Winter wk 8 – Thus.24.Feb.05
advertisement

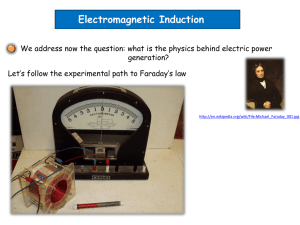
Winter wk 8 – Thus.24.Feb.05 Review Ch.30 – Faraday and Lenz laws Ch.32: Maxwell Equations! • Gauss: q E • Ampere: I B • Faraday: dB/dt E (applications) • Maxwell: dE/dt B Magnetism in matter Energy Systems, EJZ Gauss: charge q E field E No magnetic charges Practice: P2 (p.883) E dA B qenc 0 B dA 0 Ampere: current I B field B ds 0ienc Faraday: dB/dt E field dB dt d B dA E ds dt Lenz’s law tells DIRECTION of Induced emf opposes change in flux: dB dt Induced current Ii creates an induced field Bi to oppose any change in the external flux. In what direction does current flow, in each diagram? Practice with Lenz’s law In what direction does current flow, in each loop Generators & Transformers d N BA cos t NBA sin t dt dB V N dt shared flux : d B V1 V2 dt N1 N 2 V2 ________ V1 Power I1V1 I 2V2 I2 ________ I1 AC power depends on transformers Step-up transformer: higher voltage, lower current Step-down: lower voltage, higher current Induced magnetic fields: dE/dt B Recall Faraday: changing magnetic flux E field dB E ds dt Symmetry: changing electric flux B dE 0 0 B ds dt Practice: P 5, 10 (p.884) Ampere-Maxwell Law What can cause a magnetic field B? 0ienc B ds Ampere: Current IB: Maxwell: changing EB: 0 0 d E B ds dt dE B ds i 0 0 0 enc dt Practice with magnetic induction Q1 (p.882): Is E increasing or decreasing? Q2: Which loop has the greatest magnetic circulation? Maxwell Eqns EM waves Next week we will combine the Maxwell equations to • Derive electromagnetic waves • Derive the speed of light Magnetism in matter Earth’s B field is due to currents in the molten outer core Electron spin ~ current loop magnetic moment =IA Magnetic materials have regions of aligned electron spin Probs. 67, 72, 73