) _____4. Planet A. A nuclear power plant; a giant ball of super-hot gas. _____5. Meteor B. A sun and everything with reach of its gravity. _____6. Solar System C. An asteroid that has plunged into the atmosphere. _____7. Dwarf Planet D. Ball of ice, dust, rocks, and gas a few miles across. _____8. Comets E. Composed of rocky fragments located in a ring between Mars and Jupiter. _____9. Moon F. Must have clear other objects from its orbit and is round. _____10. Asteroid _____11. Sun G. Orbits a planet or a dwarf planet; can be less than a mile in diameter or as big as a small planet. H. Orbits a star, but has not cleared other objects from its orbit. ~1~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Use the diagram to answer questions #12–#17. D A B E C F Match the letter with the correct part of the Sun. _____12. Chromosphere A. A _____13. Core B. B _____14. Corona C. C _____15. Flare D. D _____16. Photosphere E. E _____17. Sunspot F. F ~2~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Match the part of the Sun with its description. _____18. Chromosphere A. Dark blotches on the Sun’s surface. _____19. Core B. Sudden blasts of burning gas. _____20. Corona C. The surface; glows bright white thanks to heat below it. _____21. Flare _____22. Photosphere D. This is like the Sun’s atmosphere; it’s a layer of gas above the photosphere. _____23. Sunspot E. This is the Sun’s upper atmosphere. F. This is where atomic blasts take place; hydrogen is changed to helium. 24. ______________ men have walked on the Moon. (Enter a number) 25. The Sun’s most direct, hottest rays hit the… a. Antarctic Circle. b. Arctic Circle c. Equator d. Tropic of Cancer e. Tropic of Capricorn 26. Identify the rocks ‘n the hood. a. Earth b. Jupiter c. Mars d. Mercury e. Neptune f. Saturn g. Uranus h. Venus ~3~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Match the planet with the correct fact. _____27 Earth A. Lead, tin, and zinc would melt on its surface. _____28. Mars B. Most likely planet to support life after Earth. _____29. Mercury C. One side is 800o F. and the other side is -300o F. _____30. Venus D. Slightly warmer than its distance from Sun would indicate; greenhouse effect keeps planet warmer. 31. Why are planets near the Sun rocky and planets far from the Sun mostly gas? a. There was little gas near the Sun. b. The gases became the atmosphere of the planets. c. Most of the gas is under the surface. d. Being so close to the Sun caused most of the gas to be blown away. 32. Identify the gas giants. a. Earth b. Jupiter c. Mars d. Mercury e. Neptune f. Saturn g. Uranus h. Venus Match the planet with the correct fact. _____33. Jupiter A. Winds may be the fastest in the Solar System – 1,200 mph. _____34. Neptune B. Tilted on its side; sometimes poles point towards the Sun. _____35. Saturn C. Has prominent rings and less than a mile thick. _____36. Uranus D. Has a cloudy atmosphere with raging storms and lightning. ~4~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Name ______________________________________________________________ Kids Discover Solar System Magazine Worksheet, the Sequel 1. Jupiter’s four moons are named after the scientist who discovered them. a. Copernicus b. Galileo c. Huygens d. Kepler Match the Moon with its description. _____2. Callisto _____3. Europa _____4. Ganymede _____5 Io _____6. Miranda A. An asteroid blasted apart this moon but gravity caused it to come back together. B Ice coated surface makes it the smoothest in the Solar System. C. Icy, dusty surface covered with craters. D. Looks like a pizza with “with works.” E. The largest moon. 7. This a dwarf planet. It’s twice as big as its moon, ____________________. (There are two answers to this question. Be sure to put both answers in the clicker!) a. Charon b. Eris c. Pluto d. Styx 8. This red storm is big enough to swallow Earth. You would find the storm on… a. Jupiter b. Neptune c. Saturn d. Uranus 9. The dust tail of a comet is sometimes in front of the comet. Why? a. Because of the speed of the comet. b. Gravity controls the direction of the tail. c. The comet turns around and travels away from the Sun backwards. d. The solar winds blow the tail away from the comet. ~5~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. 10. Jupiter’s gravity ripped Comet Shoemaker Levy 9 into dozens of pieces. These pieces collided with Jupiter in __________________. (Enter a number0 11. A comet leaves a trail of dust and debris that says in space for a long time. When the dust or debris enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it is called a… a. meteoroid shower. b. meteor shower. c. meteorite shower. 