Department of Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering & Technology IME 361
advertisement
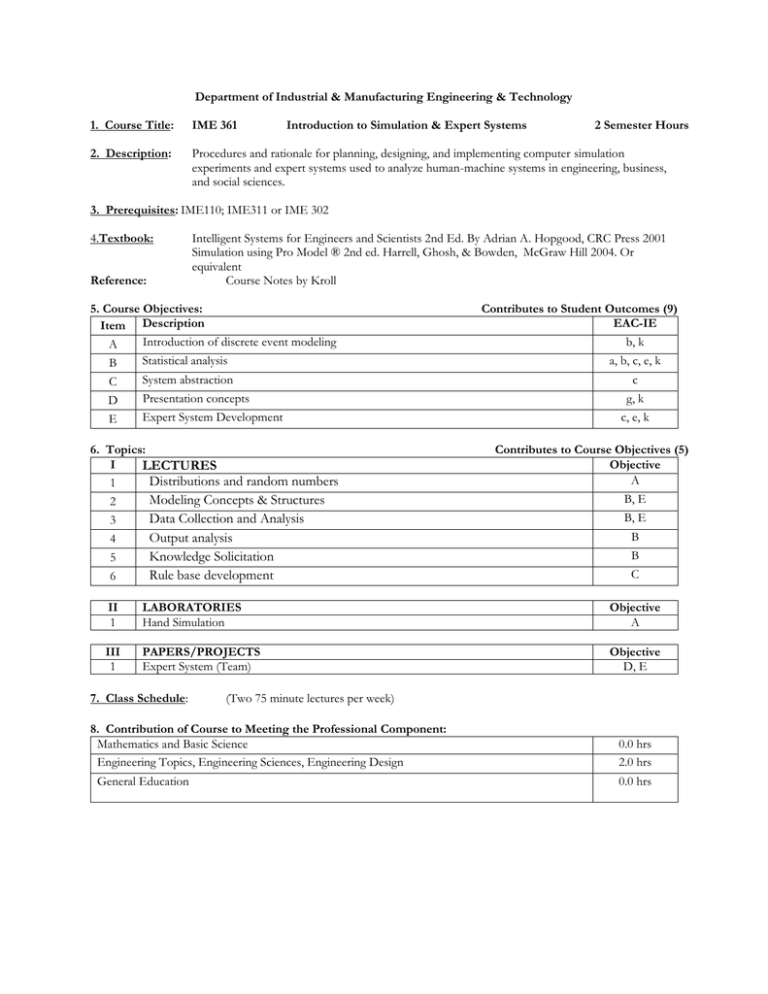
Department of Industrial & Manufacturing Engineering & Technology 1. Course Title: IME 361 Introduction to Simulation & Expert Systems 2 Semester Hours 2. Description: Procedures and rationale for planning, designing, and implementing computer simulation experiments and expert systems used to analyze human-machine systems in engineering, business, and social sciences. 3. Prerequisites: IME110; IME311 or IME 302 4.Textbook: Reference: Intelligent Systems for Engineers and Scientists 2nd Ed. By Adrian A. Hopgood, CRC Press 2001 Simulation using Pro Model ® 2nd ed. Harrell, Ghosh, & Bowden, McGraw Hill 2004. Or equivalent Course Notes by Kroll 5. Course Objectives: Item Description Introduction of discrete event modeling A Statistical analysis B C D E System abstraction Presentation concepts Expert System Development 6. Topics: I LECTURES Distributions and random numbers 1 Modeling Concepts & Structures 2 3 4 5 6 Data Collection and Analysis Output analysis Knowledge Solicitation Rule base development Contributes to Student Outcomes (9) EAC-IE b, k a, b, c, e, k c g, k c, e, k Contributes to Course Objectives (5) Objective A B, E B, E B B C II 1 LABORATORIES Hand Simulation Objective A III 1 PAPERS/PROJECTS Expert System (Team) Objective D, E 7. Class Schedule: (Two 75 minute lectures per week) 8. Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component: Mathematics and Basic Science Engineering Topics, Engineering Sciences, Engineering Design General Education 0.0 hrs 2.0 hrs 0.0 hrs 9. Relationship of Course to IE Student Outcomes: (Note: Contribution ranks from 0.5 to 5.0) Code A Graduate from Industrial Engineering Program Will Have: Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics and science to system modeling and to problems related to production processes or a services. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to design and conduct experiments, b and to analyze and interpret data. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to design, select, implement, and control a manufacturing or service system and its components or processes to meet desired c needs. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams d and the ability to apply a concurrent approach and project management to process and product development. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to identify, formulate, and determine optimal solutions to system problems, while considering physical and economic constraints e as well as safety and ergonomic issues. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the professional and ethical f responsibilities of an industrial engineer. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to effectively communicate technical g and social concepts through appropriate methods. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an understanding of the impact of industrial h engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context. Industrial Engineering graduates will have the recognition of the need for, and an ability to i engage in lifelong learning. Industrial Engineering graduates will have knowledge of contemporary issues facing j engineers. Industrial Engineering graduates will have an ability to use the proper techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for industrial engineering practice utilizing k supporting technologies. 10. Prepared by: Gary Lin, 3/12/2013 Reviewed by: Curriculum Committee Contribution 3.25 1.92 3.00 2.50 1.00 2.25



