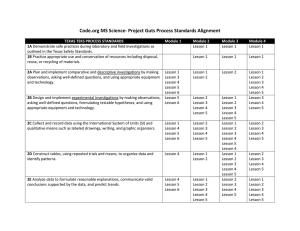
John Drugan 43 instructional Days
advertisement
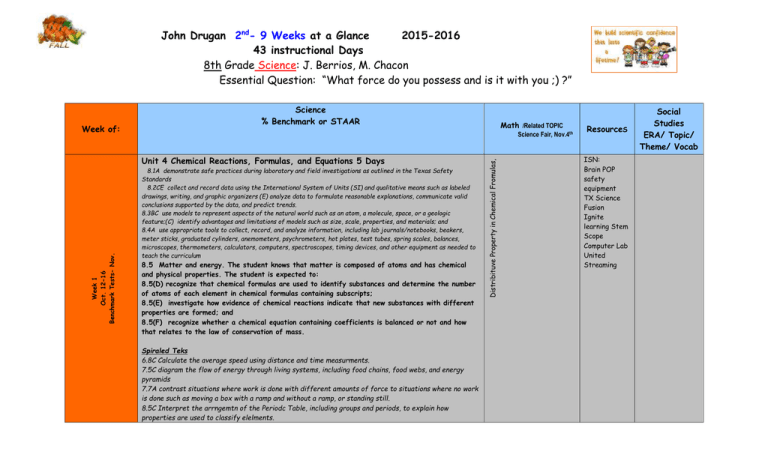
John Drugan 2nd- 9 Weeks at a Glance 2015-2016 43 instructional Days 8th Grade Science: J. Berrios, M. Chacon Essential Question: “What force do you possess and is it with you ;) ?” Science Fair, Nov.4th Unit 4 Chemical Reactions, Formulas, and Equations 5 Days Week 1 Oct. 12-16 Benchmark Tests- Nov. Math /Related TOPIC 8.1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards 8.2CE collect and record data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative means such as labeled drawings, writing, and graphic organizers (E) analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3BC use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature;(C) identify advantages and limitations of models such as size, scale, properties, and materials; and 8.4A use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum 8.5 Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: 8.5(D) recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts; 8.5(E) investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed; and 8.5(F) recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Distribituve Property in Chemical Fromulas, Week of: Science % Benchmark or STAAR ResourceS ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming Social Studies ERA/ Topic/ Theme/ Vocab Unit 4 Test Week 2 Oct. 19-23 Benchmark Tests- -Nov. Unit 4 Chemical Reactions, Formulas, and Equations 5 Days 8.1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards 8.2CE collect and record data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative means such as labeled drawings, writing, and graphic organizers (E) analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3BC use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature;(C) identify advantages and limitations of models such as size, scale, properties, and materials; and 8.4A use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum 8.5 Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: 8.5(D) recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts; 8.5(E) investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed; and 8.5(F) recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Distribituve Property in Chemical Fromulas, ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming Benchmark Tests-Nov. Red Ribbon Week Week 3 Oct. 26-30 Early Release Oct. 28 Unit 4 Chemical Reactions, Formulas, and Equations 4 Days 8.1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards 8.2CE collect and record data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative means such as labeled drawings, writing, and graphic organizers (E) analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3BC use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature;(C) identify advantages and limitations of models such as size, scale, properties, and materials; and 8.4A use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum 8.5 Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: 8.5(D) recognize that chemical formulas are used to identify substances and determine the number of atoms of each element in chemical formulas containing subscripts; 8.5(E) investigate how evidence of chemical reactions indicate that new substances with different properties are formed; and 8.5(F) recognize whether a chemical equation containing coefficients is balanced or not and how that relates to the law of conservation of mass. Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Distribituve Property in Chemical Fromulas, ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming Week 4 Nov. 2-6 Unit 5 Force and Motion (5 Days) 8.1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 8.2BCDE design and implement comparative and experimental investigations by making observations, asking welldefined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and using appropriate equipment and technology€ collect and record data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative means such as labeled drawings, writing, and graphic organizers; (D) construct tables and graphs, using repeated trials and means, to organize data and identify patterns; and€ analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3AB in all fields of science, analyze, evaluate, and critique scientific explanations by using empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and experimental and observational testing, including examining all sides of scientific evidence of those scientific explanations, so as to encourage critical thinking by the student; (B) use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature 8.4AB use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum (B) (B) use preventative safety equipment, including chemical splash goggles, aprons, and gloves, and be prepared to use emergency safety equipment, including an eye/face wash, a fire blanket, and a fire extinguisher. 8.(6) Force, motion, and energy. The student knows that there is a relationship between force, motion, and energy. The student is expected to: 8.6(A) demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed or direction of an object’s motion; 8.6(B) differentiate between speed, velocity, and acceleration; Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Calculating Net forces by grouping integers and finding absolute values ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming Week 5 Nov. 9-13 Veteran’s Day Nov. 11 No School Unit 5 Force and Motion (3 Days) 8.1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 8.2BCDE design and implement comparative and experimental investigations by making observations, asking welldefined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and using appropriate equipment and technology€ collect and record data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative means such as labeled drawings, writing, and graphic organizers; (D) construct tables and graphs, using repeated trials and means, to organize data and identify patterns; and€ analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3AB in all fields of science, analyze, evaluate, and critique scientific explanations by using empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and experimental and observational testing, including examining all sides of scientific evidence of those scientific explanations, so as to encourage critical thinking by the student; (B) use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature 8.4AB use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum (B) (B) use preventative safety equipment, including chemical splash goggles, aprons, and gloves, and be prepared to use emergency safety equipment, including an eye/face wash, a fire blanket, and a fire extinguisher. 8.