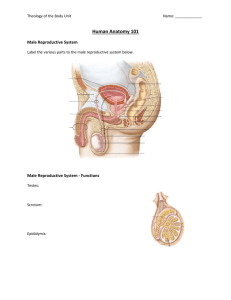
Name:_________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____

Name:_________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____
Agenda Week of 10 March – 14 March 2008 Unit 5 Evolution Exam 3/11/08
Class website: www.marric.us/teaching
Unit 6 Quiz 1 March 18, 2008
Monday 3/10/08
-
Review for Exam
HW: Study for Exam
Tuesday 3/11/08 (LEAP 2:30 -3:30)
-
Unit 5 Evolution EXAM
HW: Unit Essay
1-4 The correct path of sperm through the male reproductive system is ___________________ to
_________________ to _________________ to
_________________________,.
Wednesday 3/12/08 –Late Start
-
Portfolio Preparation
HW: Portfolio Completion Reviews – parent/student
5. Fertilization occurs in the
_________________________, and implantation occurs in the ______________.
6. The male parent produces sex cells called ________.
Thursday 3/13/08 – Block Day
-
Staple Portfolios
-
Miracle of Birth
-
Anatomy/Physiology Unit
Overview
HW: Vocabulary 1-20 due 3/20/08
Friday 3/14/08 – Block Day
-
Staple Portfolios
-
Miracle of Birth
-
Anatomy/Physiology Unit
Overview
HW: Vocabulary 1-20 due 3/20/08
7. The female parent produces sex cells called_______.
8. During ______________________, an egg is released when a follicle ruptures.
9. A healthy adult male produces several hundred million _______________ each day.
10. The scrotum is about ___________ the body.
11. Which hormone causes the final preparation of the uterus to receive the embryo and inhibits initiation of the next menstrual cycle.
Parents/Guardian –
I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of
3/10/08- 3/14/08.
I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is ready for the exam on 3/11/08, and has completed all assignments this week.
12. The average length of the menstrual cycle of a woman is _____________
Vocabulary Matching
Egg
Embryo
Epididymous
Estrogen
Fertilization
Fetus
Hormones
Menstruation
Penis
Progesterone
Scrotum
Testosterone
I understand if my child needs to retake a quiz that the original quiz
Fallopian tube Ovary Semen with corrected answers, signed by a parent, must be turned in when the quiz is retaken on Tuesday after school.
The last Unit of study begins this week and includes the detailed study of the reproductive system , nervous system, immune system, and cardiovascular system, and digestive system.
Parent/Guardian Printed Name Signature Date
Bell Ringers: Week of 10 Mar – 14 Mar 2008 CST Review Questions
Monday – Which of these would have the least effect on natural selection in a subspecies of giraffes that is geographically isolated from other subspecies of giraffes? a) available niches b) existing predators c) chromosome number d) available food resources
Explain
Tuesday -
Mutations within a DNA sequence are: a) natural processes that produce genetic diversity b) natural process that always affect the phenotype c) unnatural process that always affect the phenotype d) unnatural process that are harmful to genetic diversity
Explain
Wednesday –
A small population of chimpanzees lives in a habitat that undergoes no changes for a long period. How will genetic drift probably affect this population? a) It will accelerate the appearance of new traits. b) It will promote the survival of chimpanzees with beneficial traits c) It will increase the number of alleles for specific traits d) It will reduce genetic diversity.
Explain
Thursday/Friday
Fossil evidence suggests that a number of members of one fish species from an ancient lake in Death
Valley, California, became several isolated species. Each of these new species lived in a different pond.
Which of the following best explains the cause of this speciation? a) episodic isolation b) temporal isolation d) behavioral isolation
Explain c) geographic isolation
If a paleontologist finds fossils of many different species existing in the same area at approximately the same time, the paleontologist can conclude that the ecosystem in this area had a high degree of a) climatic variation b) episodic speciation d) geographical isolation
Explain c) biological diversity
Name:_______________________________ Date:____________________ Period:______
Unit 6 Quiz 1 March 18, 2008 (27 points)
1-4 The correct path of sperm through the male reproductive system is ___________________ to
____________________________ to ____________________________ to
_________________________,.
5. The female parent produces sex cells called____________.
6. The average length of the menstrual cycle of a woman is _____________
7. Fertilization occurs in the _________________________, and implantation occurs in the
______________.
8. During ______________________, an egg is released when a follicle ruptures.
9. Which hormone causes the final preparation of the uterus to receive the embryo and inhibits initiation of the next menstrual cycle.
10. The male parent produces sex cells called ______________.
11. A healthy adult male produces several hundred million _______________ each day.
12. The scrotum is about ______________________ the body.
Extra Credit
______The jackrabbit population sometimes decreases dramatically. One possible explanation for this decrease is that the coyote population has increased. This explanation is a scientific ____.
A conclusion. B experiment. C hypothesis. D law.
_______Which structure stores most of the genetic information?
A mitochondrion B lysosome C nucleus D tail
_____Which of the following cell types is formed by meiosis?
A muscle cells B sperm cells C skin cells D blood cells
_____The inheritance of a trait in humans is best described as being determined by
A a single allele. B one or more pairs of alleles.
C one pair of chromosomes. D the sex chromosomes of the offspring.
Vocabulary Matching
____ Egg A. the monthly reproductive cycle that helps prepare the human female body for pregnancy; involves the shedding of blood, tissue fluid, mucus, and epithelial cells if an egg is not fertilized.
_____ Embryo B. One of many types of circulating chemical signals in all multicellular organisms that are formed in specialized cells, travel in body fluids, and coordinate the various parts of the organism by target cells interaction.
_____ Epididymous C. a branch of biology dealing with embryos and their development
_____ Estrogen D. A steroid hormone secreted by the corpus luteum of the ovary; maintains the uterine lining during pregnancy.
_____ Embryology E. A female gamete, which usually contains abundant cytoplasm and yolk; nonmotile and often larger than a male gamete.
___ Fallopian tube F. In animals, the structure that produces female gametes and reproductive hormones.
_____ Fertilization G. An unborn or unhatched vertebrate that has passed through the earliest development stages; a developing human from about the second month of gestation until birth.
_____ Fetus
_____ Hormones
H. The most abundant androgen (produced in the adrenal gland) hormone in the male body which stimulate the development and maintenance of the male reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics
I. The sac (pouch) that contains the testes, blood vessels, and part of the spermatic cord.
It is located behind the penis.
____ Menstruation J. structure on top of each testis where sperm mature and are stored. A long coiled tube into which sperm pass from the testis and are stored until mature and ejaculated.
_____ Penis K. A tube passing from the ovary to the uterus in vertebrates or to the vagina in invertebrates.
_____Ovary L. The stage in the development of offspring from the first division of the zygote until body structures begin to appear; about the ninth week of gestation, in humans,.
_____Progesterone M. fluid that contains sperm, nourishment, and other male reproductive system fluids.
_____Scrotum
_____Semen
N. The union of haploid gametes to produce a diploid zygote.
0. the male organ of copulation (sexual intercourse).
_____Testosterone P. The primary female steroid sex hormones, which are produced in the ovary by the developing follicle during the first half of the cycle and in smaller quantities by the corpus luteum during the second half.