European religions today
advertisement
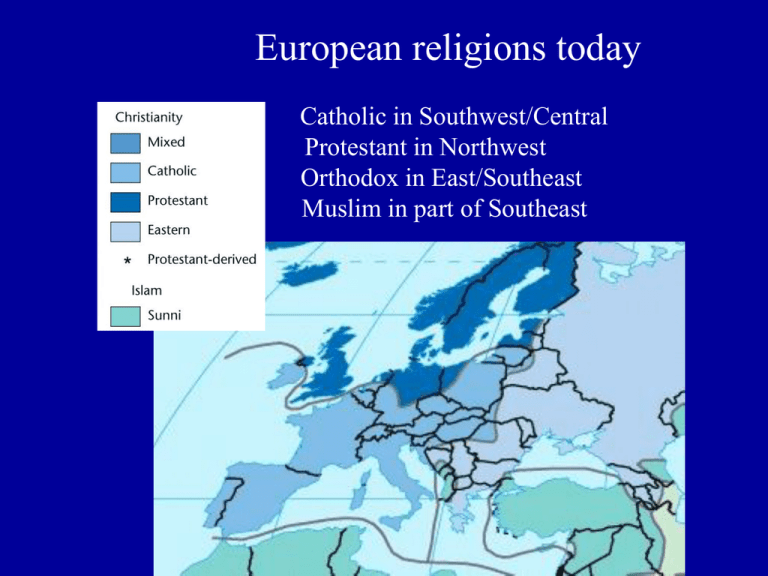
European religions today Catholic in Southwest/Central Protestant in Northwest Orthodox in East/Southeast Muslim in part of Southeast Balkans shatterbelt Balkans shatterbelt Ethnic diversity Meeting of Orthodox, Catholics, Muslims Competition between Russian, Ottoman, Austrian spheres “Balkanization” Austro-Hungarian Empire Ottoman Empire Losses, 1878 Macedonia claimed by Setbia, Bulgaria, Greece Muslims as Ottoman Legacy SANJAK (Serb.-Mont.) ALBANIANS (Albania, Kosovo, Macedonia) BOSNIANS (Bosniaks: converted Serbo-Croats) Turkey Pécs church in Hungary (former mosque) TURKS (Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova) Types of territoriality State Ethnic Religious Fears of Balkanization (splitting state into ethnic or religious parts) State territoriality (“patriotism”) Place identity based on political unit (Serbian, Croatian) “I am an American.” (Civil wars) “I am a Nigerian.” NATION Not a state: A cultural group with a territorial identity; stitching together many local identities Over 5,000 ethnic “nations” cannot all become states, yet many are large enough to survive (larger than some states). Theories of nationhood Primordialism (nation is essential/family, in the “blood”) Instrumentalism (nation is top-down, self-serving project of elites) Constructivism (nation is constructed both by elites and masses) Ethnic territoriality (“nationalism”) Place identity based on ethnicity (Serb, Croat) Basques in Spain/France Québecois in Canada Homeland Territorialization of national identity: Past “golden age” Present security Future prosperity/glory Battle of Kosovo Polje (Blackbird Field), 1389 Battle of Kosovo Polje (Blackbird Field), 1389 Muslim Turks defeat Serbian (and Albanian) Christians under Prince Lazar. Knights’ blood “turns into” red poppies. Sacred site for Serbian nationalism NATION-STATE State with one nation (none “pure” but some close) Nearly all states multiethnic (more than one nation) Nation-States and Multiethnic States National Congruence Desire for state boundaries to match ethnic boundaries ( Greater _________ ) * If majority does not want minority * If minority wants self-determination Boundaries of Albania in different eras Religious Territoriality States defined by religion Vatican City Saudi Arabia Vatican City Israel Iran Core group States are constructed around a dominant ethnic, racial or religious group English in U.K. Russians in U.S.S.R. & Russia Whites in U.S. Majority nationalism Equating “patriotism” with “nationalism” State usually represents core group, but also needs loyal minorities Hindu mobs attack Indian Muslim neighborhood English attack immigrants KKK rally against immigrants, 1925 German skinheads attack Turks Minority nationalism For “self-determination” Not only secession but autonomy Reaction to majority nationalism? What if minority becomes majority? Puerto Rico East Timor Lithuania Secession Separation from state (independence) Autonomy (self-rule) not offered, or not enough Irredentism Joining ethnic minority with a country where they are majority, To form Greater________ Germany annexes ethnic German region of Czechoslovakia, 1938 State response to minority: Coercion Ethnocide (forced assimilation) Hungarian sign defaced in Romania. Turks forced to Change names in Bulgaria. Genocide (extermination) Holocaust in Europe (Not only Germany)



