Department of Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering & Technology Engineering Economy I
advertisement
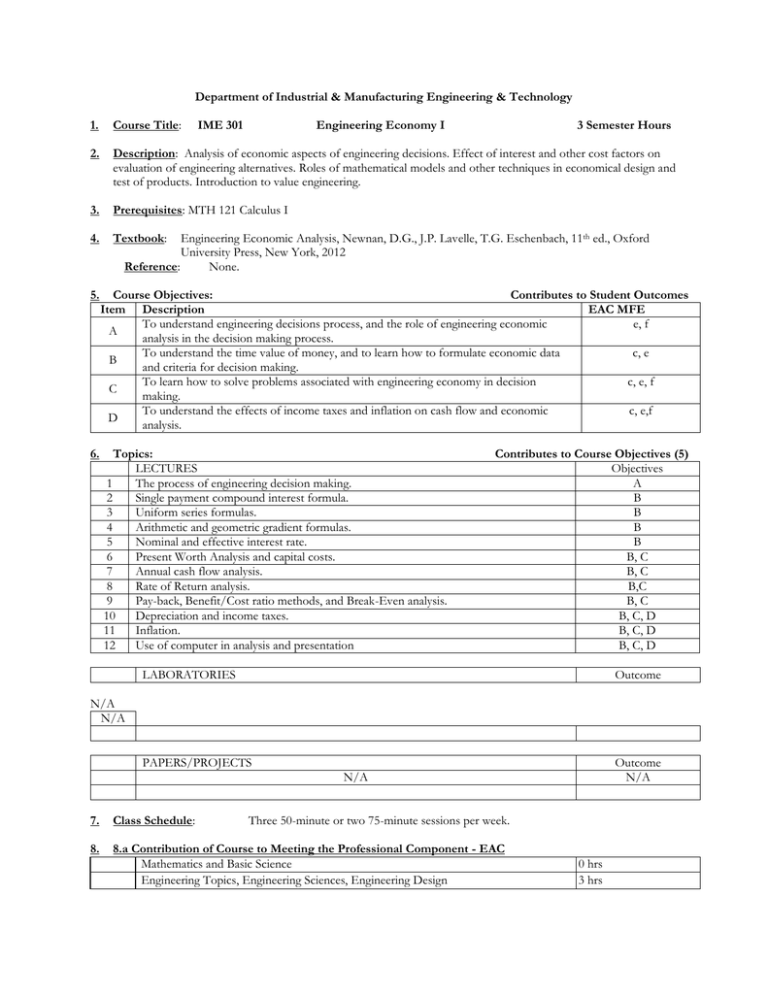
Department of Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering & Technology 1. Course Title: IME 301 Engineering Economy I 3 Semester Hours 2. Description: Analysis of economic aspects of engineering decisions. Effect of interest and other cost factors on evaluation of engineering alternatives. Roles of mathematical models and other techniques in economical design and test of products. Introduction to value engineering. 3. Prerequisites: MTH 121 Calculus I 4. Textbook: Engineering Economic Analysis, Newnan, D.G., J.P. Lavelle, T.G. Eschenbach, 11th ed., Oxford University Press, New York, 2012 Reference: None. 5. Course Objectives: Contributes to Student Outcomes Item Description EAC MFE To understand engineering decisions process, and the role of engineering economic e, f A analysis in the decision making process. To understand the time value of money, and to learn how to formulate economic data c, e B and criteria for decision making. To learn how to solve problems associated with engineering economy in decision c, e, f C making. To understand the effects of income taxes and inflation on cash flow and economic c, e,f D analysis. 6. Topics: LECTURES 1 The process of engineering decision making. 2 Single payment compound interest formula. 3 Uniform series formulas. 4 Arithmetic and geometric gradient formulas. 5 Nominal and effective interest rate. 6 Present Worth Analysis and capital costs. 7 Annual cash flow analysis. 8 Rate of Return analysis. 9 Pay-back, Benefit/Cost ratio methods, and Break-Even analysis. 10 Depreciation and income taxes. 11 Inflation. 12 Use of computer in analysis and presentation Contributes to Course Objectives (5) Objectives A B B B B B, C B, C B,C B, C B, C, D B, C, D B, C, D LABORATORIES Outcome N/A N/A PAPERS/PROJECTS Outcome N/A N/A 7. Class Schedule: Three 50-minute or two 75-minute sessions per week. 8. 8.a Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component - EAC Mathematics and Basic Science Engineering Topics, Engineering Sciences, Engineering Design 0 hrs 3 hrs General Education 0 hrs 5 scales, 5 denotes very strong continuation to the student outcome and blank cell denotes that the course does not continue the related student outcome) 9a. Relationship of Course to MFE Student Outcomes: (based on 1 to Code a b c d e f g h i j k Student Outcomes, A Graduate from the Program Will Have: Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics and science to manufacturing processes, materials, and design of manufacturing systems Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to design and conduct experiments, and to analyze and interpret data related to manufacturing processes, materials evaluation, and manufacturing systems Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to design, select, implement, and control a manufacturing system and its components or processes to meet desired needs Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams and the ability to apply a concurrent approach and project management to process and product development Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to identify, formulate, and solve manufacturing engineering problems through a hands-on approach that considers constraints, costs, benefits, and comparative processes and materials Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the professional and ethical responsibilities of a manufacturing engineer Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to effectively communicate technical concepts through appropriate methods Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the impact of manufacturing engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have a recognition of the need to engage in lifelong learning Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have a knowledge of contemporary issues facing manufacturing engineers Manufacturing Engineering graduates will have an ability to use the proper techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for manufacturing engineering practice utilizing supporting technologies 10. Prepared By: Fred Tayyari 10/2013 Contribution — — 1.00 — 3.20 1.00 — — — — — Reviewed by: Curriculum Committee