(6) Force, motion, and energy. The student knows that there is a relationship between force, motion, and energy. The student is expected to: 8.6(A) demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed or direction of an object’s motion; 8.6(B) differentiate between speed, velocity, and acceleration; Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Unit 5 test Calculating Net forces by grouping integers and finding absolute values ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming Week 6 Nov. 16-20 Unit 6 Newton Laws (5 Days) 8.1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 8.2BD design and implement comparative and experimental investigations by making observations, asking well-defined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and using appropriate equipment and technology (D) construct tables and graphs, using repeated trials and means, to organize data and identify patterns; and(E) analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3BD use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature (D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, including the history of science and contributions of scientists as related to the content. 8.4AB use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum 8.(6) Force, motion, and energy. The student knows that there is a relationship between force, motion, and energy. The student is expected to: 8.6(C) investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle restraints, sports activities, amusement park rides, Earth's tectonic activities, and rocket launches. Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Solving real world word problems and using F=MxA to calculate for information applying to Newton’s Laws. ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming Week 7 Nov.30-Dec.4 Unit 6 Newton Laws (5 Days) 8.1A demonstrate safe practices during laboratory and field investigations as outlined in the Texas Safety Standards; and 8.2BD design and implement comparative and experimental investigations by making observations, asking well-defined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and using appropriate equipment and technology (D) construct tables and graphs, using repeated trials and means, to organize data and identify patterns; and(E) analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3BD use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature (D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, including the history of science and contributions of scientists as related to the content. 8.4AB use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum 8.(6) Force, motion, and energy. The student knows that there is a relationship between force, motion, and energy. The student is expected to: 8.6(C) investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle restraints, sports activities, amusement park rides, Earth's tectonic activities, and rocket launches. Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Unit 6 Test Solving real world word problems and using F=MxA to calculate for information applying to Newton’s Laws. ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming 8.2E analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3ABCD in all fields of science, analyze, evaluate, and critique scientific explanations by using empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and experimental and observational testing, including examining all sides of scientific evidence of those scientific explanations, so as to encourage critical thinking by the student; (B) use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature (C) identify advantages and limitations of models such as size, scale, properties, and materials; and(D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, including the history of science and contributions of scientists as related to the content. 8.4AB use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum. 8.6(C) investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle restraints, sports activities, am(9) Earth and space. The student knows that natural events can impact Earth systems. The student is expected to: (A) describe the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory; (B) relate plate tectonics to the formation of crustal features; and (C) interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering amusement park rides, Earth's tectonic activities, and rocket launches. Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Solving real world word problems and using F=MxA to calculate for information applying to Newton’s Laws. Author’s Wall Post Week 8 Dec. 7-11 Unit 7: Forces that Change the Earth (5 Days) ISN: Brain POP safety equipment TX Science Fusion Ignite learning Stem Scope Computer Lab United Streaming Unit 7: Forces that Change the Earth (3 Days) Week 9 Dec. 14-18 (3 days) Early Release Dec. 18 8.2E analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. 8.3ABCD in all fields of science, analyze, evaluate, and critique scientific explanations by using empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and experimental and observational testing, including examining all sides of scientific evidence of those scientific explanations, so as to encourage critical thinking by the student; (B) use models to represent aspects of the natural world such as an atom, a molecule, space, or a geologic feature (C) identify advantages and limitations of models such as size, scale, properties, and materials; and(D) relate the impact of research on scientific thought and society, including the history of science and contributions of scientists as related to the content. 8.4AB use appropriate tools to collect, record, and analyze information, including lab journals/notebooks, beakers, meter sticks, graduated cylinders, anemometers, psychrometers, hot plates, test tubes, spring scales, balances, microscopes, thermometers, calculators, computers, spectroscopes, timing devices, and other equipment as needed to teach the curriculum. 8.6(C) investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle restraints, sports activities, am(9) Earth and space. The student knows that natural events can impact Earth systems. The student is expected to: (A) describe the historical development of evidence that supports plate tectonic theory; (B) relate plate tectonics to the formation of crustal features; and (C) interpret topographic maps and satellite views to identify land and erosional features and predict how these features may be reshaped by weathering amusement park rides, Earth's tectonic activities, and rocket launches. Spiraled Teks 6.8C Calculate the average speed using distance and time measurments. 7.5C diagram the flow of energy through living systems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids 7.7A contrast situations where work is done with different amounts of force to situations where no work is done such as moving a box with a ramp and without a ramp, or standing still. 8.5C Interpret the arrngemtn of the Periodc Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elelments. Technology Projects: Powerpoint Scientist that made a contribution in the Americas Take Home Project: Newton’s Laws( Video, Skit, Nearpod, Prezi) Solving real world word problems and using F=MxA to calculate for information applying to Newton’s Laws.