12. The Galileo space probe discovered the asteroid Ida has a moon. a. True b. False 13. The distance between __________________ and __________________ is about the same as the distance between Saturn and the Sun. (There are two answers to this question. Be sure to enter both in the clicker.) a. Jupiter b. Neptune c. Saturn d. Uranus 14. Nearly __________________ Earths could fit inside of Jupiter. (Enter a number) Match the planet with the description of the Roman God is was named after. _____15. Jupiter A. God of the Sea _____16. Mercury B. Goddess of love; married to Mars. _____17. Neptune C. Ruler of heaven and Earth. _____18. Pluto D. Ruler of the underworld. _____19. Venus E. The messenger of the gods. ~6~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Kids Discover Solar System Magazine Worksheet, the First – Key 1. Planets circle. The Moon circles Earth. Earth circles the Sun. Everything in the Solar System circles the Sun. Another term for “circles” is… a. rotation. b. revolution. c. spinning. d. turning b. revolution. 2. Spinning, circling, crashing – why don’t all the planets and moons and asteroids just stay put? a. Weak atomic force b. Strong atomic force c. Magnetism d. Gravity d. gravity 3. The Sun has ______________% of the mass of the Solar System. (Enter a number) 99.9 F 4. Planet (8 choices) C 5. Meteor (8 choices) B 6. Solar System (8 choices) H 7. Dwarf Planet (8 choices) D 8. Comets (8 choices) G 9. Moon (8 choices) E 10. Asteroid (8 choices) ~7~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. A 11. Sun (8 choices) A 12. Chromosphere (6 choices) C 13. Core (6 choices) D 14. Corona (6 choices) F 15. Flare (6 choices) B 16. Photosphere (6 choices) E 17. Sunspot (6 choices) D 18. Chromosphere (6 choices) F 19. Core (6 choices) E 20. Corona (6 choices) B 21. Flare (6 choices) C 22. Photosphere (6 choices) A 23. Sunspot (6 choices) 24. ______________ men have walked on the Moon. (Enter a number) 12 25. The Sun’s most direct, hottest rays hit the… a. Antarctic Circle. b. Arctic Circle c. Equator d. Tropic of Cancer e. Tropic of Capricorn c. Equator (5 choices) ~8~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. 26. Identify the rocks ‘n the hood. a. Earth b. Jupiter c. Mars d. Mercury e. Neptune f. Saturn g. Uranus h. Venus a. Earth; c. Mars; d. Mercury; h. Venus (8 choices) D 27 Earth B 28. Mars C 29. Mercury A 30. Venus 31. Why are planets near the Sun rocky and planets far from the Sun mostly gas? a. There was little gas near the Sun. b. The gases became the atmosphere of the planets. c. Most of the gas is under the surface. d. Being so close to the Sun caused most of the gas to be blown away. d. Being so close to the Sun caused most of the gas to be blown away. 32. Identify the gas giants. a. Earth b. Jupiter c. Mars d. Mercury e. Neptune f. Saturn g. Uranus h. Venus b. Jupiter; e. Neptune; f. Saturn; g. Uranus D 33. Jupiter ~9~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. A 34. Neptune C 35. Saturn B 36. Uranus ~10~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Kids Discover Solar System Magazine Worksheet, the Sequel – Key 1. Jupiter’s four moons are named after the scientist who discovered them. a. Copernicus b. Galileo c. Huygens d. Kepler b. Galileo C 2. Callisto (5 choices) B 3. Europa (5 choices) E 4. Ganymede (5 choices) D 5 Io (5 choices) A 6. Miranda (5 choices) 7. This a dwarf planet. It’s twice as big as its moon, ____________________. (There are two answers to this question. Be sure to put both answers in the clicker!) a. Charon b. Eris c. Pluto d. Styx a. Charon; c. Pluto 8. This red storm is big enough to swallow Earth. You would find the storm on… a. Jupiter b. Neptune c. Saturn d. Uranus a. Jupiter ~11~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. 9. The dust tail of a comet is sometimes in front of the comet. Why? a. Because of the speed of the comet. b. Gravity controls the direction of the tail. c. The comet turns around and travels away from the Sun backwards. d. The solar winds blow the tail away from the comet. d. The solar winds blow the tail away from the comet. 10. Jupiter’s gravity ripped Comet Shoemaker Levy 9 into dozens of pieces. These pieces collided with Jupiter in __________________. (Enter a number0 1994 11. A comet leaves a trail of dust and debris that says in space for a long time. When the dust or debris enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it is called a… a. meteoroid shower. b. meteor shower. c. meteorite shower. b. meteor shower (3 choices) 12. The Galileo space probe discovered the asteroid Ida has a moon. a. True b. False a. True (2 choices) 13. The distance between __________________ and __________________ is about the same as the distance between Saturn and the Sun. (There are two answers to this question. Be sure to enter both in the clicker.) a. Jupiter b. Neptune c. Saturn d. Uranus c. Saturn; d. Uranus ~12~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. 14. Nearly __________________ Earths could fit inside of Jupiter. (Enter a number) 1500 C 16. Jupiter (5 choices) E 17. Mercury (5 choices) A 18. Neptune (5 choices) D 19. Pluto (5 choices) B 20. Venus (5 choices) ~13~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Kids Discover Solar System Magazine Worksheet, the First – Scoring Guide 35-36 – 4 34 – 3.5 29-33 – 3 26-28 – 2.5 22-25 – 2 19-21 – 1.5 15-18 – 1 1-14 – .5 0–0 ~14~ Objective – Students will understand the relationship and attributes of objects in the Solar System. Kids Discover Solar System Magazine Worksheet, the Sequel – Scoring Guide 19-20 – 4 18 – 3.5 14-17 – 3 13 – 2.5 11-12 – 2 9-10 – 1.5 7-8 – 1 1-6 – .5 ~15~