Postulates Common Notions Postulate 1. Common notion 1.
advertisement

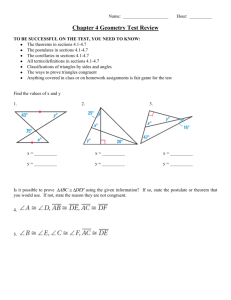
Postulates Commo n Notions Postulate 1. To draw a straight line from any point to any point. Common notion 1. Things which equal the same thing also equal one another. Postulate 2 To produce a finite straight line continuously in a straight line. Common notion 2. If equals are added to equals, then the wholes are equal. Postulate 3. To describe a circle with any center and radius. Common notion 3. If equals are subtracted from equals, then the remainders are equal. Postulate 4. That all right angles equal one another. Common notion 4. Things which coincide with one another equal one another. Postulate 5. Given a line and a point not on the line there exists exactly one line thr ough the point and parallel to the given line. Common notion 5. The whole is greater than the part. The distance from any point on a circle to the center is a constant called the radius. The length of any line segment from a point on a circle to the center of the circle is a constant called the radius. All radii of a circle are the same length. B A C B A C Alternate interior angles are equal. Vertical Angles are equal. Alternate exterior angles are equal. Corresponding angles are equal. C A B A C B A C B A C B A Proposition 4. SAS Congruence Theorem If two triangles have two sides and the angle included (formed) by the sides equal, then the triangles are congruent. Remember: things that are congruent are equal, in every respect. Proposition 5. Base angles of an isosceles triangle are equal. Proposition: Bisect a given angle. Propostion 8. SSS Congruence Theorem If two triangles have all three sides equal, then the triangles are congruent. Remember: things that are congruent are equal, in every respect.